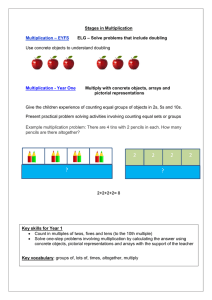
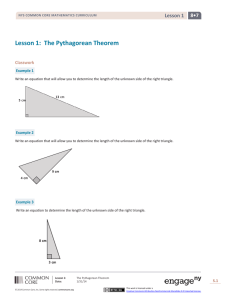
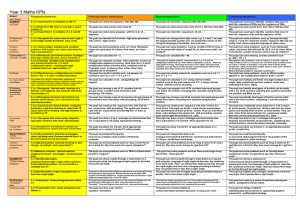
3.1 Using and Expressing Measurements
... • In chemistry, the meanings of accuracy and precision are quite different. • Accuracy is a measure of how close a measurement comes to the actual or true value of whatever is measured. • Precision is a measure of how close a series of measurements are to one another, irrespective of the actual valu ...
... • In chemistry, the meanings of accuracy and precision are quite different. • Accuracy is a measure of how close a measurement comes to the actual or true value of whatever is measured. • Precision is a measure of how close a series of measurements are to one another, irrespective of the actual valu ...
PowerPoint
... • This effect is very important for two kinds of numbers: – Numbers like 0.1 that can be written exactly in base 10, but cannot be stored exactly in base 2. – Real numbers (like or e) that have an infinite number of digits in their “real” representation can only be stored in a finite number of dig ...
... • This effect is very important for two kinds of numbers: – Numbers like 0.1 that can be written exactly in base 10, but cannot be stored exactly in base 2. – Real numbers (like or e) that have an infinite number of digits in their “real” representation can only be stored in a finite number of dig ...