109_lecture4_fall05
... To calculate Q(x) and R(x) it suffices to find R(x) since we can divide A(x)- R(x) by B(x) to get R(x) The uniqueness of the remainder says if in any way you arrange to write A(x) = B(x)K(x) + P(x) where P(x) is zero or of smaller degree than B(x) then it must be that P(x) is the R(x) you would get ...
... To calculate Q(x) and R(x) it suffices to find R(x) since we can divide A(x)- R(x) by B(x) to get R(x) The uniqueness of the remainder says if in any way you arrange to write A(x) = B(x)K(x) + P(x) where P(x) is zero or of smaller degree than B(x) then it must be that P(x) is the R(x) you would get ...
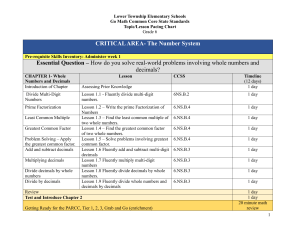
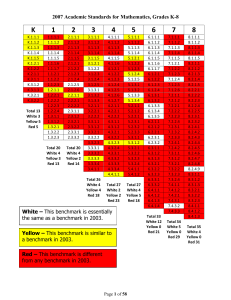
Standards with notes regarding 2003 Standards
... 2007 Academic Standards for Mathematics, Grades K-8 with Notes Regarding 2003 Highlighted items indicate content that differs from the same grade in the 2003 standards. No. Benchmark Notes 2.3.1.1 Describe, compare, and classify two- and threedimensional figures according to number and shape ...
... 2007 Academic Standards for Mathematics, Grades K-8 with Notes Regarding 2003 Highlighted items indicate content that differs from the same grade in the 2003 standards. No. Benchmark Notes 2.3.1.1 Describe, compare, and classify two- and threedimensional figures according to number and shape ...
Math Curriculum Guide - Grades 1 to 10
... Mathematics is one subject that pervades life at any age and in any circumstance. Thus, its value goes beyond the classroom and the school. Mathematics as a school subject, therefore, must be learned comprehensively and with much depth. The twin goals of mathematics in the basic education levels, K- ...
... Mathematics is one subject that pervades life at any age and in any circumstance. Thus, its value goes beyond the classroom and the school. Mathematics as a school subject, therefore, must be learned comprehensively and with much depth. The twin goals of mathematics in the basic education levels, K- ...
Fractions Decimals and Percentages
... 8 is the biggest number we can divide both by and 3/5 uses the smallest possible numbers as we cannot divide them by anything else. ...
... 8 is the biggest number we can divide both by and 3/5 uses the smallest possible numbers as we cannot divide them by anything else. ...
Chapter 3_Old
... 3b. if remainder <0, restore the original value by adding divisor to the left half of remainder, and place the sum in the left of the remainder. also shift remainder to left and setting new least significant bit 0 4. n repetitions ? if yes, done, if no, go to 2. ...
... 3b. if remainder <0, restore the original value by adding divisor to the left half of remainder, and place the sum in the left of the remainder. also shift remainder to left and setting new least significant bit 0 4. n repetitions ? if yes, done, if no, go to 2. ...
Area - Miss B Resources
... school hall. We need chocolate brownies for everyone but they come in packs of 6. How many packs do we need to buy? ...
... school hall. We need chocolate brownies for everyone but they come in packs of 6. How many packs do we need to buy? ...
4 / 8
... How do we know that two fractions are the same? We cannot tell whether two fractions are the same until we simplify them to their lowest terms. A fraction is in its lowest terms (simplified) if we cannot find a whole number (other than 1) that can divide into both its numerator and denominator (A c ...
... How do we know that two fractions are the same? We cannot tell whether two fractions are the same until we simplify them to their lowest terms. A fraction is in its lowest terms (simplified) if we cannot find a whole number (other than 1) that can divide into both its numerator and denominator (A c ...
Arithmetic

Arithmetic or arithmetics (from the Greek ἀριθμός arithmos, ""number"") is the oldest and most elementary branch of mathematics. It consists of the study of numbers, especially the properties of the traditional operations between them—addition, subtraction, multiplication and division. Arithmetic is an elementary part of number theory, and number theory is considered to be one of the top-level divisions of modern mathematics, along with algebra, geometry, and analysis. The terms arithmetic and higher arithmetic were used until the beginning of the 20th century as synonyms for number theory and are sometimes still used to refer to a wider part of number theory.