lecture_1_mbu - X-ray and Observational Astronomy Group
... Cool, dense clouds suspended above surface by magnetic field. ...
... Cool, dense clouds suspended above surface by magnetic field. ...
Lab 6
... class of variable stars called the Cepheids. These stars vary in brightness in a cyclical pattern, and are bright enough to be seen within another galaxy. Leavitt determined that absolute magnitude (M) of a Cepheid variable was mathematically related to the period (P, measured in days) of its bright ...
... class of variable stars called the Cepheids. These stars vary in brightness in a cyclical pattern, and are bright enough to be seen within another galaxy. Leavitt determined that absolute magnitude (M) of a Cepheid variable was mathematically related to the period (P, measured in days) of its bright ...
I. Determination of stellar Parameters
... disk (independent of metallcity there!) • also Sun is more metal-rich than local average and might have formed at inner Galactic radii • model: metallicity-correlation from radial mixing of different Galactic components ...
... disk (independent of metallcity there!) • also Sun is more metal-rich than local average and might have formed at inner Galactic radii • model: metallicity-correlation from radial mixing of different Galactic components ...
4 Distances in Astronomy
... reliably. The best ground-based telescopes can achieve a resolution of about 0:500 , which can sometimes be reduced to about 0:0100 by averaging over many measurements. This corresponds to a distance of about 300 ly. Spacebased telescopes can do better (see the discussion of Hipparcos below), but so ...
... reliably. The best ground-based telescopes can achieve a resolution of about 0:500 , which can sometimes be reduced to about 0:0100 by averaging over many measurements. This corresponds to a distance of about 300 ly. Spacebased telescopes can do better (see the discussion of Hipparcos below), but so ...
Eruptive Variables - Scientific Research Publishing
... As regards the conditions of equilibrium of a star, it is necessary to take account the radiation pressure. The formulae from the theory enable in to calculate what proportion of the weight of the stellar mass is borne by the radiation pressure, and what part being supported by the hot gases pressur ...
... As regards the conditions of equilibrium of a star, it is necessary to take account the radiation pressure. The formulae from the theory enable in to calculate what proportion of the weight of the stellar mass is borne by the radiation pressure, and what part being supported by the hot gases pressur ...
Classifying Spectra PDF version - the Home Page for Voyager2
... Each spectral line always appears at the same wavelength (except for Doppler shift which is not happening here). Not every star shows the same spectral lines. Although most stars are made of same materials, temperature is the main factor determining which absorption lines are seen and how strong the ...
... Each spectral line always appears at the same wavelength (except for Doppler shift which is not happening here). Not every star shows the same spectral lines. Although most stars are made of same materials, temperature is the main factor determining which absorption lines are seen and how strong the ...
Study Guide for the Comprehensive Final Exam
... State the contribution of binary stars to our knowledge of stellar masses and give the range of main sequence stellar masses. Describe the physical characteristics of a giant molecular cloud. Identify the source of heating (energy production) in protostars. Explain why more low-mass K & M main seque ...
... State the contribution of binary stars to our knowledge of stellar masses and give the range of main sequence stellar masses. Describe the physical characteristics of a giant molecular cloud. Identify the source of heating (energy production) in protostars. Explain why more low-mass K & M main seque ...
5 Understanding stars and star ClUsters
... and r denotes rich clusters with over 100 stars. For example the Pleiades (M45) is classified as I 3 r, meaning well concentrated with fairly luminous stars and over 100 members. Open clusters are not all stable; in fact many will drift apart over several millions of years as tidal forces from diffe ...
... and r denotes rich clusters with over 100 stars. For example the Pleiades (M45) is classified as I 3 r, meaning well concentrated with fairly luminous stars and over 100 members. Open clusters are not all stable; in fact many will drift apart over several millions of years as tidal forces from diffe ...
Fulltext PDF - Indian Academy of Sciences
... the detector. Typically, a stellar spectrum shows a continuum, similar to a blackbody but crossed by hundreds of dark lines. The spectra show an enormous variety with certain recurring patterns. This led to the classification of stellar spectra. The scheme of spectral classification was almost compl ...
... the detector. Typically, a stellar spectrum shows a continuum, similar to a blackbody but crossed by hundreds of dark lines. The spectra show an enormous variety with certain recurring patterns. This led to the classification of stellar spectra. The scheme of spectral classification was almost compl ...
astrophysics - Collegiate Quiz Bowl Packet
... is defender of the Ptolemaic theory and eventually loses the argument. The book this event takes place in was written in Italian to reach a wider audience, much to the disdain of the Church. FTP, idenifify this work of Galileo showing his proof of the heliocentric theory. Dialogue Concerning the Two ...
... is defender of the Ptolemaic theory and eventually loses the argument. The book this event takes place in was written in Italian to reach a wider audience, much to the disdain of the Church. FTP, idenifify this work of Galileo showing his proof of the heliocentric theory. Dialogue Concerning the Two ...
Where to begin the adventure with variable stars?
... In this way we have found the stars and we can begin photometric observations. Their result will probably impress not only us, but also other students and our friends. Also the acquired skills of navigating in the sky will be a source of satisfaction! ...
... In this way we have found the stars and we can begin photometric observations. Their result will probably impress not only us, but also other students and our friends. Also the acquired skills of navigating in the sky will be a source of satisfaction! ...
Ch. 20
... This outline of stellar formation and extinction can be compared to observations of star clusters; here a globular cluster: ...
... This outline of stellar formation and extinction can be compared to observations of star clusters; here a globular cluster: ...
Investigating Supernova Remnants - Chandra X
... then contract in repeating cycles with periods ranging from several months to more than a year. The material ejected by the star forms a planetary nebula which expands into the surrounding interstellar medium at ~17to35 km/s. The core of the star left in the center of the planetary nebula is called ...
... then contract in repeating cycles with periods ranging from several months to more than a year. The material ejected by the star forms a planetary nebula which expands into the surrounding interstellar medium at ~17to35 km/s. The core of the star left in the center of the planetary nebula is called ...
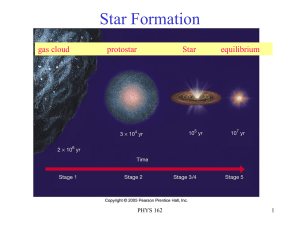
Lecture 15 Star Formation and Evolution 3/7
... Supernovas • 10-20 supernovas occur every1000 years in a galaxy the size of the Milky Way (~200 billion stars) with ~15% being type Ia • 8 observed in last 2000 years (185, 386, ...
... Supernovas • 10-20 supernovas occur every1000 years in a galaxy the size of the Milky Way (~200 billion stars) with ~15% being type Ia • 8 observed in last 2000 years (185, 386, ...
HR Diagram Explorer
... a) Draw in an arrow on the y axis showing the direction of increasing “intrinsic luminosity” of the stars. (This is complete for you.) b) Draw in an arrow on the x-axis showing the direction of increasing surface temperature of the stars. c) Draw in an arrow showing the direction of increasing radiu ...
... a) Draw in an arrow on the y axis showing the direction of increasing “intrinsic luminosity” of the stars. (This is complete for you.) b) Draw in an arrow on the x-axis showing the direction of increasing surface temperature of the stars. c) Draw in an arrow showing the direction of increasing radiu ...
ASTR3007/4007/6007, Class 1: Observing the Stars 23 February
... two energy levels in some atom or molecule in the stellar atmosphere. Those photons are strongly absorbed by those atoms or molecules, leading to a drop in the light we see coming out of the star at those wavelengths. Although this is not the case for the Sun, in some stars there are strong emissio ...
... two energy levels in some atom or molecule in the stellar atmosphere. Those photons are strongly absorbed by those atoms or molecules, leading to a drop in the light we see coming out of the star at those wavelengths. Although this is not the case for the Sun, in some stars there are strong emissio ...
Cepheid Calibration
... finding the missing link for measuring cosmic distance: the period-luminosity relation of Cepheid variable stars. Leavitt’s job at the observatory was to measure the brightness of stars on photographic plates from Harvard’s telescopes in Massachusetts and abroad. Her product was a record of results ...
... finding the missing link for measuring cosmic distance: the period-luminosity relation of Cepheid variable stars. Leavitt’s job at the observatory was to measure the brightness of stars on photographic plates from Harvard’s telescopes in Massachusetts and abroad. Her product was a record of results ...
H-R Diagram
... To compare the life cycle stages of stars based on their positions in the diagram Background The Hertzsprung-Russell diagram, or H-R diagram, is a graph in which a star's temperature is plotted against its absolute magnitude. From such a diagram, other information about a star's properties and life ...
... To compare the life cycle stages of stars based on their positions in the diagram Background The Hertzsprung-Russell diagram, or H-R diagram, is a graph in which a star's temperature is plotted against its absolute magnitude. From such a diagram, other information about a star's properties and life ...
Astrophysics notes
... (the wavelength at which the emitted radiation is at its highest peak) to determine the temperature of the star. We can use Wiens law (max W) to calculate the ...
... (the wavelength at which the emitted radiation is at its highest peak) to determine the temperature of the star. We can use Wiens law (max W) to calculate the ...
stars - Moore Public Schools
... Billions and billions of stars were created through this process and grouped together to form the galaxies within the universe today. Galaxies are massive systems of stars, dust, and gas held together by gravity. Gravity causes stars to attract each other and clump together into groups. Because star ...
... Billions and billions of stars were created through this process and grouped together to form the galaxies within the universe today. Galaxies are massive systems of stars, dust, and gas held together by gravity. Gravity causes stars to attract each other and clump together into groups. Because star ...
Observations with Herschel: High-mass star formation and the
... The capture and interpretation of the electromagnetic radiation we receive from space is essential to our understanding of the cosmos. When the Earth’s opaque atmosphere prevents the far-infrared radiation to reach ground based antennas, space observatories become crucial to collect that important p ...
... The capture and interpretation of the electromagnetic radiation we receive from space is essential to our understanding of the cosmos. When the Earth’s opaque atmosphere prevents the far-infrared radiation to reach ground based antennas, space observatories become crucial to collect that important p ...
Lesson Plan G2 The Stars
... All stars form from cold clouds of hydrogen gas that collapse under their own gravity. The center of the cloud heats up from the resulting increase in pressure and friction. Eventually the heat and pressure are great enough to force hydrogen nuclei to fuse together and form helium nuclei. This nucle ...
... All stars form from cold clouds of hydrogen gas that collapse under their own gravity. The center of the cloud heats up from the resulting increase in pressure and friction. Eventually the heat and pressure are great enough to force hydrogen nuclei to fuse together and form helium nuclei. This nucle ...
chapter 7 review questions
... 23. The binding energy of the first level in an atom is 2.210-18 J, and the binding energy of the second energy level is 1.610-18 J. What is the energy of the photon that is emitted if an electron moves from the second level to the first? a. ...
... 23. The binding energy of the first level in an atom is 2.210-18 J, and the binding energy of the second energy level is 1.610-18 J. What is the energy of the photon that is emitted if an electron moves from the second level to the first? a. ...
Calculating the Age of a Planetary Nebula
... If you get the error message Use x1 zoom, simply click on the x1 button alongside the zoom buttons described above to bring the image back to the original size. The cursor will change shape and an Output window will pop up on the screen. Click at one edge of the main shell and the x,y-coordinates wi ...
... If you get the error message Use x1 zoom, simply click on the x1 button alongside the zoom buttons described above to bring the image back to the original size. The cursor will change shape and an Output window will pop up on the screen. Click at one edge of the main shell and the x,y-coordinates wi ...
S T A R S
... about 68 light years away. Aldebaran is one of the few first magnitude stars that may be occulted by the moon. The disappearance of the star is startlingly abrupt, particularly so at the moons dark edge. The V shaped central group is the Hyades star cluster group and represents the bull’s head – Ald ...
... about 68 light years away. Aldebaran is one of the few first magnitude stars that may be occulted by the moon. The disappearance of the star is startlingly abrupt, particularly so at the moons dark edge. The V shaped central group is the Hyades star cluster group and represents the bull’s head – Ald ...
H II region

An H II region is a large, low-density cloud of partially ionized gas in which star formation has recently taken place. The short-lived blue stars forged in these regions emit copious amounts of ultraviolet light that ionize the surrounding gas. H II regions—sometimes several hundred light-years across—are often associated with giant molecular clouds. The first known H II region was the Orion Nebula, which was discovered in 1610 by Nicolas-Claude Fabri de Peiresc.H II regions are named for the large amount of ionised atomic hydrogen they contain, referred to as H II, pronounced H-two by astronomers (an H I region being neutral atomic hydrogen, and H2 being molecular hydrogen). Such regions have extremely diverse shapes, because the distribution of the stars and gas inside them is irregular. They often appear clumpy and filamentary, sometimes showing bizarre shapes such as the Horsehead Nebula. H II regions may give birth to thousands of stars over a period of several million years. In the end, supernova explosions and strong stellar winds from the most massive stars in the resulting star cluster will disperse the gases of the H II region, leaving behind a cluster of birthed stars such as the Pleiades.H II regions can be seen to considerable distances in the universe, and the study of extragalactic H II regions is important in determining the distance and chemical composition of other galaxies. Spiral and irregular galaxies contain many H II regions, while elliptical galaxies are almost devoid of them. In the spiral galaxies, including the Milky Way, H II regions are concentrated in the spiral arms, while in the irregular galaxies they are distributed chaotically. Some galaxies contain huge H II regions, which may contain tens of thousands of stars. Examples include the 30 Doradus region in the Large Magellanic Cloud and NGC 604 in the Triangulum Galaxy.