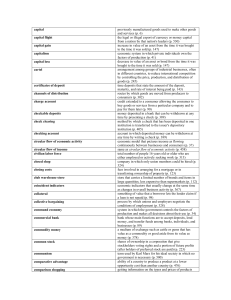
Course:
... being imported exceeds the value of those being exported? Express that no other sector of the U.S. economy has the strong comparative advantage of agriculture, for example we sell more dollars of Ag products than we buy. ...
... being imported exceeds the value of those being exported? Express that no other sector of the U.S. economy has the strong comparative advantage of agriculture, for example we sell more dollars of Ag products than we buy. ...
International Trade (Tuesdays 1
... a2 = 1 and in order to produce one unit of good 1 you need two hours of work a1 = 2. In this case the opportunity cost of good 2 expressed in terms of good 1 equals ½. (i.e. in order to produce an additional unit of good 2 in England you need to give up ½ of a unit of good 1.) In Foreign country (Po ...
... a2 = 1 and in order to produce one unit of good 1 you need two hours of work a1 = 2. In this case the opportunity cost of good 2 expressed in terms of good 1 equals ½. (i.e. in order to produce an additional unit of good 2 in England you need to give up ½ of a unit of good 1.) In Foreign country (Po ...
29 (b) Efficiency in Production
... Q = F (K, L) Where Q = Quantity produced K = Capital L = Labor Labor and Capital are considered as factors of production. In short run, Capital is considered as a fixed factor of production i.e. amount of capital for production cannot be adjusted in order to change the amount of output. Whereas in t ...
... Q = F (K, L) Where Q = Quantity produced K = Capital L = Labor Labor and Capital are considered as factors of production. In short run, Capital is considered as a fixed factor of production i.e. amount of capital for production cannot be adjusted in order to change the amount of output. Whereas in t ...
Chapter 5 Lecture
... Trade increases the demand of goods produced by relatively abundant factors, indirectly increasing the demand of these factors, raising the prices of the relatively abundant factors. In the real world, factor prices are not equal across countries. The model assumes that trading countries produ ...
... Trade increases the demand of goods produced by relatively abundant factors, indirectly increasing the demand of these factors, raising the prices of the relatively abundant factors. In the real world, factor prices are not equal across countries. The model assumes that trading countries produ ...
P c
... using the domestic technology. Can it do better by specializing in wine and trading wine with Home for cheese? In the presence of trade, Foreign can use one unit of labor to produce 1/a*LW = 1/3 gallon of wine. Since the world price of wine is PW / PC = 1 pound of cheese per gallon, Foreign can obta ...
... using the domestic technology. Can it do better by specializing in wine and trading wine with Home for cheese? In the presence of trade, Foreign can use one unit of labor to produce 1/a*LW = 1/3 gallon of wine. Since the world price of wine is PW / PC = 1 pound of cheese per gallon, Foreign can obta ...
Lecture 3: Specific Factors Model of Trade
... Prices, Wages and Labor Allocation How much labor will be employed in each sector?. To answer the above question we need to look at supply and demand in the labor market. ...
... Prices, Wages and Labor Allocation How much labor will be employed in each sector?. To answer the above question we need to look at supply and demand in the labor market. ...