CS 413, Assignment 1
... 4. The components of a knapsack problem are shown. Give the mathematical expression (equation) showing their relationship, assuming that the vector V is a solution. V = (v1, v2, …, vn), vi an element of {0, 1) S = (a1, a2, …, an), ai an element of {the positive integers) T, a positive integer 5. Her ...
... 4. The components of a knapsack problem are shown. Give the mathematical expression (equation) showing their relationship, assuming that the vector V is a solution. V = (v1, v2, …, vn), vi an element of {0, 1) S = (a1, a2, …, an), ai an element of {the positive integers) T, a positive integer 5. Her ...
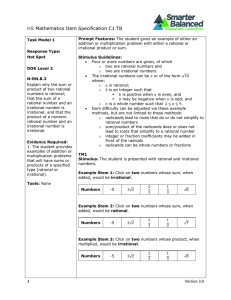
Enriched Pre-Algebra - End of the Year Test Review Short Answer
... 8. A smokestack of a factory casts a 35-meter shadow at the same time as a 10-meter utility pole casts a 6.3meter shadow. What is the height of the smokestack? Write a percent proportion to solve each problem. Then solve. Round to the nearest tenth if necessary. 9. 175 is 19% of what number? Solve e ...
... 8. A smokestack of a factory casts a 35-meter shadow at the same time as a 10-meter utility pole casts a 6.3meter shadow. What is the height of the smokestack? Write a percent proportion to solve each problem. Then solve. Round to the nearest tenth if necessary. 9. 175 is 19% of what number? Solve e ...
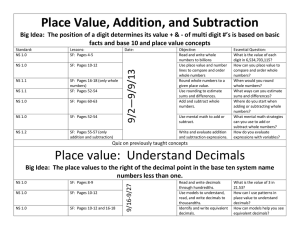
Place Value, Addition, and Subtraction Big Idea: The position of a
... What is the value of each digit in 6,534,703,115? How can you place value to compare and order whole numbers? When would you round whole numbers? What ways can you estimate sums and differences? Where do you start when adding or subtracting whole numbers? What mental math strategies can you use to a ...
... What is the value of each digit in 6,534,703,115? How can you place value to compare and order whole numbers? When would you round whole numbers? What ways can you estimate sums and differences? Where do you start when adding or subtracting whole numbers? What mental math strategies can you use to a ...
chap4
... Irrational numbers cannot be expressed as a ratio of two integers. When expressed as floats, irrational numbers have non repeating decimals with no determined bounds. Some examples of irrational numbers include 2 , π , and the exponential constant e . To maintain exactness, Maple will typically “ref ...
... Irrational numbers cannot be expressed as a ratio of two integers. When expressed as floats, irrational numbers have non repeating decimals with no determined bounds. Some examples of irrational numbers include 2 , π , and the exponential constant e . To maintain exactness, Maple will typically “ref ...
Class 6 Integers
... Following picture shows that negative numbers are on lef t hand side of 0 on number line, while natural numbers are on right hand side of 0 ...
... Following picture shows that negative numbers are on lef t hand side of 0 on number line, while natural numbers are on right hand side of 0 ...