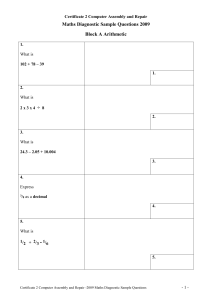
Busy Ant Activity Sheet 10
... simplest form. To multiply fractions, multiply the numerators of the fractions to find the new numerator and multiply the denominators of the fractions to find the new denominator. To remember the method, it can help to carry out the simplest possible calculation, i.e. ...
... simplest form. To multiply fractions, multiply the numerators of the fractions to find the new numerator and multiply the denominators of the fractions to find the new denominator. To remember the method, it can help to carry out the simplest possible calculation, i.e. ...
Lesson 1.2 - GEOCITIES.ws
... You shall be capable of multiplying two or more fractions. [Example 1.2.13, 1.2.14] You shall be capable of dividing two fractions. [Example 1.2.15, 1.2.16, 1.2.17] You shall be capable of adding or subtracting two fractions with a common denominator. [Example 1.2.18, 1.2.19] You shall be capable of ...
... You shall be capable of multiplying two or more fractions. [Example 1.2.13, 1.2.14] You shall be capable of dividing two fractions. [Example 1.2.15, 1.2.16, 1.2.17] You shall be capable of adding or subtracting two fractions with a common denominator. [Example 1.2.18, 1.2.19] You shall be capable of ...
Full text
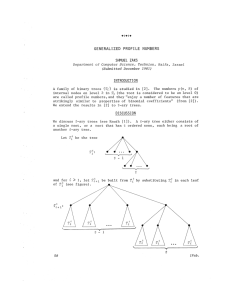
... A family of binary trees {T^} is studied in [2]. The numbers p(n, k) of internal nodes on level k in Tn (the root is considered to be on level 0) are called profile numbers, and they "enjoy a number of features that are strikingly similar to properties of binomial coefficients" (from [2]). We extend ...
... A family of binary trees {T^} is studied in [2]. The numbers p(n, k) of internal nodes on level k in Tn (the root is considered to be on level 0) are called profile numbers, and they "enjoy a number of features that are strikingly similar to properties of binomial coefficients" (from [2]). We extend ...