Fuse (electrical)

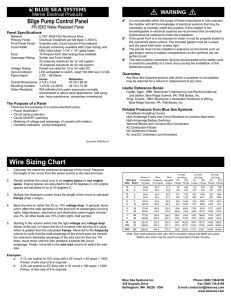
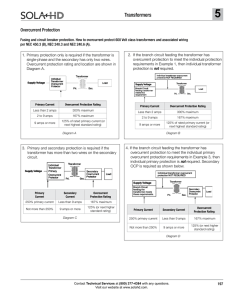
In electronics and electrical engineering, a fuse (from the French fusée, Italian fuso, ""spindle"") is a type of low resistance resistor that acts as a sacrificial device to provide overcurrent protection, of either the load or source circuit. Its essential component is a metal wire or strip that melts when too much current flows through it, interrupting the circuit that it connects. Short circuits, overloading, mismatched loads, or device failure are the prime reasons for excessive current. Fuses are an alternative to circuit breakers.A fuse interrupts excessive current (""blows"") so that further damage by overheating or fire is prevented. Wiring regulations often define a maximum fuse current rating for particular circuits. Overcurrent protection devices are essential in electrical systems to limit threats to human life and property damage. The time and current operating characteristics of fuses are chosen to provide adequate protection without needless interruption. Slow blow fuses are designed to allow harmless short term currents over their rating while still interrupting a sustained overload. Fuses are manufactured in a wide range of current and voltage ratings to protect wiring systems and electrical equipment. Self-resetting fuses automatically restore the circuit after the overload has cleared, and are useful in environments where a human replacing a blown fuse would be difficult or impossible, for example in aerospace or nuclear applications.