Hubble Telescope Pictures
... distance of these objects from earth, i.e. one(1) light year = 5,865,696,000,000 or 6 trillion miles. ...
... distance of these objects from earth, i.e. one(1) light year = 5,865,696,000,000 or 6 trillion miles. ...
Mason_Engines of Cha..
... • Illustrative - Other nations have similar plans, and many missions likely to be realised by international collaboration to make them affordable • So what are the prospects for the next few years? ...
... • Illustrative - Other nations have similar plans, and many missions likely to be realised by international collaboration to make them affordable • So what are the prospects for the next few years? ...
Pressemitteilung - Micro
... globally operating sensor manufacturer employs around 1,000 people in the Group, with almost 400 at its Lower Bavarian headquarters. ...
... globally operating sensor manufacturer employs around 1,000 people in the Group, with almost 400 at its Lower Bavarian headquarters. ...
Stellar Explosion has Many Layers
... sky. Calculating its expansion back, astronomers have found that the supernova must have blown up around ...
... sky. Calculating its expansion back, astronomers have found that the supernova must have blown up around ...
Document
... • Excellent for lunar, planetary and binary star observing especially in larger apertures. • High contrast images with no secondary mirror or diagonal obstruction. • Sealed optical tube reduces image degrading air currents and protects ...
... • Excellent for lunar, planetary and binary star observing especially in larger apertures. • High contrast images with no secondary mirror or diagonal obstruction. • Sealed optical tube reduces image degrading air currents and protects ...
dtu7ech03 pt 2 - Fort Thomas Independent Schools
... visibility of celestial objects. This is called light pollution, and has been an increasing problem in recent years. The view from Kitt Peak National Observatory of the Tuscon, Arizona skyline in 1959 ...
... visibility of celestial objects. This is called light pollution, and has been an increasing problem in recent years. The view from Kitt Peak National Observatory of the Tuscon, Arizona skyline in 1959 ...
Document
... – How can we measure the Point Spread Function while we observe? – How accurate can we make our photometry? astrometry? – What methods will allow us to do high-precision spectroscopy? ...
... – How can we measure the Point Spread Function while we observe? – How accurate can we make our photometry? astrometry? – What methods will allow us to do high-precision spectroscopy? ...
Document
... 2. Resolving power (or resolution) is the smallest angular separation detectable with an instrument. It is a measure of an instrument’s ability to see detail. 3. The resolving power of a human eye is about 1 arcminute (1/60 of a degree). A 15-cm (6-inch) telescope has a maximum resolving power of 1 ...
... 2. Resolving power (or resolution) is the smallest angular separation detectable with an instrument. It is a measure of an instrument’s ability to see detail. 3. The resolving power of a human eye is about 1 arcminute (1/60 of a degree). A 15-cm (6-inch) telescope has a maximum resolving power of 1 ...
Telesopes
... • Astronomical objects radiate in wavelengths other than visible (thermal radiators) – Cold gas clouds – Dust clouds – Hot gases around black holes ...
... • Astronomical objects radiate in wavelengths other than visible (thermal radiators) – Cold gas clouds – Dust clouds – Hot gases around black holes ...
Lecture9 - Physics
... The percentage of radiation that can penetrate the Earth’s atmosphere at different wavelengths. Regions in which the curve is high are called “windows,” because the atmosphere is relatively transparent at those wavelengths. There are also three wavelength ranges in which the atmosphere is opaque a ...
... The percentage of radiation that can penetrate the Earth’s atmosphere at different wavelengths. Regions in which the curve is high are called “windows,” because the atmosphere is relatively transparent at those wavelengths. There are also three wavelength ranges in which the atmosphere is opaque a ...
186,000 miles per second
... So, if you double the size of the telescope, it increases its light gathering potential by ____? ...
... So, if you double the size of the telescope, it increases its light gathering potential by ____? ...
Prop 17 - WM Keck Observatory
... emission from spiders, secondary obscuration, and (3) evaluate the potential of coronagraphic instruments at Keck that look for exo-planets. Description (Please describe your night-time engineering plan; provide justification for the time request, and include figures, ECR description and other attac ...
... emission from spiders, secondary obscuration, and (3) evaluate the potential of coronagraphic instruments at Keck that look for exo-planets. Description (Please describe your night-time engineering plan; provide justification for the time request, and include figures, ECR description and other attac ...
Slide 1
... Can get radio images whose resolution is close to optical Interferometry can also be done with visible light but is much more difficult due to shorter wavelengths ...
... Can get radio images whose resolution is close to optical Interferometry can also be done with visible light but is much more difficult due to shorter wavelengths ...
Introduction to Astronomy
... • Only stars emit visible light, everything else (planets & moons) are reflecting light • Other instruments can detect the other electromagnetic waves ...
... • Only stars emit visible light, everything else (planets & moons) are reflecting light • Other instruments can detect the other electromagnetic waves ...
Space Science Ch. 1 Notes - Mr. Ruggiero`s Science 8-2
... Galileo started it all with his hand-held telescope. It was powerful enough to see some of Jupiter’s moons and show that the Earth isn’t the center of the universe. Space exploration has mushroomed in the past 50 years. Rockets that originally lofted weapons during World War II were converted to car ...
... Galileo started it all with his hand-held telescope. It was powerful enough to see some of Jupiter’s moons and show that the Earth isn’t the center of the universe. Space exploration has mushroomed in the past 50 years. Rockets that originally lofted weapons during World War II were converted to car ...
Snímka 1
... Nasmyth foci by software control. Rapid and precise focus change between the two Nasmyth foci gets a simple standard task to be able to use two different instruments at two foci at practically the same time. The lower Serrurier truss part holds the mirror cell with the M1 primary mirror. The mirror ...
... Nasmyth foci by software control. Rapid and precise focus change between the two Nasmyth foci gets a simple standard task to be able to use two different instruments at two foci at practically the same time. The lower Serrurier truss part holds the mirror cell with the M1 primary mirror. The mirror ...
Large Diameter Telescopes
... The Charge Coupled Device (CCD) is an important part of the detection system of many modern telescopes due to its high quantum efficiency. Explain what is meant by quantum efficiency and compare the quantum efficiency of a CCD with that of the eye. ...
... The Charge Coupled Device (CCD) is an important part of the detection system of many modern telescopes due to its high quantum efficiency. Explain what is meant by quantum efficiency and compare the quantum efficiency of a CCD with that of the eye. ...
Light and Telescopes II
... Must be done from space Gamma rays can not be focused, so only detectors are used ...
... Must be done from space Gamma rays can not be focused, so only detectors are used ...
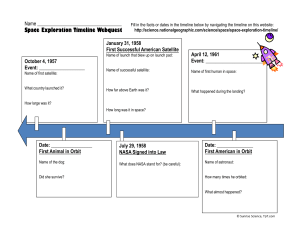
Space Exploration Timeline Webquest
... Date: _______________ First Manned Moon Landing What is the name of the capsule? ...
... Date: _______________ First Manned Moon Landing What is the name of the capsule? ...
Earthrise at Christmas Thirty-five years ago this Christmas, a
... Hubble eXtreme Deep Field – October 2012 The photo was assembled by combining 10 years of NASA Hubble Space Telescope photographs taken of a patch of sky at the center of the original Hubble Ultra Deep Field. The Hubble Ultra Deep Field is an image of a small area of space in the constellation Forn ...
... Hubble eXtreme Deep Field – October 2012 The photo was assembled by combining 10 years of NASA Hubble Space Telescope photographs taken of a patch of sky at the center of the original Hubble Ultra Deep Field. The Hubble Ultra Deep Field is an image of a small area of space in the constellation Forn ...
YCCC Jeopardy Vocabulary PowerPoint Presentation
... A collection of many billions of stars, gas and dust (including nebulae), all held together by the force of gravity. ...
... A collection of many billions of stars, gas and dust (including nebulae), all held together by the force of gravity. ...
Astronomy 212 EXAM 2 2011 October 26 Except for questions 38
... 15. Radio waves move slower through space than X-rays. 16. The main reason for building large Earth-based telescopes is to magnify the tiny images of stars. 17. Smaller resolution is the aim of a radio interferometer. 18. A telescope able to resolve two arc seconds is better than one able to resolve ...
... 15. Radio waves move slower through space than X-rays. 16. The main reason for building large Earth-based telescopes is to magnify the tiny images of stars. 17. Smaller resolution is the aim of a radio interferometer. 18. A telescope able to resolve two arc seconds is better than one able to resolve ...
James Webb Space Telescope

The James Webb Space Telescope (JWST), previously known as Next Generation Space Telescope (NGST), is a space observatory under construction and scheduled to launch in October 2018. The JWST will offer unprecedented resolution and sensitivity from long-wavelength visible to the mid-infrared, and is a successor instrument to the Hubble Space Telescope and the Spitzer Space Telescope. The telescope features a segmented 6.5-meter (21 ft) diameter primary mirror and will be located near the Earth–Sun L2 point. A large sunshield will keep its mirror and four science instruments below 50 K (−220 °C; −370 °F).JWST's capabilities will enable a broad range of investigations across the fields of astronomy and cosmology. One particular goal involves observing some of the most distant objects in the Universe, beyond the reach of current ground and space based instruments. This includes the very first stars, the epoch of reionization, and the formation of the first galaxies. Another goal is understanding the formation of stars and planets. This will include imaging molecular clouds and star-forming clusters, studying the debris disks around stars, direct imaging of planets, and spectroscopic examination of planetary transits.In gestation since 1996, the project represents an international collaboration of about 17 countries led by NASA, and with significant contributions from the European Space Agency and the Canadian Space Agency. It is named after James E. Webb, the second administrator of NASA, who played an integral role in the Apollo program.The JWST has a history of major cost overruns and delays. The first realistic budget estimates were that the observatory would cost $1.6 billion and launch in 2011. NASA has now scheduled the telescope for a 2018 launch. In 2011, the United States House of Representatives voted to terminate funding, after about $3 billion had been spent and 75 percent of its hardware was in production. Funding was restored in compromise legislation with the US Senate, and spending on the program was capped at $8 billion. As of December 2014, the telescope remained on schedule and within budget, but at risk of further delays.