Abell 1656: the Coma Cluster of galaxies - Euro-VO
... services. Each “S” corresponds to the location of a spectrum. Open the “Hubble Space Telescope Spectra” menu and click on the QSO 1257+2840 name. This opens the Data Info Frame that gives access to information about this observation. Click on “FoV in stack” and visualize the slit location on the ima ...
... services. Each “S” corresponds to the location of a spectrum. Open the “Hubble Space Telescope Spectra” menu and click on the QSO 1257+2840 name. This opens the Data Info Frame that gives access to information about this observation. Click on “FoV in stack” and visualize the slit location on the ima ...
Challenging our Understanding of Stellar Structure and Evolution
... parallaxes of millions of stars to unprecedented precision. Even so, there remain rare, astrophysically compelling objects at such great distances in the Galaxy that only astrometers with precision better than 10 microseconds of arc (10 µas) and heretofore unprecedented sensitivity can provide accur ...
... parallaxes of millions of stars to unprecedented precision. Even so, there remain rare, astrophysically compelling objects at such great distances in the Galaxy that only astrometers with precision better than 10 microseconds of arc (10 µas) and heretofore unprecedented sensitivity can provide accur ...
Chapter 12 Star Stuff How do stars form?
... The star has become a red giant called a “double-shell burning star” This double-shell-burning stage is unsteady, and the fusion rate periodically spikes upward in a series of thermal pulses. With each pulse, carbon gets dredged up from the core and transported into the overlying “envelope” Soon tha ...
... The star has become a red giant called a “double-shell burning star” This double-shell-burning stage is unsteady, and the fusion rate periodically spikes upward in a series of thermal pulses. With each pulse, carbon gets dredged up from the core and transported into the overlying “envelope” Soon tha ...
lab 11 only - Penn State University
... spherical cloud of stars that surrounds the entire galaxy). The halo is much larger than the bulge. Our Milky Way Galaxy is made up of mostly stars, gas, and dust. The dust blocks out light from distant stars, and makes it hard to see a lot of the galaxy, especially the bulge and parts of the disk. ...
... spherical cloud of stars that surrounds the entire galaxy). The halo is much larger than the bulge. Our Milky Way Galaxy is made up of mostly stars, gas, and dust. The dust blocks out light from distant stars, and makes it hard to see a lot of the galaxy, especially the bulge and parts of the disk. ...
X-ray output should be time variable
... Bright stars in the spectral range earlier than about B3 are soft X-ray sources, with LX ~ 10-7 LBol THEORY •O star X-ray emission comes from shock-heated gas present in their stellar winds; for B stars, the situation is more uncertain, and their Xrays may be related to magnetic fields, at least in ...
... Bright stars in the spectral range earlier than about B3 are soft X-ray sources, with LX ~ 10-7 LBol THEORY •O star X-ray emission comes from shock-heated gas present in their stellar winds; for B stars, the situation is more uncertain, and their Xrays may be related to magnetic fields, at least in ...
Astronomy - Career Account Web Pages
... The most distant objects in the universe appear extremely red because their light is stretched to longer, redder wavelengths by the expansion of the universe. This object is at an extremely faint magnitude of 29, which is 500 million times fainter that the faintest stars seen by the human eye. The d ...
... The most distant objects in the universe appear extremely red because their light is stretched to longer, redder wavelengths by the expansion of the universe. This object is at an extremely faint magnitude of 29, which is 500 million times fainter that the faintest stars seen by the human eye. The d ...
Stellar Evolution in the HR Diagram
... • The timescales of most post-AGB stars are such that the mass lost will still be nearby when the star becomes hot. The high energy photons from the star will ionize the surrounding material. This is called a planetary nebulae (PNe). • PNe are often asymmetrical, and there is no good theory to exp ...
... • The timescales of most post-AGB stars are such that the mass lost will still be nearby when the star becomes hot. The high energy photons from the star will ionize the surrounding material. This is called a planetary nebulae (PNe). • PNe are often asymmetrical, and there is no good theory to exp ...
Distance to the SMC
... Shapley in his calibration must be about 1.5 magnitudes fainter than the spiral arm Cepheids observed by Leavitt. That is, because Shapley based his scale on intrinsically fainter Population II stars, his scale needed to be adjusted to accommodate the intrinsically brighter Population I stars studie ...
... Shapley in his calibration must be about 1.5 magnitudes fainter than the spiral arm Cepheids observed by Leavitt. That is, because Shapley based his scale on intrinsically fainter Population II stars, his scale needed to be adjusted to accommodate the intrinsically brighter Population I stars studie ...
Characteristics of Stars
... Astronomers use a unit called the light-year to measure distances between the stars. A light-year is the distance that light travels in one year, about 9.5 million million kilometers. Standing on Earth looking up at the sky, it may seem as if there is no way to tell how far away the stars are. Howev ...
... Astronomers use a unit called the light-year to measure distances between the stars. A light-year is the distance that light travels in one year, about 9.5 million million kilometers. Standing on Earth looking up at the sky, it may seem as if there is no way to tell how far away the stars are. Howev ...
script
... • therefore, stellar wind takes away angular momentum and the stellar rotation is braked ...
... • therefore, stellar wind takes away angular momentum and the stellar rotation is braked ...
Document
... he Milky Way is one of the most impressive features of the night sky. The band of stars that we observe is in fact a projection of a galaxy that contains hundreds of billions of stars, including the sun. The stars are mostly confined to a thin disk, in which they form a multitude of spiral arms that ...
... he Milky Way is one of the most impressive features of the night sky. The band of stars that we observe is in fact a projection of a galaxy that contains hundreds of billions of stars, including the sun. The stars are mostly confined to a thin disk, in which they form a multitude of spiral arms that ...
CCD BVRI and 2MASS Photometry of the Poorly Studied Open
... Key words: Galaxy: open clusters and associations – individual: NGC 6631 – astrometry – Stars: luminosity function – Mass function. Open star clusters (OCs) are ideal objects for studying the main properties of the Milky Way Galaxy, i.e. star formation, stellar evolution, and distance scale of the G ...
... Key words: Galaxy: open clusters and associations – individual: NGC 6631 – astrometry – Stars: luminosity function – Mass function. Open star clusters (OCs) are ideal objects for studying the main properties of the Milky Way Galaxy, i.e. star formation, stellar evolution, and distance scale of the G ...
PSC100 Summary Chapters 10 to Chapter 20
... learned in lesson 3 that the light from these distant points can be carefully analyzed to give us much more information than just the brightness and spatial location of the stars. A few of the light sources that can be seen in the night sky have a "fuzzy structure" that was the subject of great myst ...
... learned in lesson 3 that the light from these distant points can be carefully analyzed to give us much more information than just the brightness and spatial location of the stars. A few of the light sources that can be seen in the night sky have a "fuzzy structure" that was the subject of great myst ...
PH607 – Galaxies
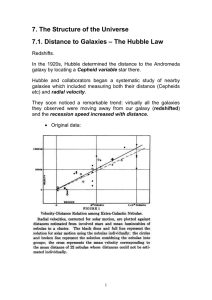
... where v is the recession velocity, D is the distance to the galaxy, and Ho is the constant of proportionality known as Hubble's constant Hubble found H0 ~ 500 km/s/Mpc !! Hubble had confused two different kinds of Cepheid variable stars used for calibrating distances and also that what Hubble though ...
... where v is the recession velocity, D is the distance to the galaxy, and Ho is the constant of proportionality known as Hubble's constant Hubble found H0 ~ 500 km/s/Mpc !! Hubble had confused two different kinds of Cepheid variable stars used for calibrating distances and also that what Hubble though ...
key for the HR Diagram Lab Handout
... questions about what they are seeing before getting to the answers! Many students will focus on color and be surprised that stars come in so many. These observations will likely also include temperature, brightness, and lifespan information. If your students are not familiar with or confident in sci ...
... questions about what they are seeing before getting to the answers! Many students will focus on color and be surprised that stars come in so many. These observations will likely also include temperature, brightness, and lifespan information. If your students are not familiar with or confident in sci ...
Sternentstehung - Star Formation
... - At ~22Msun bubbles become Rayleigh-Taylor instable and collapse again. This happens when radiation force gets too low and the bubble walls encounter net gravitational force. (Rayleigh-Taylor instabilities naturally occur when heavy fluids (gas) are accelerated by light fluids (radiation).) ...
... - At ~22Msun bubbles become Rayleigh-Taylor instable and collapse again. This happens when radiation force gets too low and the bubble walls encounter net gravitational force. (Rayleigh-Taylor instabilities naturally occur when heavy fluids (gas) are accelerated by light fluids (radiation).) ...
An introduce of the spectrograph of the GALEX
... distribution of the sources detected by our survey peaks at around z=0.6-1.0 (the location of the peak being affected by cosmic variance) and decays monotonically from z~1 to z~3. (...) The cosmic star formation rate (SFR) density goes as (1+z)4.0+/-0.2 from z=0 to 0.8. From z=0.8 to z~1.2, the SFR ...
... distribution of the sources detected by our survey peaks at around z=0.6-1.0 (the location of the peak being affected by cosmic variance) and decays monotonically from z~1 to z~3. (...) The cosmic star formation rate (SFR) density goes as (1+z)4.0+/-0.2 from z=0 to 0.8. From z=0.8 to z~1.2, the SFR ...
MOLECULAR GAS, KINEMATICS, AND OB STAR FORMATION IN
... size of the smoothing box is 0.5 kpc, smaller than the typical width of spiral arms. There are three galactocentric radial regions, marked in Fig. 4 top, where V (R) increases monotonically, so that the radial derivative is positive and roughly constant, i.e. the signature of solid body rotation. Th ...
... size of the smoothing box is 0.5 kpc, smaller than the typical width of spiral arms. There are three galactocentric radial regions, marked in Fig. 4 top, where V (R) increases monotonically, so that the radial derivative is positive and roughly constant, i.e. the signature of solid body rotation. Th ...
The Universe - HMXEarthScience
... of light from galaxies moving away from Earth in stage 3 are observed to be A) shorter than normal (a red shift) B) shorter than normal (a blue shift) C) longer than normal (a red shift) D) longer than normal (a blue shift) 16. In a Doppler red shift, the observed wavelengths of light from distant c ...
... of light from galaxies moving away from Earth in stage 3 are observed to be A) shorter than normal (a red shift) B) shorter than normal (a blue shift) C) longer than normal (a red shift) D) longer than normal (a blue shift) 16. In a Doppler red shift, the observed wavelengths of light from distant c ...
Questions - Clever Teach
... candidates devoted a large part of their answer in doing so. Some candidates used much of the available response area by effectively writing out the question again. Some common inaccuracies were to write about planets expanding or moving away and galaxies being “red-shifted” (rather than the light f ...
... candidates devoted a large part of their answer in doing so. Some candidates used much of the available response area by effectively writing out the question again. Some common inaccuracies were to write about planets expanding or moving away and galaxies being “red-shifted” (rather than the light f ...
PeGASus Newsletter Issue #68 – Oct. 1996
... New Hubble Space Telescope images reveal what may be galaxies under construction in the early universe, out of a long sought ancient population of "galactic building blocks." These detailed images reveal a grouping of 18 gigantic star clusters that appear to be the same distance from Earth, and clos ...
... New Hubble Space Telescope images reveal what may be galaxies under construction in the early universe, out of a long sought ancient population of "galactic building blocks." These detailed images reveal a grouping of 18 gigantic star clusters that appear to be the same distance from Earth, and clos ...
Society News - Bristol Astronomical Society
... number of galaxies that are located with its boundaries including 5 that made it into Messiers list of nebulous objects. The bright stars form a reasonable outline of a prone lion, the brightest member of Leo, alpha (α) Leonis, has the proper name Regulus and shines at magnitude +1.35. it marks one ...
... number of galaxies that are located with its boundaries including 5 that made it into Messiers list of nebulous objects. The bright stars form a reasonable outline of a prone lion, the brightest member of Leo, alpha (α) Leonis, has the proper name Regulus and shines at magnitude +1.35. it marks one ...
Introduc on to the Fundamental Astrophysics Course
... within molecular clouds in interstellar space, commonly referred to as "stellar nurseries", collapse into spheres of plasma to form stars. • As a branch of astronomy star forma)on includes the study of ...
... within molecular clouds in interstellar space, commonly referred to as "stellar nurseries", collapse into spheres of plasma to form stars. • As a branch of astronomy star forma)on includes the study of ...
Hot HB stars in globular clusters
... Horizontal Branch (EHB) stars. Such objects are now believed to be the dominant source of UV radiation causing the UV upturn phenomenon in elliptical galaxies and galaxy bulges (Dorman et al., 1995). While there are more than a thousand sdBs known in the field of our galaxy (Kilkenny et al., 1988), ...
... Horizontal Branch (EHB) stars. Such objects are now believed to be the dominant source of UV radiation causing the UV upturn phenomenon in elliptical galaxies and galaxy bulges (Dorman et al., 1995). While there are more than a thousand sdBs known in the field of our galaxy (Kilkenny et al., 1988), ...
plagiarism - things to know - Science Department
... Stars, rocks and people all emit light, and and people included. The temperature of which wavelength of light will be most the star, rock or person determines which strongly radiated depends on the wavelength of light will be most strongly temperature of the star, rock or person. For radiated. In th ...
... Stars, rocks and people all emit light, and and people included. The temperature of which wavelength of light will be most the star, rock or person determines which strongly radiated depends on the wavelength of light will be most strongly temperature of the star, rock or person. For radiated. In th ...
H II region

An H II region is a large, low-density cloud of partially ionized gas in which star formation has recently taken place. The short-lived blue stars forged in these regions emit copious amounts of ultraviolet light that ionize the surrounding gas. H II regions—sometimes several hundred light-years across—are often associated with giant molecular clouds. The first known H II region was the Orion Nebula, which was discovered in 1610 by Nicolas-Claude Fabri de Peiresc.H II regions are named for the large amount of ionised atomic hydrogen they contain, referred to as H II, pronounced H-two by astronomers (an H I region being neutral atomic hydrogen, and H2 being molecular hydrogen). Such regions have extremely diverse shapes, because the distribution of the stars and gas inside them is irregular. They often appear clumpy and filamentary, sometimes showing bizarre shapes such as the Horsehead Nebula. H II regions may give birth to thousands of stars over a period of several million years. In the end, supernova explosions and strong stellar winds from the most massive stars in the resulting star cluster will disperse the gases of the H II region, leaving behind a cluster of birthed stars such as the Pleiades.H II regions can be seen to considerable distances in the universe, and the study of extragalactic H II regions is important in determining the distance and chemical composition of other galaxies. Spiral and irregular galaxies contain many H II regions, while elliptical galaxies are almost devoid of them. In the spiral galaxies, including the Milky Way, H II regions are concentrated in the spiral arms, while in the irregular galaxies they are distributed chaotically. Some galaxies contain huge H II regions, which may contain tens of thousands of stars. Examples include the 30 Doradus region in the Large Magellanic Cloud and NGC 604 in the Triangulum Galaxy.