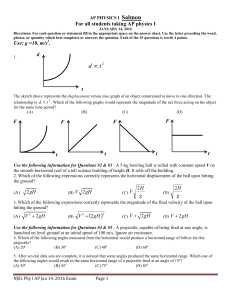
Physics 30 Worksheet #22: Cathode Ray Tubes
... 169. In the above fission reaction, the mass of the reactants is 236.05 atomic mass units, and the mass of the products is 235.86 atomic mass units. Which of the following explanations best describes the change in mass that occurs in this nuclear fission reaction? A. Mass and energy are equivalent, ...
... 169. In the above fission reaction, the mass of the reactants is 236.05 atomic mass units, and the mass of the products is 235.86 atomic mass units. Which of the following explanations best describes the change in mass that occurs in this nuclear fission reaction? A. Mass and energy are equivalent, ...
Lecture 7
... ESI and Charge State Distributions For a single protein, ESI will almost always generate several charge states. The intensities of these charge states are arranged in a roughly Gaussian distribution (although there is no physical justification for this). This is called the charge state distribution ...
... ESI and Charge State Distributions For a single protein, ESI will almost always generate several charge states. The intensities of these charge states are arranged in a roughly Gaussian distribution (although there is no physical justification for this). This is called the charge state distribution ...
FROM ANTI-GRAVITY TO ZERO-POINT ENERGY
... and gravitational constant, this difference in velocities c - v is only .1 m/s. This tiny, virtually unmeasurable difference in c results from the same phenomenon responsible for the gravitational potential. (Millis has approached this gravitational refractive index by considering distance as "stiff ...
... and gravitational constant, this difference in velocities c - v is only .1 m/s. This tiny, virtually unmeasurable difference in c results from the same phenomenon responsible for the gravitational potential. (Millis has approached this gravitational refractive index by considering distance as "stiff ...
L8.ppt - University of Iowa Physics
... L-8 (M-7) I. Collisions II. Work and Energy • Momentum: an object of mass m, moving with velocity v has a momentum p = m v. • Momentum is an important and useful concept that is used to analyze collisions – The colliding objects exert strong forces on each other over relatively short time intervals ...
... L-8 (M-7) I. Collisions II. Work and Energy • Momentum: an object of mass m, moving with velocity v has a momentum p = m v. • Momentum is an important and useful concept that is used to analyze collisions – The colliding objects exert strong forces on each other over relatively short time intervals ...
Plane Kinetics of Rigid Bodies
... Resultant of the applied forces will only be couple Ī α Center of Percussion • The resultant-force comp (māt = m r̅ α) and the resultant couple Ī α can be combined to form an equivalent system with the force m r̅ α acting at a point Q along OG. Point Q can be located by: Using parallel axis t ...
... Resultant of the applied forces will only be couple Ī α Center of Percussion • The resultant-force comp (māt = m r̅ α) and the resultant couple Ī α can be combined to form an equivalent system with the force m r̅ α acting at a point Q along OG. Point Q can be located by: Using parallel axis t ...
A moving clock ticks slower.
... One important aspect of relativity is that there is only one reality. If I see the muon arrive at the surface of the earth, the muon must agree that it actually did arrive at the surface of the earth. Our average muon “says” there is no doubt whatsoever that its lifetime is 2.2 s, and during that ...
... One important aspect of relativity is that there is only one reality. If I see the muon arrive at the surface of the earth, the muon must agree that it actually did arrive at the surface of the earth. Our average muon “says” there is no doubt whatsoever that its lifetime is 2.2 s, and during that ...
Chemical Principles: The Quest for Insight Fourth Edition
... oxidation number if more than one charge is possible). Followed by the name of the anion; hydrates are named by adding the word hydrate, preceded by a Greek prefix indicating the number of water molecules in the formula unit. ...
... oxidation number if more than one charge is possible). Followed by the name of the anion; hydrates are named by adding the word hydrate, preceded by a Greek prefix indicating the number of water molecules in the formula unit. ...
CH04.AST1001.F16.EDS
... smaller, or the same as the force you exert on it? A. Earth exerts a larger force on you. B. You exert a larger force on Earth. C. Earth and you exert equal and opposite forces on each other. ...
... smaller, or the same as the force you exert on it? A. Earth exerts a larger force on you. B. You exert a larger force on Earth. C. Earth and you exert equal and opposite forces on each other. ...
Chapter 4: Making Sense of the Universe Understanding Motion
... A compact car and a large truck have a head-on collision. Are the following true or false? • The force of the car on the truck is equal and opposite to the force of the truck on the car. T • The momentum transferred from the truck to the car is equal and opposite to the momentum transferred from t ...
... A compact car and a large truck have a head-on collision. Are the following true or false? • The force of the car on the truck is equal and opposite to the force of the truck on the car. T • The momentum transferred from the truck to the car is equal and opposite to the momentum transferred from t ...
Chapter 22 Electrostatics Exercise Answers
... 40. An ion polarizes a nearby neutral atom, so that the part of the atom nearer to the ion acquires a charge opposite to the charge of the ion, and the part of the atom farther from the ion acquires a charge of the same sign as the ion. The side of the atom closer to the ion is then attracted more ...
... 40. An ion polarizes a nearby neutral atom, so that the part of the atom nearer to the ion acquires a charge opposite to the charge of the ion, and the part of the atom farther from the ion acquires a charge of the same sign as the ion. The side of the atom closer to the ion is then attracted more ...
Newton`s Third Law and Momentum
... Action and Reaction cont. Example: When hanging a picture, you use a hammer to drive a nail into the wall. The hammer strikes the nail, it applies a force to the nail (action) The nail also applies an equal and opposite force to the hammer (reaction force) ...
... Action and Reaction cont. Example: When hanging a picture, you use a hammer to drive a nail into the wall. The hammer strikes the nail, it applies a force to the nail (action) The nail also applies an equal and opposite force to the hammer (reaction force) ...