Lecture 1 - ODU Computer Science
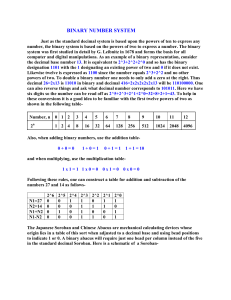
... •Instructions and data are stored in memory and are read and written as numbers All computers use the binary number system (base 2) (basic nature of electronic circuits ON/OFF, current flow/does not flow) Machine alphabet has two letters “0”, “1” Each letter is a binary digit “bit”. Byte is 8 bits L ...
... •Instructions and data are stored in memory and are read and written as numbers All computers use the binary number system (base 2) (basic nature of electronic circuits ON/OFF, current flow/does not flow) Machine alphabet has two letters “0”, “1” Each letter is a binary digit “bit”. Byte is 8 bits L ...
binary number system
... number, the binary system is based on the powers of two to express a number. The binary system was first studied in detail by G. Leibnitz in 1678 and forms the basis for all computer and digital manipulations. As an example of a binary representation, consider the decimal base number 13. It is equiv ...
... number, the binary system is based on the powers of two to express a number. The binary system was first studied in detail by G. Leibnitz in 1678 and forms the basis for all computer and digital manipulations. As an example of a binary representation, consider the decimal base number 13. It is equiv ...
Chapter 1
... 2.4.3.4.1. based on multiples of 60 2.4.3.4.2. utilized only two symbols 2.4.3.4.3. each symbol had multiple meanings 2.4.3.4.4. meaning determined by context or the position in which it appeared 2.4.3.4.5. see fig. 2.37 and 2.38 p. 108-109 2.4.3.5. Your turn p. 109: Do the practice and the reflect ...
... 2.4.3.4.1. based on multiples of 60 2.4.3.4.2. utilized only two symbols 2.4.3.4.3. each symbol had multiple meanings 2.4.3.4.4. meaning determined by context or the position in which it appeared 2.4.3.4.5. see fig. 2.37 and 2.38 p. 108-109 2.4.3.5. Your turn p. 109: Do the practice and the reflect ...
6.2 Law of Exponents / Scientific Notation
... base, subtract the exponent of the denominator from the exponent of the numerator. ...
... base, subtract the exponent of the denominator from the exponent of the numerator. ...
Physics 11 - Course Assessment Assignment Hand in the last two
... PART C: Scientific Notation Scientific notation is a short-hand of writing numbers. It will not only save you time and writing, but actually simplifies numbers that are very large or very small. In chemistry you will deal with both very large and very small numbers as we deal with atoms and molecule ...
... PART C: Scientific Notation Scientific notation is a short-hand of writing numbers. It will not only save you time and writing, but actually simplifies numbers that are very large or very small. In chemistry you will deal with both very large and very small numbers as we deal with atoms and molecule ...
Chapter 7
... • A negative exponent means I over. • Usually a negative exponent means a fraction. ...
... • A negative exponent means I over. • Usually a negative exponent means a fraction. ...
Fraction-3
... Find an equivalent fraction for each with the same denominator 35, the least common multiple of 5 and 7. 2/5 = 14/35 and 3/7 = 15/35. Since 15/35 > 14/35, hence 3/7 > 2/5. Practice B: Compare these fractions. Circle the larger fraction. ...
... Find an equivalent fraction for each with the same denominator 35, the least common multiple of 5 and 7. 2/5 = 14/35 and 3/7 = 15/35. Since 15/35 > 14/35, hence 3/7 > 2/5. Practice B: Compare these fractions. Circle the larger fraction. ...