BUDDHIST ETHICS - Cirencester College
... the Buddha, one generates good karma, this will lead Buddhists closer to their goal. And vice versa, acting immorally generates bad karma and takes Buddhists away from their goal. ...
... the Buddha, one generates good karma, this will lead Buddhists closer to their goal. And vice versa, acting immorally generates bad karma and takes Buddhists away from their goal. ...
Buddhism and Confucianism
... Beliefs continued • By following the Four Noble Truths and in effect the Eight Fold Path, one moves closer to the destination of Nirvana. • Nirvana is considered a place of peace and harmony. ...
... Beliefs continued • By following the Four Noble Truths and in effect the Eight Fold Path, one moves closer to the destination of Nirvana. • Nirvana is considered a place of peace and harmony. ...
introduction to buddhism
... Buddhism is a nontheistic religion that encompasses a variety of traditions, beliefs and practices largely based on teachings attributed to Siddhartha Gautama, commonly known as the Buddha ("the awakened one"). According to Buddhist tradition, the Buddha lived and taught in the eastern part of the I ...
... Buddhism is a nontheistic religion that encompasses a variety of traditions, beliefs and practices largely based on teachings attributed to Siddhartha Gautama, commonly known as the Buddha ("the awakened one"). According to Buddhist tradition, the Buddha lived and taught in the eastern part of the I ...
Buddhism in the Subcontinent The essence of Buddhism
... Found in southeast Asia, including Burma (Myanmar). The monastic life is the best way to achieve nirvana. Focus on wisdom and meditation. Goal is to become a “Buddha,” or “Enlightened One.” ...
... Found in southeast Asia, including Burma (Myanmar). The monastic life is the best way to achieve nirvana. Focus on wisdom and meditation. Goal is to become a “Buddha,” or “Enlightened One.” ...
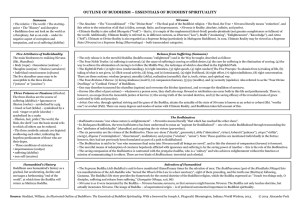
3 Rafts of Buddhism
... Exist beyond an earthly ream and are believed to dwell in one of the Buddhist heavens, from which they provide divine assistance to those who worship them Transfer merit of their karma to their devotees On occasion they appear in the world as human beings The ideal type rather than the arhat ...
... Exist beyond an earthly ream and are believed to dwell in one of the Buddhist heavens, from which they provide divine assistance to those who worship them Transfer merit of their karma to their devotees On occasion they appear in the world as human beings The ideal type rather than the arhat ...
Aspects of Buddhism - UU Small Group Ministry Network
... person decides for themselves and takes responsibility for their own actions and understanding. This makes Buddhism less of a fixed package of beliefs which is to be accepted in its entirety, and more of a teaching which each person learns and uses in their own way. Beliefs A key concept of Buddhism ...
... person decides for themselves and takes responsibility for their own actions and understanding. This makes Buddhism less of a fixed package of beliefs which is to be accepted in its entirety, and more of a teaching which each person learns and uses in their own way. Beliefs A key concept of Buddhism ...
Unit 2 The Bible is a Primary Source of Christian Belief
... Followed a strict ascetic lifestyle for six years. Rejected this extreme, sat in meditation, achieved Nirvana – an awakening to the truth about life, becoming a Buddha, the “Awakened One” at the age of 35. Spent the remaining 45 years of his life teaching others how to achieve the peace of min ...
... Followed a strict ascetic lifestyle for six years. Rejected this extreme, sat in meditation, achieved Nirvana – an awakening to the truth about life, becoming a Buddha, the “Awakened One” at the age of 35. Spent the remaining 45 years of his life teaching others how to achieve the peace of min ...
File - ASIA 100: Introduction to Asian Civilizations
... The Mahabharata featured Krishna, an incarnation of Vishnu. Krishna became a major deity in Hinduism. The Bhagavad Gita, a part of the Mahabharata, emphasized the need for people to play their proper roles in society, even if they are warriors. the Ramayana featured Rama, another incarnation of Vish ...
... The Mahabharata featured Krishna, an incarnation of Vishnu. Krishna became a major deity in Hinduism. The Bhagavad Gita, a part of the Mahabharata, emphasized the need for people to play their proper roles in society, even if they are warriors. the Ramayana featured Rama, another incarnation of Vish ...
The Essentials of Buddhist Spirituality
... ▪ Bodhisattva means "one whose nature is enlightenment". ▪ Paramita means literally "that which has reached the other shore". ▪ In Mahayana Buddhism, the term bodhisattva has been understood to mean an "aspirant for Buddhahood" – one who seeks Buddhahood through transcending the five "attributes of ...
... ▪ Bodhisattva means "one whose nature is enlightenment". ▪ Paramita means literally "that which has reached the other shore". ▪ In Mahayana Buddhism, the term bodhisattva has been understood to mean an "aspirant for Buddhahood" – one who seeks Buddhahood through transcending the five "attributes of ...
buddhism
... holy life. There is not a rule about clothing, but there is a cloth that Buddhist wears. The Buddhist wears robe cloth. They wore 25 centuries ago. One of the robe cloths is called uttarasanga or kashaya. The uttarasanga or kashaya is the most well-known robe. It is a large ...
... holy life. There is not a rule about clothing, but there is a cloth that Buddhist wears. The Buddhist wears robe cloth. They wore 25 centuries ago. One of the robe cloths is called uttarasanga or kashaya. The uttarasanga or kashaya is the most well-known robe. It is a large ...
Buddhism an Introduction Vedic Beginnings The Vedic Scriptures
... Mahayanan Buddhists aspire to become a Bodhisattva. The Bodhisattva refers to a being with the essence of enlightenment who delays his entry into nirvana in order to help all sentient beings. Out of compassion he or she returns to the samsaric realm to help others along the path. The rationale is to ...
... Mahayanan Buddhists aspire to become a Bodhisattva. The Bodhisattva refers to a being with the essence of enlightenment who delays his entry into nirvana in order to help all sentient beings. Out of compassion he or she returns to the samsaric realm to help others along the path. The rationale is to ...
File - World Religions
... • The image of the Buddha doesn't necessarily represent the historical figure who founded Buddhism. • The image may also represent enlightenment or the dharma. • In Mahayana Buddhism, the Buddha image may represent Buddha Nature, which is the fundamental nature of all beings. • The central function ...
... • The image of the Buddha doesn't necessarily represent the historical figure who founded Buddhism. • The image may also represent enlightenment or the dharma. • In Mahayana Buddhism, the Buddha image may represent Buddha Nature, which is the fundamental nature of all beings. • The central function ...
Why do Buddhists meditate? Video transcript for `Finding nirvana
... Visions of pleasure and diabolic dread raced through his mind, but nothing could distract him. And then, after many days, it suddenly seemed as though he had been released from all the things that had been troubling him. Siddhartha was able to see things as they truly were. He was free from desire a ...
... Visions of pleasure and diabolic dread raced through his mind, but nothing could distract him. And then, after many days, it suddenly seemed as though he had been released from all the things that had been troubling him. Siddhartha was able to see things as they truly were. He was free from desire a ...
The Dharma (Teaching) - Traditional Yoga Studies
... are impermanent they are unstable configurations of five distinct and shortlived factors or groups (skandha): body (rûpa) sensation (vedanâ) perception (samjnâ) mental activity (samskâra) consciousness (vijnâna) ...
... are impermanent they are unstable configurations of five distinct and shortlived factors or groups (skandha): body (rûpa) sensation (vedanâ) perception (samjnâ) mental activity (samskâra) consciousness (vijnâna) ...
Buddhism PP Pres
... these were passed down by word of mouth and later were compiled into scriptures written in Pali Basket of Discipline - 227 rules for monks and ...
... these were passed down by word of mouth and later were compiled into scriptures written in Pali Basket of Discipline - 227 rules for monks and ...
Death and Dying Presentation
... agreed upon within Buddhist thought. • In Tibetan Buddhism, after the last breath is taken, the individual is in an intermediate state between their previous life and their new life. This state, known as the bardo can last up to 49 days. • In Theravāda Buddhist doctrine rebirth is immediate. However ...
... agreed upon within Buddhist thought. • In Tibetan Buddhism, after the last breath is taken, the individual is in an intermediate state between their previous life and their new life. This state, known as the bardo can last up to 49 days. • In Theravāda Buddhist doctrine rebirth is immediate. However ...
Polytheistic Religions
... people who are ready to reach nirvana but chose to help others along the path to enlightenment ...
... people who are ready to reach nirvana but chose to help others along the path to enlightenment ...
Thai Buddhism
... As Australia is one of the most multicultural countries in the world it is important that each society has a sound understanding of the diverse cultures and religions that are living in their area. We are striving to make everyone aware, appreciative and more understanding of a very prominent religi ...
... As Australia is one of the most multicultural countries in the world it is important that each society has a sound understanding of the diverse cultures and religions that are living in their area. We are striving to make everyone aware, appreciative and more understanding of a very prominent religi ...
Buddhism - CLAS Users
... In Tibet __________ combined with _________ to become the dominant Buddhist sect. What are Tantrism’s antecedents? Tantrism strove to symbolize the entire cosmic plan. For example, in Tantrism, stupa burial sites represented what? True or False: Tantrists were very open and vocal with their rites an ...
... In Tibet __________ combined with _________ to become the dominant Buddhist sect. What are Tantrism’s antecedents? Tantrism strove to symbolize the entire cosmic plan. For example, in Tantrism, stupa burial sites represented what? True or False: Tantrists were very open and vocal with their rites an ...
Buddhist identities
... Although there may be different traditions within each school, the central teaching is common – the teaching of Buddha Shakyamuni. The differences between the schools of Buddhism rest on the emphasis they place on particular aspects of the teachings and the interpretation of rules governing the cond ...
... Although there may be different traditions within each school, the central teaching is common – the teaching of Buddha Shakyamuni. The differences between the schools of Buddhism rest on the emphasis they place on particular aspects of the teachings and the interpretation of rules governing the cond ...
Reviews
... Early Buddhist Perspective. De Silva argues that the early Buddhist perspective on suicide should be understood in terms of the interplay of bhava taõhà and vibhava taõhà, claiming that [t]he ambivalence which emerges in the inter-play of these two forms of craving, perhaps, provide [sic] a litt ...
... Early Buddhist Perspective. De Silva argues that the early Buddhist perspective on suicide should be understood in terms of the interplay of bhava taõhà and vibhava taõhà, claiming that [t]he ambivalence which emerges in the inter-play of these two forms of craving, perhaps, provide [sic] a litt ...
Buddhism
.jpeg?width=300)
Buddhism /ˈbudɪzəm/ is a nontheistic religion or philosophy (Sanskrit: dharma; Pali: धम्म dhamma) that encompasses a variety of traditions, beliefs and spiritual practices largely based on teachings attributed to Gautama Buddha, commonly known as the Buddha (""the awakened one"").According to Buddhist tradition, the Buddha lived and taught in the northeastern part of the Indian subcontinent sometime between the 6th and 4th centuries BCE. He is recognized by Buddhists as an awakened or enlightened teacher who shared his insights to help sentient beings end their suffering through the elimination of ignorance and craving. Buddhists believe that this is accomplished through the direct understanding and perception of dependent origination and the Four Noble Truths.Two major extant branches of Buddhism are generally recognized by scholars: Theravada (""The School of the Elders"") and Mahayana (""The Great Vehicle""). Theravada has a widespread following in Sri Lanka and Southeast Asia (Thailand, Burma, Laos, Cambodia, etc.). Mahayana is found throughout East Asia (China, Korea, Japan, Vietnam, Singapore, Taiwan, etc.) and includes the traditions of Pure Land, Zen, Nichiren Buddhism, Shingon, and Tiantai (Tendai). Vajrayana, a body of teachings attributed to Indian siddhas, may be viewed as a third branch or merely a part of Mahayana. Tibetan Buddhism, as practiced in Tibet, Bhutan, Nepal, the Himalayan region of India, Kalmykia, Mongolia and surrounding areas, preserves the Vajrayana teachings of eighth century India. Buddhists number between an estimated 488 million and 535 million, making it one of the world's major religions.In Theravada Buddhism, the ultimate goal is the attainment of the sublime state of Nirvana, achieved by practicing the Noble Eightfold Path (also known as the Middle Way), thus escaping what is seen as a cycle of suffering and rebirth. Mahayana Buddhism instead aspires to Buddhahood via the bodhisattva path, a state wherein one remains in this cycle to help other beings reach awakening. Tibetan Buddhism aspires to Buddhahood or rainbow body.Buddhist schools vary on the exact nature of the path to liberation, the importance and canonicity of various teachings and scriptures, and especially their respective practices. One consistent belief held by all Buddhist schools is the lack of a creator deity. The foundations of Buddhist tradition and practice are the Three Jewels: the Buddha, the Dharma (the teachings), and the Sangha (the community). Taking ""refuge in the triple gem"" has traditionally been a declaration and commitment to being on the Buddhist path, and in general distinguishes a Buddhist from a non-Buddhist. Other practices may include following ethical precepts; support of the monastic community; renouncing conventional living and becoming a monastic; the development of mindfulness and practice of meditation; cultivation of higher wisdom and discernment; study of scriptures; devotional practices; ceremonies; and in the Mahayana tradition, invocation of buddhas and bodhisattvas.