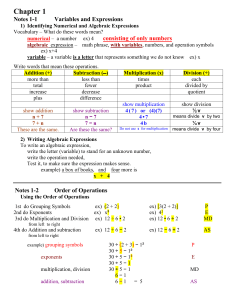
Big Numbers
... Suppose there is a set of six people, and every pair either knows each other or does not know each other. Show that there is either a set of three people, all of whom know each other, or a set of three people, none of whom know each other. The problem is usually solved by drawing a mathematical grap ...
... Suppose there is a set of six people, and every pair either knows each other or does not know each other. Show that there is either a set of three people, all of whom know each other, or a set of three people, none of whom know each other. The problem is usually solved by drawing a mathematical grap ...
Sig Figs
... Rules for determining if a digit is significant 1. If it is not a zero, it is significant.123 2. If a zero is between two significant digits, it is significant. 309 3. Zeros at the end of a number with a decimal point are significant. 56.0 4. Zeros at the end of a number that do not have a decimal ...
... Rules for determining if a digit is significant 1. If it is not a zero, it is significant.123 2. If a zero is between two significant digits, it is significant. 309 3. Zeros at the end of a number with a decimal point are significant. 56.0 4. Zeros at the end of a number that do not have a decimal ...
Sig Figs
... numbers that we didn’t report because we couldn’t measure accurately enough. The number was rounded! ...
... numbers that we didn’t report because we couldn’t measure accurately enough. The number was rounded! ...
Lesson 4: The Number System
... to the right of point 0. The line itself extends forever in both directions, as represented by the arrows. The points on the number line correspond to real numbers. Every point corresponds to a real number, such as 1, 2, 3, 4, –1, –2, –3, –4, etc. It is important to note that a number line includes ...
... to the right of point 0. The line itself extends forever in both directions, as represented by the arrows. The points on the number line correspond to real numbers. Every point corresponds to a real number, such as 1, 2, 3, 4, –1, –2, –3, –4, etc. It is important to note that a number line includes ...
Infinity

Infinity (symbol: ∞) is an abstract concept describing something without any limit and is relevant in a number of fields, predominantly mathematics and physics.In mathematics, ""infinity"" is often treated as if it were a number (i.e., it counts or measures things: ""an infinite number of terms"") but it is not the same sort of number as natural or real numbers. In number systems incorporating infinitesimals, the reciprocal of an infinitesimal is an infinite number, i.e., a number greater than any real number; see 1/∞.Georg Cantor formalized many ideas related to infinity and infinite sets during the late 19th and early 20th centuries. In the theory he developed, there are infinite sets of different sizes (called cardinalities). For example, the set of integers is countably infinite, while the infinite set of real numbers is uncountable.