Algebra - Eircom
... In algebra we use letters to stand for numbers. I think of a number, add seven to it and the result is 11. If we let x stand for the number we can write this as follows: ...
... In algebra we use letters to stand for numbers. I think of a number, add seven to it and the result is 11. If we let x stand for the number we can write this as follows: ...
Inequality
... laptop during this quiz. No other calculator may be used. • IMPORTANT NOTE: If you have time left after you finish the problems on this quiz, use it to check your answers before you submit the quiz! ...
... laptop during this quiz. No other calculator may be used. • IMPORTANT NOTE: If you have time left after you finish the problems on this quiz, use it to check your answers before you submit the quiz! ...
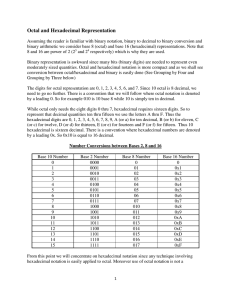
Octal and Hexadecimal Representation
... This requires knowing the powers of 16 (the powers of 2 are more easily obtained by doubling) and conversion the hexadecimal digits 0xA thru 0xF to 10 thru 15. Horner’s Method also works (?). ...
... This requires knowing the powers of 16 (the powers of 2 are more easily obtained by doubling) and conversion the hexadecimal digits 0xA thru 0xF to 10 thru 15. Horner’s Method also works (?). ...
pptx - Dave Reed
... there exists an O(N log N) divide-and-conquer solution Assume the points are sorted by x-coordinate (can be done in O(N log N)) 1. partition the points into equal parts using a vertical line in the plane 2. recursively determine the closest pair on left side (Ldist) and the closest pair on the rig ...
... there exists an O(N log N) divide-and-conquer solution Assume the points are sorted by x-coordinate (can be done in O(N log N)) 1. partition the points into equal parts using a vertical line in the plane 2. recursively determine the closest pair on left side (Ldist) and the closest pair on the rig ...
FUNCTIONS AND EQUATIONS 1.1. Definition of a set. A set is any
... We can reduce a fraction by finding common multipliers or factors in the numerator and denominator of a fraction. A fail safe way to do this is to factor a number into the primes of which it is made. We can factor 12 as 2 × 2 × 3. And 2 and 3 are both prime. Definition 1 (Prime Factorization). The p ...
... We can reduce a fraction by finding common multipliers or factors in the numerator and denominator of a fraction. A fail safe way to do this is to factor a number into the primes of which it is made. We can factor 12 as 2 × 2 × 3. And 2 and 3 are both prime. Definition 1 (Prime Factorization). The p ...
Module 2 - PDHonline
... For practice, convert the decimal number 95 to a binary number. The answer is 1011111. Also convert the binary number 1000111 to a decimal number. The answer is 71. To process numbers in electronic circuits, such as in a PLC or a computer, the numerical quantities must be represented by electrical s ...
... For practice, convert the decimal number 95 to a binary number. The answer is 1011111. Also convert the binary number 1000111 to a decimal number. The answer is 71. To process numbers in electronic circuits, such as in a PLC or a computer, the numerical quantities must be represented by electrical s ...
Three Meanings of Fractions
... Operations with Fractions • The key to helping children understand operations with fractions is to make sure they understand fractions, especially the idea of equivalent fractions. • They should be able to extend what they know about operations with whole numbers to operations with fractions. ...
... Operations with Fractions • The key to helping children understand operations with fractions is to make sure they understand fractions, especially the idea of equivalent fractions. • They should be able to extend what they know about operations with whole numbers to operations with fractions. ...
EXAMPLE EXERCISE 2.1 Uncertainty in Measurement
... To locate the first nonsignificant digit, count three digits from left to right. If the first nonsignificant digit is less than 5, drop all nonsignificant digits. If the first nonsignificant digit is 5 or greater, add 1 to the last significant digit. (a) 22.3 (Rule 2) (b) 0.345 (Rule 1) (c) 0.0720 ( ...
... To locate the first nonsignificant digit, count three digits from left to right. If the first nonsignificant digit is less than 5, drop all nonsignificant digits. If the first nonsignificant digit is 5 or greater, add 1 to the last significant digit. (a) 22.3 (Rule 2) (b) 0.345 (Rule 1) (c) 0.0720 ( ...
Arithmetic

Arithmetic or arithmetics (from the Greek ἀριθμός arithmos, ""number"") is the oldest and most elementary branch of mathematics. It consists of the study of numbers, especially the properties of the traditional operations between them—addition, subtraction, multiplication and division. Arithmetic is an elementary part of number theory, and number theory is considered to be one of the top-level divisions of modern mathematics, along with algebra, geometry, and analysis. The terms arithmetic and higher arithmetic were used until the beginning of the 20th century as synonyms for number theory and are sometimes still used to refer to a wider part of number theory.