CHAPTER 14 Psychological Disorders
... (GAD): chronic, uncontrollable, & excessive fear that lasts at least 6 months with no focus on particular object or situation (called “free-floating” anxiety) 2. Panic Disorder: sudden, but brief, attacks of intense apprehension (panic attacks) ...
... (GAD): chronic, uncontrollable, & excessive fear that lasts at least 6 months with no focus on particular object or situation (called “free-floating” anxiety) 2. Panic Disorder: sudden, but brief, attacks of intense apprehension (panic attacks) ...
Psychological Disorders PPT
... choking, or other frightening sensations. Anxiety is a component of both disorders. It occurs more in the panic disorder, making people avoid situations that cause it. Smokers have at least doubled risk of panic disorder. ...
... choking, or other frightening sensations. Anxiety is a component of both disorders. It occurs more in the panic disorder, making people avoid situations that cause it. Smokers have at least doubled risk of panic disorder. ...
the course and clinical features of obsessive compulsive disorder
... interfere with function, that distinguishes normal from abnormal. A patient must have had an hour of obsessive-compulsive symptoms daily for a period of 6 months that interfere with social or occupational function to meet DSM-IV criteria for the disorder (11). This requirement has traditionally been ...
... interfere with function, that distinguishes normal from abnormal. A patient must have had an hour of obsessive-compulsive symptoms daily for a period of 6 months that interfere with social or occupational function to meet DSM-IV criteria for the disorder (11). This requirement has traditionally been ...
the course and clinical features of obsessive compulsive
... interfere with function, that distinguishes normal from abnormal. A patient must have had an hour of obsessive-compulsive symptoms daily for a period of 6 months that interfere with social or occupational function to meet DSM-IV criteria for the disorder (11). This requirement has traditionally been ...
... interfere with function, that distinguishes normal from abnormal. A patient must have had an hour of obsessive-compulsive symptoms daily for a period of 6 months that interfere with social or occupational function to meet DSM-IV criteria for the disorder (11). This requirement has traditionally been ...
Risk factors
... Depression, body image, post traumatic experiences, emotional upheaval, OCD Common symptoms: ...
... Depression, body image, post traumatic experiences, emotional upheaval, OCD Common symptoms: ...
Personality Disorder
... didn't want to do it any more, but I couldn’t stop … The clothes hung … two fingers apart …I touched my bedroom wall before leaving the house … I had constant anxiety … I thought I might be nuts. Marc, diagnosed with obsessive-compulsive disorder (from Summers, 1996) ...
... didn't want to do it any more, but I couldn’t stop … The clothes hung … two fingers apart …I touched my bedroom wall before leaving the house … I had constant anxiety … I thought I might be nuts. Marc, diagnosed with obsessive-compulsive disorder (from Summers, 1996) ...
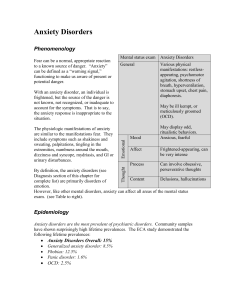
Anxiety Disorders
... withdrawal syndromes (alcohol or tranquilizers), and intoxication/therapeutic syndromes (stimulants or others). Some specific organic causes of symptoms of anxiety include excessive caffeine intake, hyperthyroidism, vitamin B12 deficiency, hypo- or hyperglycemia, cardiac arrhythmias, anemia, pulmona ...
... withdrawal syndromes (alcohol or tranquilizers), and intoxication/therapeutic syndromes (stimulants or others). Some specific organic causes of symptoms of anxiety include excessive caffeine intake, hyperthyroidism, vitamin B12 deficiency, hypo- or hyperglycemia, cardiac arrhythmias, anemia, pulmona ...
7C Anxiety and Mood Disorders
... Panic Disorder • An anxiety disorder characterized by sudden bouts of intense, unexplained anxiety ...
... Panic Disorder • An anxiety disorder characterized by sudden bouts of intense, unexplained anxiety ...
Using POCS Method of Problem
... preferences or behavior. Typically, they cause guilt, anxiety, or discomfort for one or both participants. The paraphilias cover a wide variety of behaviors, including: Pedophilia – sex with children, or child molesting. Child molesters, who are usually males, are often depicted as despicable perver ...
... preferences or behavior. Typically, they cause guilt, anxiety, or discomfort for one or both participants. The paraphilias cover a wide variety of behaviors, including: Pedophilia – sex with children, or child molesting. Child molesters, who are usually males, are often depicted as despicable perver ...
Anxiety
... intrusive thoughts, nightmares, flashbacks, or recollection of traumatic memories and images. Avoidance and emotional numbing (3/7) detachment from others; flattening of affect; loss of interest; lack of motivation; and persistent avoidance of activity, places, persons, or events associated wi ...
... intrusive thoughts, nightmares, flashbacks, or recollection of traumatic memories and images. Avoidance and emotional numbing (3/7) detachment from others; flattening of affect; loss of interest; lack of motivation; and persistent avoidance of activity, places, persons, or events associated wi ...
Pica for 36 Years with Mild Obsessive
... There are now increasing amount of cases about at least some of the pica may also belong to obsessive-compulsive spectrum disorders but there is no clinical trial about the psychiatric symptoms among pica ...
... There are now increasing amount of cases about at least some of the pica may also belong to obsessive-compulsive spectrum disorders but there is no clinical trial about the psychiatric symptoms among pica ...
314.9 Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder Not
... Attention-DeficitlHyperactivity Disorder A. Either 1 or 2: 1 six or more of the following symptoms of inattention have persisted for at least 6 months to a degree that is maladaptive and inconsistent with develop mental level: Inattention a often fails to give close attention to details or makes car ...
... Attention-DeficitlHyperactivity Disorder A. Either 1 or 2: 1 six or more of the following symptoms of inattention have persisted for at least 6 months to a degree that is maladaptive and inconsistent with develop mental level: Inattention a often fails to give close attention to details or makes car ...
15 - Chapter 14 - Psychological Disorders
... • Other: Rates are higher among the rich, nonreligious and those who are single, widowed or divorced. In the last 60 years, the global rate of annual suicide rose from 10 to 18 per 100,000. In 2006 in the US, suicide per 100,000: 11.1 (or 33,300 people). ...
... • Other: Rates are higher among the rich, nonreligious and those who are single, widowed or divorced. In the last 60 years, the global rate of annual suicide rose from 10 to 18 per 100,000. In 2006 in the US, suicide per 100,000: 11.1 (or 33,300 people). ...
Anxiety Disorders 2010
... compared to the existing external stimulus. It is an expected, normal and transient response to stress; may be a necessary cue for adaptation and coping (future event) Different from Fear: sense of dread/foreboding that occurs in response to external threatening event. ...
... compared to the existing external stimulus. It is an expected, normal and transient response to stress; may be a necessary cue for adaptation and coping (future event) Different from Fear: sense of dread/foreboding that occurs in response to external threatening event. ...
Module 12: Effects of Stress
... •Often associated with physical symptoms like choking sensations or shortness of breath ...
... •Often associated with physical symptoms like choking sensations or shortness of breath ...
Personality Disorder
... didn't want to do it any more, but I couldn’t stop … The clothes hung … two fingers apart …I touched my bedroom wall before leaving the house … I had constant anxiety … I thought I might be nuts. Marc, diagnosed with obsessive-compulsive disorder (from Summers, 1996) ...
... didn't want to do it any more, but I couldn’t stop … The clothes hung … two fingers apart …I touched my bedroom wall before leaving the house … I had constant anxiety … I thought I might be nuts. Marc, diagnosed with obsessive-compulsive disorder (from Summers, 1996) ...
Please keep track of any disorders discussed that you would like to
... • They don’t have a substitute yet. • “[A] clinically significant behavioral or psychological syndrome or pattern that occurs in an individual and that is associated with present distress (e.g., a painful symptom) or disability (i.e., impairment in one or more important areas of functioning) or with ...
... • They don’t have a substitute yet. • “[A] clinically significant behavioral or psychological syndrome or pattern that occurs in an individual and that is associated with present distress (e.g., a painful symptom) or disability (i.e., impairment in one or more important areas of functioning) or with ...
Anxiety disorders:Diagnosis and Treatment
... recurrent and persistent thoughts, impulses or images that are intrusive and unwanted that cause marked anxiety or distress The person attempts to ignore or suppress such thoughts, urges or images, or to neutralize them with some other thought or action (i.e. compulsion) ...
... recurrent and persistent thoughts, impulses or images that are intrusive and unwanted that cause marked anxiety or distress The person attempts to ignore or suppress such thoughts, urges or images, or to neutralize them with some other thought or action (i.e. compulsion) ...
AnxietyDisorders.web
... More Diffuse Response About Impending Real or Imagined “Future” Threat or Danger ...
... More Diffuse Response About Impending Real or Imagined “Future” Threat or Danger ...
Studying Psychological Disorders Studying Psychological Disorders
... fear of crowds, strangers meeting new people eating in public ...
... fear of crowds, strangers meeting new people eating in public ...
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY AND CLINICAL BIOCHEMISTRY (PAT …
... embarrassing manner two types: specific social phobia: fear of one or more discrete social situations, especially performance anxiety generalized social phobia: difficulty with most social situations ...
... embarrassing manner two types: specific social phobia: fear of one or more discrete social situations, especially performance anxiety generalized social phobia: difficulty with most social situations ...
Anxiety Disorder - Healthy Minds Clinic
... Children and teens can have more than one type of anxiety disorder at the same time. Some types of anxiety disorders are: Separation Anxiety Disorder Sometimes older children and teens become frightened of leaving their parent(s). They may worry that something bad might happen to their parent or to ...
... Children and teens can have more than one type of anxiety disorder at the same time. Some types of anxiety disorders are: Separation Anxiety Disorder Sometimes older children and teens become frightened of leaving their parent(s). They may worry that something bad might happen to their parent or to ...
Abnormal Psychology
... OCD • 4 million Americans have OCD (makes it more common than panic disorder and ...
... OCD • 4 million Americans have OCD (makes it more common than panic disorder and ...
somatoform disorder and homeopathy
... Homeopathic approach to Somatoform disorder: When a person is stumbling upon a lot of stress and is unable to cope with that stress, then they start experiencing physical symptoms. Homeopathy appreciates the psychological source of somatic symptoms. Homeopathic remedies function at the level of mind ...
... Homeopathic approach to Somatoform disorder: When a person is stumbling upon a lot of stress and is unable to cope with that stress, then they start experiencing physical symptoms. Homeopathy appreciates the psychological source of somatic symptoms. Homeopathic remedies function at the level of mind ...
Obsessive–compulsive disorder

Obsessive–compulsive disorder (OCD) is a mental disorder where people feel the need to check things repeatedly, have certain thoughts repeatedly, or feel they need to perform certain routines repeatedly. People are unable to control either the thoughts or the activities. Common activities include hand washing, counting of things, and checking to see if a door is locked. Some may have difficulty throwing things out. These activities occur to such a degree that the person's daily life is negatively affected. Often they take up more than an hour a day. Most adults realize that the behaviors do not make sense. The condition is associated with tics, anxiety disorder, and an increased risk of suicide.The cause is unknown. There appears to be some genetic components with identical twins more often affected than non-identical twins. Risk factors include a history of child abuse or other stress inducing event. Some cases have been documented to occur following infections. The diagnosis is based on the symptoms and requires ruling out other drug related or medical causes. Rating scales such as Yale–Brown Obsessive Compulsive Scale can be used to assess the severity. Other disorders with similar symptoms include: anxiety disorder, major depressive disorder, eating disorders, tic disorders, and obsessive–compulsive personality disorder.Treatment for OCD involves the use of behavioral therapy and sometimes selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs). The type of behavior therapy used involves increasing exposure to what causes the problems while not allowing the repetitive behavior to occur. Atypical antipsychotics such as quetiapine may be useful when used in addition to an SSRI in treatment-resistant cases but are associated with an increased risk of side effects. Without treament the condition often lasts decades.Obsessive–compulsive disorder affects about 2.3% of people at some point in their life. Rates during a given year are about 1.2% and it occurs worldwide. It is unusual for symptoms to begin after the age of thirty-five and half of people develop problems before twenty. Males and females are affected about equally. In English the phrase obsessive–compulsive is often used in an informal manner unrelated to OCD to describe someone who is excessively meticulous, perfectionistic, absorbed, or otherwise fixated.