8.4 Scientific Notation
... Computing with Scientific Notation Another purpose of scientific notation is to allow you to compute with large and small values easily using the rules of exponents. ...
... Computing with Scientific Notation Another purpose of scientific notation is to allow you to compute with large and small values easily using the rules of exponents. ...
firstQreview
... Negative & Zero Exponents • Negative exponents make the number or variable a reciprocal ...
... Negative & Zero Exponents • Negative exponents make the number or variable a reciprocal ...
Introduction to Signed Numbers
... Subtraction with Signed Numbers The easiest way to subtract signed numbers is to change the subtraction problem to addition. We can do this because subtracting a number is the same as adding its opposite. For example: ...
... Subtraction with Signed Numbers The easiest way to subtract signed numbers is to change the subtraction problem to addition. We can do this because subtracting a number is the same as adding its opposite. For example: ...
Lecture 1
... Conversion from Decimal to Binary (1) Perform successive division -successively divide the base 10 number by the base to which it is to be converted (2) Collect the remainder to form the number in the target base (3) 1st division yields the least significant bit as its remainder (4) Continue until ...
... Conversion from Decimal to Binary (1) Perform successive division -successively divide the base 10 number by the base to which it is to be converted (2) Collect the remainder to form the number in the target base (3) 1st division yields the least significant bit as its remainder (4) Continue until ...
Math121 Lecture 1
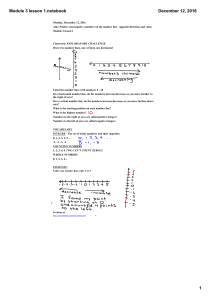
... We often use a ‘variable’ name (x, y, t, s, u) as the label or address some unspecified point on the line, that is an arbitrary real number. This idea also lets us assign labels, or addresses to arbitrary points in a plane. We choose an origin through which we draw a horizontal and a vertical line. ...
... We often use a ‘variable’ name (x, y, t, s, u) as the label or address some unspecified point on the line, that is an arbitrary real number. This idea also lets us assign labels, or addresses to arbitrary points in a plane. We choose an origin through which we draw a horizontal and a vertical line. ...
Sample Unit of Focus Lessons: Multiplication and Division Grade
... Generate a number or shape pattern that follows a given rule. Identify apparent features of the pattern that were not explicit in the rule itself. For example, given the rule “Add 3” and the starting number 1, generate terms in the resulting sequence and observe that the terms appear to alternate be ...
... Generate a number or shape pattern that follows a given rule. Identify apparent features of the pattern that were not explicit in the rule itself. For example, given the rule “Add 3” and the starting number 1, generate terms in the resulting sequence and observe that the terms appear to alternate be ...
Patterns in Multiplication and Division
... Patterns in Multiplication and Division Objective: Use multiplication facts to help you divide. Two Vocabulary Words: square number and multiple ...
... Patterns in Multiplication and Division Objective: Use multiplication facts to help you divide. Two Vocabulary Words: square number and multiple ...
Homework
... paper should clearly state relevant definitions (Abelian Group, Automorphism, Ring, Integral Domain). Such definitions should be incorporated within each proof making all appropriate connections. The paper should provide well-written justifications for relevant steps using complete and comprehensive ...
... paper should clearly state relevant definitions (Abelian Group, Automorphism, Ring, Integral Domain). Such definitions should be incorporated within each proof making all appropriate connections. The paper should provide well-written justifications for relevant steps using complete and comprehensive ...
Arithmetic

Arithmetic or arithmetics (from the Greek ἀριθμός arithmos, ""number"") is the oldest and most elementary branch of mathematics. It consists of the study of numbers, especially the properties of the traditional operations between them—addition, subtraction, multiplication and division. Arithmetic is an elementary part of number theory, and number theory is considered to be one of the top-level divisions of modern mathematics, along with algebra, geometry, and analysis. The terms arithmetic and higher arithmetic were used until the beginning of the 20th century as synonyms for number theory and are sometimes still used to refer to a wider part of number theory.