Writing a DSM-5 Diagnosis
... DSM-5 does insist that multiple diagnoses must be presented in a hierarchy descending from the condition of most significance to that of the least concern (i.e., it must reflect the client’s presentation at the time of assessment and be based on the reason for referral / focus of clinical attention ...
... DSM-5 does insist that multiple diagnoses must be presented in a hierarchy descending from the condition of most significance to that of the least concern (i.e., it must reflect the client’s presentation at the time of assessment and be based on the reason for referral / focus of clinical attention ...
Dissociative identity disorder.
... Another onset is that the child might have an ‘imagery friend’. And that ‘imagery friend’ would ‘attach itself’ to the child and start to take over the body.(ross,2012) ...
... Another onset is that the child might have an ‘imagery friend’. And that ‘imagery friend’ would ‘attach itself’ to the child and start to take over the body.(ross,2012) ...
- Journal of the American Academy of Child and
... their significance. When used appropriately, information about biological influences on sexual orientation can be relevant to patients, families, and clinicians. However, such influences do not constitute an illness. Psychological and Social Factors. Before the shift to empirically based psychiatry ...
... their significance. When used appropriately, information about biological influences on sexual orientation can be relevant to patients, families, and clinicians. However, such influences do not constitute an illness. Psychological and Social Factors. Before the shift to empirically based psychiatry ...
Psychological Disorders
... A mood disorder in which a person, for no apparent reason, experiences two or more weeks of depressed moods, feelings of worthlessness, and diminished interest or please in most activities. Manic episode A mood disorder marked by a hyperactive, wildly optimistic state. Medical model The concept tha ...
... A mood disorder in which a person, for no apparent reason, experiences two or more weeks of depressed moods, feelings of worthlessness, and diminished interest or please in most activities. Manic episode A mood disorder marked by a hyperactive, wildly optimistic state. Medical model The concept tha ...
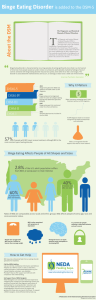
Binge Eating Disorder is added to the DSM-5
... the criteria established by the APA to diagnose them. For a particular mental disorder to be diagnosed in an individual, the individual must exhibit the symptoms listed in the criteria for that disorder. ...
... the criteria established by the APA to diagnose them. For a particular mental disorder to be diagnosed in an individual, the individual must exhibit the symptoms listed in the criteria for that disorder. ...
exploring psychology
... Sexual disorders have become sexual dysfunctions in the new DSM, and some of the labeling and the classifications and their criteria have changed. SPECIFIC LEARNING DISORDER (pp. 26, 312) Learning disorders are now identified as a group under the label of specific learning disorder (rather than sepa ...
... Sexual disorders have become sexual dysfunctions in the new DSM, and some of the labeling and the classifications and their criteria have changed. SPECIFIC LEARNING DISORDER (pp. 26, 312) Learning disorders are now identified as a group under the label of specific learning disorder (rather than sepa ...
Antisocial Personality Disorder
... Studies have shown that it is very difficult to treat because people with it may not even want or think that they need any type of treatment. Long term one on one therapy might work but getting the patient to stick to it is difficult. Treatment for depression & anxiety may be needed to be give ...
... Studies have shown that it is very difficult to treat because people with it may not even want or think that they need any type of treatment. Long term one on one therapy might work but getting the patient to stick to it is difficult. Treatment for depression & anxiety may be needed to be give ...
Crystallising Psychological Injury
... DSM-5 The DSM-5 field trials suggest that post-traumatic stress disorder can be diagnosed with very high reliability, a kappa of 0.67 (higher than any other anxiety disorder or depression) – for illustration if an illness appears in 10% of a clinic’s clients and two colleagues agree on its diagnos ...
... DSM-5 The DSM-5 field trials suggest that post-traumatic stress disorder can be diagnosed with very high reliability, a kappa of 0.67 (higher than any other anxiety disorder or depression) – for illustration if an illness appears in 10% of a clinic’s clients and two colleagues agree on its diagnos ...
DSM-IV-TR Invalidities - Professionaltrainingresourcesinc.com
... symptomatic of an underlying dysfunction within the individual and not simply a reaction to the immediate social context and that “it may be helpful for the clinician to consider the social and economic context in which the undesirable behaviors have occurred. ...
... symptomatic of an underlying dysfunction within the individual and not simply a reaction to the immediate social context and that “it may be helpful for the clinician to consider the social and economic context in which the undesirable behaviors have occurred. ...
Anxiety, Somatoform, and Dissociative Disorders Homework
... 7. Suppose a person makes an appointment with a doctor once a month to check for cancer, even though her tests are always negative. Which somatoform behavior does this behavior suggest? _______________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________ ...
... 7. Suppose a person makes an appointment with a doctor once a month to check for cancer, even though her tests are always negative. Which somatoform behavior does this behavior suggest? _______________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________ ...
hi low
... Somatization Disorder A. History of many physical complaints beginning before age 30 that result in treatment being sought or significant impairment B. Each of the following criteria must have been met: 1. Four pain symptoms 2. Two gastrointestinal symptoms 3. One sexual or reproductive symptom 4. ...
... Somatization Disorder A. History of many physical complaints beginning before age 30 that result in treatment being sought or significant impairment B. Each of the following criteria must have been met: 1. Four pain symptoms 2. Two gastrointestinal symptoms 3. One sexual or reproductive symptom 4. ...
Disruptive, Impulse Control, and Conduct Disorders
... is what type of aggressive outbursts should be considered: DSM-IV-TR required physical aggression, whereas in DSM-5 verbal aggression and nondestructive/noninjurious physical aggression also meet criteria. An important departure from past diagnostic manuals is that the substancerelated and addictive ...
... is what type of aggressive outbursts should be considered: DSM-IV-TR required physical aggression, whereas in DSM-5 verbal aggression and nondestructive/noninjurious physical aggression also meet criteria. An important departure from past diagnostic manuals is that the substancerelated and addictive ...
The DSM-IV G. Scott Sparrow, Ed.D University of Texas
... Two other controversial diagnoses would have been enshrined in the DSM III if women hadn't objected. Under Spitzer's editorship, which lasted through the publication of the DSM-IIIR, the diagnosis of "masochistic personality disorder" was briefly considered before women expressed concern that it wou ...
... Two other controversial diagnoses would have been enshrined in the DSM III if women hadn't objected. Under Spitzer's editorship, which lasted through the publication of the DSM-IIIR, the diagnosis of "masochistic personality disorder" was briefly considered before women expressed concern that it wou ...
what is abnormal psychology?
... Jumping off high roofs just for the thrill of it Talking to oneself Wash your hands 20 times a day and be happy about it ...
... Jumping off high roofs just for the thrill of it Talking to oneself Wash your hands 20 times a day and be happy about it ...
Chapter 8: Dissociative Disorders and Somatic-Symptom
... • The physical signs or diagnostic findings are internally inconsistent or incongruent with recognized neurological disorder • The symptoms are incompatible with recognized medical disorders • Symptoms cause significant distress or functional impairment or warrant medical evaluation • Note: DSM-IV-T ...
... • The physical signs or diagnostic findings are internally inconsistent or incongruent with recognized neurological disorder • The symptoms are incompatible with recognized medical disorders • Symptoms cause significant distress or functional impairment or warrant medical evaluation • Note: DSM-IV-T ...
Specify dissociative fugue subtype if the amnesia is
... • Symptoms cause significant distress or functional impairment or warrant medical evaluation • Note: DSM-IV-TR criteria specify that symptoms are related to conflict or stress and are not intentionally produced. Other changes from DSM-IV-TR are italicized ...
... • Symptoms cause significant distress or functional impairment or warrant medical evaluation • Note: DSM-IV-TR criteria specify that symptoms are related to conflict or stress and are not intentionally produced. Other changes from DSM-IV-TR are italicized ...
Chapters 1-2 DSM-IV-TR in Action
... The DSM is an essential starting point in determining the nature of a client’s problem. It does not provide treatment approaches, so companion books are necessary. It should only be used by professionals. ...
... The DSM is an essential starting point in determining the nature of a client’s problem. It does not provide treatment approaches, so companion books are necessary. It should only be used by professionals. ...
Disorders of Dissociation
... Disorder. Clients will have a primary identity that carries the individual’s legal name. Each alternative frequently has a different name and can vary from the primary identity in terms of age, gender, knowledge, and affect. ...
... Disorder. Clients will have a primary identity that carries the individual’s legal name. Each alternative frequently has a different name and can vary from the primary identity in terms of age, gender, knowledge, and affect. ...
Somatic Symptom Disorder - DSM-5
... Comprehensive assessment of patients requires the recognition that psychiatric problems often cooccur in patients with medical problems. While DSM-IV was organized centrally around the concept of medically unexplained symptoms, DSM-5 criteria instead emphasize the degree to which a patient’s though ...
... Comprehensive assessment of patients requires the recognition that psychiatric problems often cooccur in patients with medical problems. While DSM-IV was organized centrally around the concept of medically unexplained symptoms, DSM-5 criteria instead emphasize the degree to which a patient’s though ...
OCDR USC Sites Flyer_20150326_IRB Approved_No Riverside Ofc
... OCD is characterized by obsessions which are unwanted thoughts, images and impulses that “pop” into a person’s mind, generate anxiety and lead to compulsions that are actions aimed to reduce the distress generated by the obsessions. Hoarding Disorder is characterized by excessively saving items that ...
... OCD is characterized by obsessions which are unwanted thoughts, images and impulses that “pop” into a person’s mind, generate anxiety and lead to compulsions that are actions aimed to reduce the distress generated by the obsessions. Hoarding Disorder is characterized by excessively saving items that ...
PSY240H1S Introduction to Abnormal Psychology
... Somatization Disorder A. History of many physical complaints beginning before age 30 that result in treatment being sought or significant impairment B. Each of the following criteria must have been met: 1. Four pain symptoms 2. Two gastrointestinal symptoms 3. One sexual or reproductive symptom 4. ...
... Somatization Disorder A. History of many physical complaints beginning before age 30 that result in treatment being sought or significant impairment B. Each of the following criteria must have been met: 1. Four pain symptoms 2. Two gastrointestinal symptoms 3. One sexual or reproductive symptom 4. ...
Bipolar Disorder In Children: Why Are The Rates Rising
... forty times more frequent than it was just ten years ago. Can the numbers of children and adolescents with this illness increase so rapidly? Are medications being over-prescribed? The rapid increase in diagnoses in such a short period of time cannot be explained by changes in genetics, environment o ...
... forty times more frequent than it was just ten years ago. Can the numbers of children and adolescents with this illness increase so rapidly? Are medications being over-prescribed? The rapid increase in diagnoses in such a short period of time cannot be explained by changes in genetics, environment o ...
The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders * 5th
... Users encouraged to record multiple psychiatric diagnoses (in order of importance) and associated physical conditions Coincided with ICD-8 (first time ICD included mental disorders) ...
... Users encouraged to record multiple psychiatric diagnoses (in order of importance) and associated physical conditions Coincided with ICD-8 (first time ICD included mental disorders) ...
Psychiatric Classification
... No neuro, medical, substance abuse or cultural explanation Must cause marked distress ...
... No neuro, medical, substance abuse or cultural explanation Must cause marked distress ...