Stellar Winds and Hydrodynamic Atmospheres of Stars
... star with 8 Msun on main sequence ends up with 1 Msun 7 Msun re-cycled to ISM ejection of Planetary Nebula at tip of AGB ...
... star with 8 Msun on main sequence ends up with 1 Msun 7 Msun re-cycled to ISM ejection of Planetary Nebula at tip of AGB ...
document
... • Stars form in dark clouds of dusty gas in interstellar space. • The gas between the stars is called the interstellar medium. ...
... • Stars form in dark clouds of dusty gas in interstellar space. • The gas between the stars is called the interstellar medium. ...
Lecture 30
... higher temperatures for nuclear burning of heavier elements: • Initially, burn hydrogen in the core • Once hydrogen is exhausted, too cool to burn helium • Core contracts, heats up • Helium burning stars • If star is massive enough, sequence repeats for carbon burning, then oxygen, silicon etc… Domi ...
... higher temperatures for nuclear burning of heavier elements: • Initially, burn hydrogen in the core • Once hydrogen is exhausted, too cool to burn helium • Core contracts, heats up • Helium burning stars • If star is massive enough, sequence repeats for carbon burning, then oxygen, silicon etc… Domi ...
PDF - Amazing Space, STScI
... By witnessing bursts of light from faraway exploding stars, Hubble helped astronomers discover dark energy. This mysterious, invisible energy exerts a repulsive force that pervades our universe. Several years later, Hubble provided evidence that dark energy has been engaged in a tug of war with grav ...
... By witnessing bursts of light from faraway exploding stars, Hubble helped astronomers discover dark energy. This mysterious, invisible energy exerts a repulsive force that pervades our universe. Several years later, Hubble provided evidence that dark energy has been engaged in a tug of war with grav ...
Hubble Space Telescope`s
... Hubble explored the outskirts of our solar system, a region called the Kuiper Belt. This distant region contains the relics from the early solar system, and may offer clues to the origin and evolution of our Sun and planets. Photo illustration of Comet P / Shoemaker-Levy 9 and Planet Jupiter. NASA a ...
... Hubble explored the outskirts of our solar system, a region called the Kuiper Belt. This distant region contains the relics from the early solar system, and may offer clues to the origin and evolution of our Sun and planets. Photo illustration of Comet P / Shoemaker-Levy 9 and Planet Jupiter. NASA a ...
Variable star information
... pulsate on a very regular basis. Some of them change in brightness very quickly, over a period of only one day, whereas others are characterised by slower changes and have periods of up to 70 days. Their masses range between 4 and 20 times that of the Sun. Cepheid variables can be found in open clus ...
... pulsate on a very regular basis. Some of them change in brightness very quickly, over a period of only one day, whereas others are characterised by slower changes and have periods of up to 70 days. Their masses range between 4 and 20 times that of the Sun. Cepheid variables can be found in open clus ...
The cosmic distance scale
... There are no PN brighter than mPNcut , a cut-off apparent magnitude. The fact that there is such an abrupt cut-off at bright end implies that this method can be applied even when a limited number of PN (only the brightest) have been observed around a given system. The maximum luminosity in the PNLF ...
... There are no PN brighter than mPNcut , a cut-off apparent magnitude. The fact that there is such an abrupt cut-off at bright end implies that this method can be applied even when a limited number of PN (only the brightest) have been observed around a given system. The maximum luminosity in the PNLF ...
Deriving the Isoradius Lines (optional, mathematical
... a) Draw in an arrow on the y axis showing the direction of increasing “intrinsic luminosity” of the stars. (This is complete for you.) b) Draw in an arrow on the x-axis showing the direction of increasing surface temperature of the stars. c) Draw in an arrow showing the direction of increasing radiu ...
... a) Draw in an arrow on the y axis showing the direction of increasing “intrinsic luminosity” of the stars. (This is complete for you.) b) Draw in an arrow on the x-axis showing the direction of increasing surface temperature of the stars. c) Draw in an arrow showing the direction of increasing radiu ...
The Cosmic Perspective Star Stuff
... The binary star Algol has a 3.7 solar mass main sequence star and a 0.8 solar mass red giant. How could that be? a) In this system, the lower mass star must have evolved faster than the higher mass one. b) The red giant might be made of some different elements, so it evolved faster. c) The lower ...
... The binary star Algol has a 3.7 solar mass main sequence star and a 0.8 solar mass red giant. How could that be? a) In this system, the lower mass star must have evolved faster than the higher mass one. b) The red giant might be made of some different elements, so it evolved faster. c) The lower ...
Ch13_Lecture - Chemistry at Winthrop University
... ionized state • A stars have just the right temperature to put electrons into hydrogen’s 2nd energy level, which results in strong absorption lines in the visible • F, G, and K stars are of a low enough temperature to show absorption lines of metals such as calcium and iron, elements that are typica ...
... ionized state • A stars have just the right temperature to put electrons into hydrogen’s 2nd energy level, which results in strong absorption lines in the visible • F, G, and K stars are of a low enough temperature to show absorption lines of metals such as calcium and iron, elements that are typica ...
Distant Stars - How far away is it
... Radiation with longer wavelengths and smaller frequencies than red light is called infrared, and still longer wavelengths are called radio waves. Moving up the energy scale, radiation with shorter wavelengths than violet light is called ultraviolet; still shorter wavelengths are called X-rays and th ...
... Radiation with longer wavelengths and smaller frequencies than red light is called infrared, and still longer wavelengths are called radio waves. Moving up the energy scale, radiation with shorter wavelengths than violet light is called ultraviolet; still shorter wavelengths are called X-rays and th ...
The correct answers are written in bold, italic and underlined. The
... • The iron is thrown out into space, enriching the interstellar medium. The temperature reaches about 5 billion K during the core collapse that initiates the supernova explosion, and at this temperature the gamma-ray photons are energetic enough to photodisintegrate the iron nuclei into protons and ...
... • The iron is thrown out into space, enriching the interstellar medium. The temperature reaches about 5 billion K during the core collapse that initiates the supernova explosion, and at this temperature the gamma-ray photons are energetic enough to photodisintegrate the iron nuclei into protons and ...
Acceleration of Coronal Mass Ejection In Long Rising Solar
... (degenerate electron state, Earth size) to 1015 cm-3 (neutron star, city size), it releases the gravitational energy in the order of 1053 ergs, comparable to the energy released by the Sun over its whole main sequence life. The catastrophic consequence is a supernova explosion. • The product at the ...
... (degenerate electron state, Earth size) to 1015 cm-3 (neutron star, city size), it releases the gravitational energy in the order of 1053 ergs, comparable to the energy released by the Sun over its whole main sequence life. The catastrophic consequence is a supernova explosion. • The product at the ...
Name - CLC Charter School
... When the supernova is done exploding, as an effect of the large transfer of matter and energy, there is a very different kind of star left. This star is called a spinning neutron star. Neutron stars produce radio waves in a steady stream or in random bursts. But if a star is massive enough, it can l ...
... When the supernova is done exploding, as an effect of the large transfer of matter and energy, there is a very different kind of star left. This star is called a spinning neutron star. Neutron stars produce radio waves in a steady stream or in random bursts. But if a star is massive enough, it can l ...
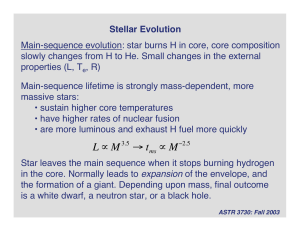
Main Sequence Lifetime
... • At this point the formation of H- ions (hydrogen atoms with 2 electrons) regulates how much radiation can escape - just as greenhouse gases in the Earth’s atmosphere trap in heat • The star is now a red giant - it can no longer cool and moves almost vertically up the red giant branch on the H-R di ...
... • At this point the formation of H- ions (hydrogen atoms with 2 electrons) regulates how much radiation can escape - just as greenhouse gases in the Earth’s atmosphere trap in heat • The star is now a red giant - it can no longer cool and moves almost vertically up the red giant branch on the H-R di ...
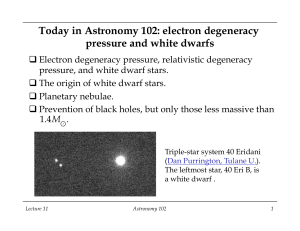
Today in Astronomy 102: electron degeneracy pressure and white
... period (plus Newton’s laws), we know that the mass of Sirius B is 1.00M . q From its observed color (blue-white), we know that its temperature is rather high: T = 29,200 K, compared to 5,800 K for the Sun and 10,000 K for Sirius A. q Its luminosity is only 0.003L , much less than that of Sirius A ...
... period (plus Newton’s laws), we know that the mass of Sirius B is 1.00M . q From its observed color (blue-white), we know that its temperature is rather high: T = 29,200 K, compared to 5,800 K for the Sun and 10,000 K for Sirius A. q Its luminosity is only 0.003L , much less than that of Sirius A ...
3-color photometry of stellar cluster - Kiepenheuer
... kind of open clusters and stand out not due to their higher star density but due to their rare spectral types. In their surroundings usually there is a lot of gas and dust. Normally they consist mainly out of O, B and T-Tauri stars which are especially young stars. The lifetime of these associations ...
... kind of open clusters and stand out not due to their higher star density but due to their rare spectral types. In their surroundings usually there is a lot of gas and dust. Normally they consist mainly out of O, B and T-Tauri stars which are especially young stars. The lifetime of these associations ...
M BH
... How much room is there for dark or obscured accretion? Can the accretion rate exceed the Eddington limit? ...
... How much room is there for dark or obscured accretion? Can the accretion rate exceed the Eddington limit? ...
Stars and Stellar Evolution The Hertzsprung
... As the star cools, the random motions of the particles slow and the electric forces between ions line them up in a crystalline lattice. ...
... As the star cools, the random motions of the particles slow and the electric forces between ions line them up in a crystalline lattice. ...
unit1-19
... observed was red shifted. So he presumed all stars and galaxies were moving apart. He quantified the redshift (z) as “the ratio of the change in wavelength to the wavelength with the source at rest”. In short … ...
... observed was red shifted. So he presumed all stars and galaxies were moving apart. He quantified the redshift (z) as “the ratio of the change in wavelength to the wavelength with the source at rest”. In short … ...
PPS
... Traditionally, spectroscopy dealt with visible light, but it has been extended to cover other wavelengths of electromagnetic radiation and even to measurements of the distribution of energy among particles, such as cosmic rays. The first spectroscopy does is to tell us what stars , galaxies and so o ...
... Traditionally, spectroscopy dealt with visible light, but it has been extended to cover other wavelengths of electromagnetic radiation and even to measurements of the distribution of energy among particles, such as cosmic rays. The first spectroscopy does is to tell us what stars , galaxies and so o ...
Globular Clusters Dynamic Lives The
... ters undergo core collapse every billion years. In that same period, several clusters evaporate under the influence of tidal shocks. Eventually there will be none left! Everything said so far presumes that stars can be treated as point masses interacting gravitationally. But stars are extended obje ...
... ters undergo core collapse every billion years. In that same period, several clusters evaporate under the influence of tidal shocks. Eventually there will be none left! Everything said so far presumes that stars can be treated as point masses interacting gravitationally. But stars are extended obje ...
Stellar Evolution
... of stars’ main sequence lives come from star clusters Most stars form in such clusters - e.g. in the Orion nebula ...
... of stars’ main sequence lives come from star clusters Most stars form in such clusters - e.g. in the Orion nebula ...
Chemical Signatures in Dwarf Galaxies
... related to one another raises an interesting series of questions. Are dwarf gal axies related to protogalactic fragments, the low mass systems that formed in a L Cold Dark Matter (LCDM) Universe that later merged to build up the large spirals that we see today? Are the dwarf spheroidal and Sloan ga ...
... related to one another raises an interesting series of questions. Are dwarf gal axies related to protogalactic fragments, the low mass systems that formed in a L Cold Dark Matter (LCDM) Universe that later merged to build up the large spirals that we see today? Are the dwarf spheroidal and Sloan ga ...
Telescopes: More Than Meets the Eye
... 1. What are the three main functions of a telescope? (the three main functions listed in order of importance are 1. light gathering 2. resolution 3. magnification) 2. What are some uses for a telescope? 3. Why does a stick appear to bend when it is placed partially in water? (refraction) Does it rea ...
... 1. What are the three main functions of a telescope? (the three main functions listed in order of importance are 1. light gathering 2. resolution 3. magnification) 2. What are some uses for a telescope? 3. Why does a stick appear to bend when it is placed partially in water? (refraction) Does it rea ...
H II region

An H II region is a large, low-density cloud of partially ionized gas in which star formation has recently taken place. The short-lived blue stars forged in these regions emit copious amounts of ultraviolet light that ionize the surrounding gas. H II regions—sometimes several hundred light-years across—are often associated with giant molecular clouds. The first known H II region was the Orion Nebula, which was discovered in 1610 by Nicolas-Claude Fabri de Peiresc.H II regions are named for the large amount of ionised atomic hydrogen they contain, referred to as H II, pronounced H-two by astronomers (an H I region being neutral atomic hydrogen, and H2 being molecular hydrogen). Such regions have extremely diverse shapes, because the distribution of the stars and gas inside them is irregular. They often appear clumpy and filamentary, sometimes showing bizarre shapes such as the Horsehead Nebula. H II regions may give birth to thousands of stars over a period of several million years. In the end, supernova explosions and strong stellar winds from the most massive stars in the resulting star cluster will disperse the gases of the H II region, leaving behind a cluster of birthed stars such as the Pleiades.H II regions can be seen to considerable distances in the universe, and the study of extragalactic H II regions is important in determining the distance and chemical composition of other galaxies. Spiral and irregular galaxies contain many H II regions, while elliptical galaxies are almost devoid of them. In the spiral galaxies, including the Milky Way, H II regions are concentrated in the spiral arms, while in the irregular galaxies they are distributed chaotically. Some galaxies contain huge H II regions, which may contain tens of thousands of stars. Examples include the 30 Doradus region in the Large Magellanic Cloud and NGC 604 in the Triangulum Galaxy.