Matt Wolf - CB East Wolf
... Apply prior knowledge of algebra in order to solve for angle measures formed by parallel lines. Section 3.3 Proving Lines Parallel Prove two lines are parallel by showing that parallel line angle relationships hold (alternate-interior angles are congruent, same-side interior angles are supplemen ...
... Apply prior knowledge of algebra in order to solve for angle measures formed by parallel lines. Section 3.3 Proving Lines Parallel Prove two lines are parallel by showing that parallel line angle relationships hold (alternate-interior angles are congruent, same-side interior angles are supplemen ...
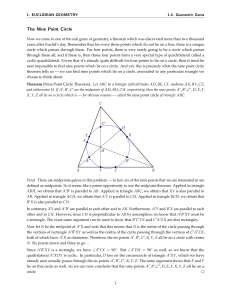
Systems of Geometry Test File Spring 2010 Test 1 1.) Consider a
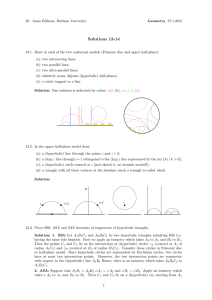
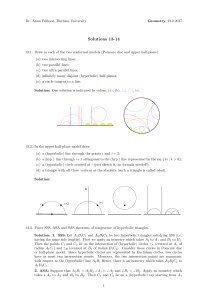
... tangent to a circle Consider a geometry with undefined terms point, line, and contains (or belongs) and the following axioms. Axiom 1. Given any two distinct points, there is exactly one line containing both of them Axiom 2. Each line contains at least two points. Axiom 3. There exist at least three ...
... tangent to a circle Consider a geometry with undefined terms point, line, and contains (or belongs) and the following axioms. Axiom 1. Given any two distinct points, there is exactly one line containing both of them Axiom 2. Each line contains at least two points. Axiom 3. There exist at least three ...