The Bigger Picture - Astronomy and Astrophysics
... dust between the stars. The dust particles are very small and have the property that they scatter blue light more efficiently than red light. This is called `interstellar reddening’. – Most stars appear to be REDDER than they really are (cooler) – Stars of a given luminosity appear FAINTER than you ...
... dust between the stars. The dust particles are very small and have the property that they scatter blue light more efficiently than red light. This is called `interstellar reddening’. – Most stars appear to be REDDER than they really are (cooler) – Stars of a given luminosity appear FAINTER than you ...
section 17 powerpoint
... the star. The spectral lines of one (or both) stars are revealed through the regular red or blue shifts of their spectral lines. Examples are shown below. ...
... the star. The spectral lines of one (or both) stars are revealed through the regular red or blue shifts of their spectral lines. Examples are shown below. ...
Astrophysics with the Computer: Propagation of Ionization Fronts in
... thin. Thus the stellar photons can penetrate even deeper into the gas. The boundary between neutral and ionised gas (the ionization front) will thus propagate away from the star in to the gas cloud, as long as there is an excess of stellar ionising photons over those which get absorbed by the gas. A ...
... thin. Thus the stellar photons can penetrate even deeper into the gas. The boundary between neutral and ionised gas (the ionization front) will thus propagate away from the star in to the gas cloud, as long as there is an excess of stellar ionising photons over those which get absorbed by the gas. A ...
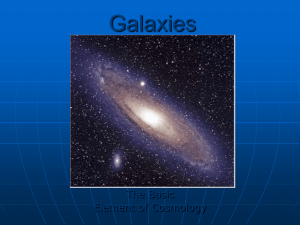
13 Galaxies - Journigan-wiki
... Subtypes of Galaxies/Barred Hubble recognized subgroups within the major types as well. The first of these is the barred spiral galaxy (denoted SB). Barred spiral galaxies have arms that emerge from an elongated central region. Barred spirals are ranked from a to d, with SBa galaxies having large b ...
... Subtypes of Galaxies/Barred Hubble recognized subgroups within the major types as well. The first of these is the barred spiral galaxy (denoted SB). Barred spiral galaxies have arms that emerge from an elongated central region. Barred spirals are ranked from a to d, with SBa galaxies having large b ...
A Deeper Look at Faint H $\ alpha $ Emission in Nearby Dwarf
... corresponding to 13 and 22 pc at 3.8 Mpc) shows that the faint Hα emission is highly structured, with well-defined loops and filaments surrounding the bright HII regions (Figure 1, top right). Similar but more diffuse structures are also evident in the galaxy halo, and numerous chimney-like spokes, ...
... corresponding to 13 and 22 pc at 3.8 Mpc) shows that the faint Hα emission is highly structured, with well-defined loops and filaments surrounding the bright HII regions (Figure 1, top right). Similar but more diffuse structures are also evident in the galaxy halo, and numerous chimney-like spokes, ...
The Sculptor dwarf irregular galaxy SDIG: present and past
... near-infrared (J andK) imaging at the Anglo-Australian Telescope (AAT). Despite the presence of many blue stars, there are at present no detectable H II regions, indicating that the galaxy is now in a relatively quiescent state. However, the ratio of the H I mass to blue luminosity is typical of oth ...
... near-infrared (J andK) imaging at the Anglo-Australian Telescope (AAT). Despite the presence of many blue stars, there are at present no detectable H II regions, indicating that the galaxy is now in a relatively quiescent state. However, the ratio of the H I mass to blue luminosity is typical of oth ...
Killer Skies
... billion Kelvin. This pattern of core ignition and shell ignition continues with a series of heavier nuclei as fusion fuel. At higher temperatures than carbon fusion, nuclei of oxygen, neon, and magnesium fuse to make silicon and sulfur. At even higher temperatures, silicon can fuse to make iron. Thu ...
... billion Kelvin. This pattern of core ignition and shell ignition continues with a series of heavier nuclei as fusion fuel. At higher temperatures than carbon fusion, nuclei of oxygen, neon, and magnesium fuse to make silicon and sulfur. At even higher temperatures, silicon can fuse to make iron. Thu ...
Plotting Variable Stars on the H
... The H-R diagram is an important astronomical tool for understanding how stars evolve over time. Stellar evolution can not be studied by observing individual stars as most changes occur over millions and billions of years. Astrophysicists observe numerous stars at various stages in their evolutionary ...
... The H-R diagram is an important astronomical tool for understanding how stars evolve over time. Stellar evolution can not be studied by observing individual stars as most changes occur over millions and billions of years. Astrophysicists observe numerous stars at various stages in their evolutionary ...
Penentuan Jarak dalam Astronomi II
... SN 1604 (Kepler’s supernova Ia in the Ophiuchus constellation) achieved -2.5m As expected, we could have miss a number of Supernovae events that have been exploded deep inside the galactic disc full of dense and opaque interstellar dust ...
... SN 1604 (Kepler’s supernova Ia in the Ophiuchus constellation) achieved -2.5m As expected, we could have miss a number of Supernovae events that have been exploded deep inside the galactic disc full of dense and opaque interstellar dust ...
MHD_of_Accretion_Disks
... but well below the stellar regime. Considerable radiation comes from the disk atmosphere, which will typically have a density less than 10^15 cm^-3 but well above the molecular cloud core value. The innermost regions of an accretion disk can be very hot. ...
... but well below the stellar regime. Considerable radiation comes from the disk atmosphere, which will typically have a density less than 10^15 cm^-3 but well above the molecular cloud core value. The innermost regions of an accretion disk can be very hot. ...
Document
... (effective temperature, gravity, etc) as well as oscillator strength f. In particular the the product of Af is obtained, the product of the abundance and the oscillator strength. • The uncertainties in the f value is what limits you in practice. These depend on laboratory measurements, and for many ...
... (effective temperature, gravity, etc) as well as oscillator strength f. In particular the the product of Af is obtained, the product of the abundance and the oscillator strength. • The uncertainties in the f value is what limits you in practice. These depend on laboratory measurements, and for many ...
1/20/09 301 Physics Chapter 12 The Family of Stars Triangulation
... ionized state • A stars have just the right temperature to put electrons into hydrogen’s 2nd energy level, which results in strong absorption lines in the visible • F, G, and K stars are of a low enough temperature to show absorption lines of metals such as calcium and iron, elements that are typica ...
... ionized state • A stars have just the right temperature to put electrons into hydrogen’s 2nd energy level, which results in strong absorption lines in the visible • F, G, and K stars are of a low enough temperature to show absorption lines of metals such as calcium and iron, elements that are typica ...
AN OPTICAL INFRARED ASTROMETRIC - Cosmos
... determination of trigonometric parallaxes of about 120 000 stars of various kinds is epoch-making with its precision of about 1 milliarcsec. A large fraction of the catalogued stars are located within a few hundred parsecs from the sun. The accuracy of the distances determined by using the observed ...
... determination of trigonometric parallaxes of about 120 000 stars of various kinds is epoch-making with its precision of about 1 milliarcsec. A large fraction of the catalogued stars are located within a few hundred parsecs from the sun. The accuracy of the distances determined by using the observed ...
a MS Word version.
... series of equations, since there is actually more than one equation within some of the four equation "descriptions"), that describe the physics that can be used to calculate the internal structure and time evolution of the Sun and stars. For each equation give a short description of the physical pro ...
... series of equations, since there is actually more than one equation within some of the four equation "descriptions"), that describe the physics that can be used to calculate the internal structure and time evolution of the Sun and stars. For each equation give a short description of the physical pro ...
Triangulation Trigonometric Parallax
... ionized state • A stars have just the right temperature to put electrons into hydrogen’s 2nd energy level, which results in strong absorption lines in the visible • F, G, and K stars are of a low enough temperature to show absorption lines of metals such as calcium and iron, elements that are typica ...
... ionized state • A stars have just the right temperature to put electrons into hydrogen’s 2nd energy level, which results in strong absorption lines in the visible • F, G, and K stars are of a low enough temperature to show absorption lines of metals such as calcium and iron, elements that are typica ...
Name:
... diagram is shown to the upper right. Note that is a graph showing luminosity versus temperature. Note, too, that the luminosity is in terms of solar luminosities (Lo). That is, if a star has a luminosity of 10Lo, it will be ten times brighter than our sun. The temperature is given in Kelvins (K), a ...
... diagram is shown to the upper right. Note that is a graph showing luminosity versus temperature. Note, too, that the luminosity is in terms of solar luminosities (Lo). That is, if a star has a luminosity of 10Lo, it will be ten times brighter than our sun. The temperature is given in Kelvins (K), a ...
The Interstellar Medium in High Redshift Galaxies Comes of Age
... molecular gas in galaxy formation and for providing fundamental constraints on galaxy evolution. To date, a fairly small number of species, other than CO, have been detected at z > 2 (e.g. HCN, HNC, CN, H2 O, HCO+ ) and used as tracers of molecular gas. Recent observations with the Herschel Space Ob ...
... molecular gas in galaxy formation and for providing fundamental constraints on galaxy evolution. To date, a fairly small number of species, other than CO, have been detected at z > 2 (e.g. HCN, HNC, CN, H2 O, HCO+ ) and used as tracers of molecular gas. Recent observations with the Herschel Space Ob ...
EarthComm_c1s3
... see amazing details in the gas and dust clouds. The Orion Nebula is very much like the one that formed Earth’s star, the Sun. There are many star nurseries like this one scattered around our galaxy. On a dark night, with binoculars or a small telescope, you can see many gas clouds that are forming s ...
... see amazing details in the gas and dust clouds. The Orion Nebula is very much like the one that formed Earth’s star, the Sun. There are many star nurseries like this one scattered around our galaxy. On a dark night, with binoculars or a small telescope, you can see many gas clouds that are forming s ...
Untitled - Notion Press
... tons of mass goes? The rest of mass is converted into energy. This energy is equivalent to detonating 400 billions of one megaton nuclear bombs. This amount of energy is created in only a second, amazing! The sun is radiating energy from these many years by the process of nuclear fusion of the hydro ...
... tons of mass goes? The rest of mass is converted into energy. This energy is equivalent to detonating 400 billions of one megaton nuclear bombs. This amount of energy is created in only a second, amazing! The sun is radiating energy from these many years by the process of nuclear fusion of the hydro ...
Gravitational redshifts
... synthetic line profiles) are shorter than laboratory values due to convective blueshift. Curves before and after mid-transit (µ = 0.21, 0.59, 0.87) are not exact mirror images due to intrinsic stellar line asymmetries. This simulation from a CO5BOLD model predicts the behavior of an Fe I line ( 620 ...
... synthetic line profiles) are shorter than laboratory values due to convective blueshift. Curves before and after mid-transit (µ = 0.21, 0.59, 0.87) are not exact mirror images due to intrinsic stellar line asymmetries. This simulation from a CO5BOLD model predicts the behavior of an Fe I line ( 620 ...
The cosmic distance scale
... individual Cepheids can be resolved as far away as the Virgo cluster of galaxies. Cepheids have periods from a few to about 70 days and this depends on their absolute magnitudes. In Table 1 HST observations of six Cepheids are listed. They were observed at 12 epochs (times) in order to find their pe ...
... individual Cepheids can be resolved as far away as the Virgo cluster of galaxies. Cepheids have periods from a few to about 70 days and this depends on their absolute magnitudes. In Table 1 HST observations of six Cepheids are listed. They were observed at 12 epochs (times) in order to find their pe ...
The chemical case for no winds in dwarf irregular galaxies
... dIrrs constitute two structurally distinct populations. In this work, we focus our attention on the evolution of isolated gas-rich dwarf galaxies, not affected by external environmental processes. One of the agents that may regulate the star formation history of these objects is the presence of stro ...
... dIrrs constitute two structurally distinct populations. In this work, we focus our attention on the evolution of isolated gas-rich dwarf galaxies, not affected by external environmental processes. One of the agents that may regulate the star formation history of these objects is the presence of stro ...
Part 2 - Stellar Evolution
... 56Ni then beta-decays to 56Fe (days) 56Fe is the most tight element, meaning no more energy can be generated by burning 56Fe 56Fe ash accumulates in the core When the core reaches a critical mass (~ 1.2 Msun), degenerate electron pressure can not support the gravity The core collapses, and the star ...
... 56Ni then beta-decays to 56Fe (days) 56Fe is the most tight element, meaning no more energy can be generated by burning 56Fe 56Fe ash accumulates in the core When the core reaches a critical mass (~ 1.2 Msun), degenerate electron pressure can not support the gravity The core collapses, and the star ...
hydrogen deficient stars and related objects
... The first helium star was discovered in 1942, the first scientific meeting on the subject, however, took place in 1985. The meeting was hence long overdue for, in the meantime, a substantial amount of material had been accumulated by a rather small, but active scientific community. Hence, it appeare ...
... The first helium star was discovered in 1942, the first scientific meeting on the subject, however, took place in 1985. The meeting was hence long overdue for, in the meantime, a substantial amount of material had been accumulated by a rather small, but active scientific community. Hence, it appeare ...
End of the line for a star like ours
... 3. What do you think will happen to the Earth and other planets in the solar system as the Sun grows to red-giant-star size with a diameter many times that of the Sun’s present size? (This could be part of an exercise in creative writing as students research the effects of an expanding Sun. For exam ...
... 3. What do you think will happen to the Earth and other planets in the solar system as the Sun grows to red-giant-star size with a diameter many times that of the Sun’s present size? (This could be part of an exercise in creative writing as students research the effects of an expanding Sun. For exam ...
H II region

An H II region is a large, low-density cloud of partially ionized gas in which star formation has recently taken place. The short-lived blue stars forged in these regions emit copious amounts of ultraviolet light that ionize the surrounding gas. H II regions—sometimes several hundred light-years across—are often associated with giant molecular clouds. The first known H II region was the Orion Nebula, which was discovered in 1610 by Nicolas-Claude Fabri de Peiresc.H II regions are named for the large amount of ionised atomic hydrogen they contain, referred to as H II, pronounced H-two by astronomers (an H I region being neutral atomic hydrogen, and H2 being molecular hydrogen). Such regions have extremely diverse shapes, because the distribution of the stars and gas inside them is irregular. They often appear clumpy and filamentary, sometimes showing bizarre shapes such as the Horsehead Nebula. H II regions may give birth to thousands of stars over a period of several million years. In the end, supernova explosions and strong stellar winds from the most massive stars in the resulting star cluster will disperse the gases of the H II region, leaving behind a cluster of birthed stars such as the Pleiades.H II regions can be seen to considerable distances in the universe, and the study of extragalactic H II regions is important in determining the distance and chemical composition of other galaxies. Spiral and irregular galaxies contain many H II regions, while elliptical galaxies are almost devoid of them. In the spiral galaxies, including the Milky Way, H II regions are concentrated in the spiral arms, while in the irregular galaxies they are distributed chaotically. Some galaxies contain huge H II regions, which may contain tens of thousands of stars. Examples include the 30 Doradus region in the Large Magellanic Cloud and NGC 604 in the Triangulum Galaxy.