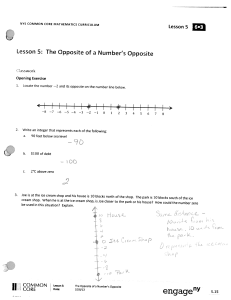
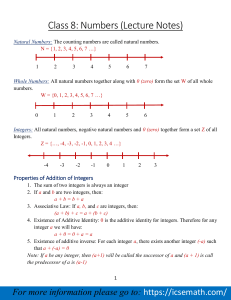
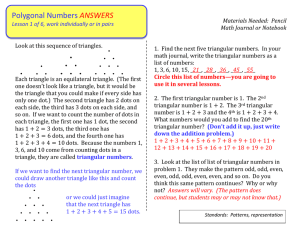
1-4
... 1-4 Integers and Absolute Value A number’s absolute value is its distance from 0 on a number line. Absolute value is always positive or 0 because distance cannot be negative. “The absolute value of –4” is written as |–4|. Additive inverses have the same absolute value. ...
... 1-4 Integers and Absolute Value A number’s absolute value is its distance from 0 on a number line. Absolute value is always positive or 0 because distance cannot be negative. “The absolute value of –4” is written as |–4|. Additive inverses have the same absolute value. ...
1 ,a
... • Addition: standard • Overflow: when the result needs more bits to be represented • Monitor MSB: if it changes there may be an overflow When Pos + Pos or Neg + Neg the sign bit should not change: if it does there is an overflow ...
... • Addition: standard • Overflow: when the result needs more bits to be represented • Monitor MSB: if it changes there may be an overflow When Pos + Pos or Neg + Neg the sign bit should not change: if it does there is an overflow ...
Key performance indicators maths
... The pupil can answer questions such as 'How many more people had school lunch on Tuesday than on Monday?' from an appropriate tally chart, table or pictogram. The pupil can use appropriate data to solve problems such as 'How many more people choose blue than yellow as their favourite colour?' They e ...
... The pupil can answer questions such as 'How many more people had school lunch on Tuesday than on Monday?' from an appropriate tally chart, table or pictogram. The pupil can use appropriate data to solve problems such as 'How many more people choose blue than yellow as their favourite colour?' They e ...
Arithmetic

Arithmetic or arithmetics (from the Greek ἀριθμός arithmos, ""number"") is the oldest and most elementary branch of mathematics. It consists of the study of numbers, especially the properties of the traditional operations between them—addition, subtraction, multiplication and division. Arithmetic is an elementary part of number theory, and number theory is considered to be one of the top-level divisions of modern mathematics, along with algebra, geometry, and analysis. The terms arithmetic and higher arithmetic were used until the beginning of the 20th century as synonyms for number theory and are sometimes still used to refer to a wider part of number theory.