La-STEM Math Academies
... •Understand fractions and decimals represented as parts of a unit or area, parts of a collection of objects, and locations on a number line •Use concrete materials to represent fractions and decimals as parts of a unit or area, parts of a collection of objects, and locations on a number line •Name f ...
... •Understand fractions and decimals represented as parts of a unit or area, parts of a collection of objects, and locations on a number line •Use concrete materials to represent fractions and decimals as parts of a unit or area, parts of a collection of objects, and locations on a number line •Name f ...
Fractions Notes - CLC Charter School
... factorization of 12 is 2x2x3 the prime factorization of 16 is 2x2x2x2; 2x2 matches, so the GCF is 4. To compare fractions; find the common denominator by finding the LCM. The LCM becomes the new denominator and the numerator is multiplied by the same factor as the denominator. Remember whatever you ...
... factorization of 12 is 2x2x3 the prime factorization of 16 is 2x2x2x2; 2x2 matches, so the GCF is 4. To compare fractions; find the common denominator by finding the LCM. The LCM becomes the new denominator and the numerator is multiplied by the same factor as the denominator. Remember whatever you ...
Ready Set Math!
... G.10 Complete the addition sentence up to two digits G.11 Write the addition sentence - up to two digits G.12 Balance addition equations - up to two digits G.13 Add three or more numbers up to two digits each G.14 Add three or more numbers up to two digits - word problems Subtraction - two ...
... G.10 Complete the addition sentence up to two digits G.11 Write the addition sentence - up to two digits G.12 Balance addition equations - up to two digits G.13 Add three or more numbers up to two digits each G.14 Add three or more numbers up to two digits - word problems Subtraction - two ...
Full text
... Fig. 4. Limited Rook Paths in Fibonacci Notation Comparing Fig. 4 with Fig. 2, it is noted that F 0 corresponds to ( n J Il4t\ and Fj4 corresponds to 1 7 J. Comparing Fig. 3 with Fig. 1, we see that the number of Fibonacci rook paths from corner to corner is 610, whereas the number of unrestricted p ...
... Fig. 4. Limited Rook Paths in Fibonacci Notation Comparing Fig. 4 with Fig. 2, it is noted that F 0 corresponds to ( n J Il4t\ and Fj4 corresponds to 1 7 J. Comparing Fig. 3 with Fig. 1, we see that the number of Fibonacci rook paths from corner to corner is 610, whereas the number of unrestricted p ...
L13
... • Associativity: right to left • Increment and decrement operators can only be applied to variables, NOT to constants or expressions ...
... • Associativity: right to left • Increment and decrement operators can only be applied to variables, NOT to constants or expressions ...
Euclid`s algorithm and multiplicative inverse
... divisibility (Def. 1.1) does not involve division, only multiplication. So 0 | 0 because there exists x such that 0 · x = 0 (for instance, x = 17 is a solution). ...
... divisibility (Def. 1.1) does not involve division, only multiplication. So 0 | 0 because there exists x such that 0 · x = 0 (for instance, x = 17 is a solution). ...
notes on rational and real numbers
... thorough discussion of the objects being studied. As examples, one can mention integers, functions, limits, rational and complex numbers. It took many centuries between their appearance and use in mathematics, and the time when they were defined at the level meeting now days standards. Of course, ma ...
... thorough discussion of the objects being studied. As examples, one can mention integers, functions, limits, rational and complex numbers. It took many centuries between their appearance and use in mathematics, and the time when they were defined at the level meeting now days standards. Of course, ma ...
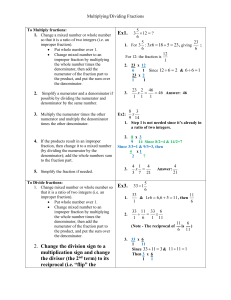
To Multiply fractions:
... 5. Simplify the fraction if needed. To Divide fractions: 1. Change mixed number or whole number so that it is a ratio of two integers (i.e. an improper fraction). Put whole number over 1. Change mixed number to an improper fraction by multiplying the whole number times the denominator, then add ...
... 5. Simplify the fraction if needed. To Divide fractions: 1. Change mixed number or whole number so that it is a ratio of two integers (i.e. an improper fraction). Put whole number over 1. Change mixed number to an improper fraction by multiplying the whole number times the denominator, then add ...
Arithmetic

Arithmetic or arithmetics (from the Greek ἀριθμός arithmos, ""number"") is the oldest and most elementary branch of mathematics. It consists of the study of numbers, especially the properties of the traditional operations between them—addition, subtraction, multiplication and division. Arithmetic is an elementary part of number theory, and number theory is considered to be one of the top-level divisions of modern mathematics, along with algebra, geometry, and analysis. The terms arithmetic and higher arithmetic were used until the beginning of the 20th century as synonyms for number theory and are sometimes still used to refer to a wider part of number theory.