Spring Stargazing - Trimble County Schools
... one of the brightest known stars in the galaxy. It 20,000 times brighter than our sun, but is 2,000 ly away. • Epsilon Aurigau has a companion star, which eclipses it every 27 years, making it noticeably dimmer. This happens in 2009-2011. ...
... one of the brightest known stars in the galaxy. It 20,000 times brighter than our sun, but is 2,000 ly away. • Epsilon Aurigau has a companion star, which eclipses it every 27 years, making it noticeably dimmer. This happens in 2009-2011. ...
The Chemical Composition of Stars in Open Clusters
... possible abundance gradients in the galactic disk, requires however the VLT, because in this case it is important to be able to study clusters at distances of up to 6 kpc or so. Recent work has shown that large-scale abundance gradients are indeed present in the disko I may refer again to the work o ...
... possible abundance gradients in the galactic disk, requires however the VLT, because in this case it is important to be able to study clusters at distances of up to 6 kpc or so. Recent work has shown that large-scale abundance gradients are indeed present in the disko I may refer again to the work o ...
Stars
... Kepler’s 3rd law) imply a mass of 2.6106 solar masses inside a volume 0.03 light years in diameter. It is impossible to pack stars together that tightly – they would collide, destroying each other very quickly. It is likely that the object at the center of our galaxy is a super massive black hole. ...
... Kepler’s 3rd law) imply a mass of 2.6106 solar masses inside a volume 0.03 light years in diameter. It is impossible to pack stars together that tightly – they would collide, destroying each other very quickly. It is likely that the object at the center of our galaxy is a super massive black hole. ...
ASTRONOMY WEBQUEST…… EXPLORE THE UNIVERSE
... Stars and planets are made from gases in a __________________. The Milky Way Galaxy is approximately _______________ light years across. How much longer will our Sun last? _________________________ Lifetimes of stars range from ___________ to ____________ years. Our star orbits the centre of our gal ...
... Stars and planets are made from gases in a __________________. The Milky Way Galaxy is approximately _______________ light years across. How much longer will our Sun last? _________________________ Lifetimes of stars range from ___________ to ____________ years. Our star orbits the centre of our gal ...
journey to the stars - American Museum of Natural History
... The Sun’s interior will also change. Incredibly, that bright yellow center will be larger than the Sun is today. Finally, the Sun—like most stars--will blow its ashes out into the Galaxy….seeding new stars…new planets…and potentially, new life. The remains of the Sun’s core--called a white dwarf-wil ...
... The Sun’s interior will also change. Incredibly, that bright yellow center will be larger than the Sun is today. Finally, the Sun—like most stars--will blow its ashes out into the Galaxy….seeding new stars…new planets…and potentially, new life. The remains of the Sun’s core--called a white dwarf-wil ...
Solar System where_are_we
... Earth travels 595 million miles around the sun each year. Its orbit is an ellipse, which is a long oval shape. As it travels around the sun, it also rotates around its own axis. So, even though the sun appears to be moving across the sky, it is our earth that is turning and moving ...
... Earth travels 595 million miles around the sun each year. Its orbit is an ellipse, which is a long oval shape. As it travels around the sun, it also rotates around its own axis. So, even though the sun appears to be moving across the sky, it is our earth that is turning and moving ...
Solutions - UC Berkeley Astronomy w
... The original Big Bang theory did not explain the incredible uniformity of the Universe nor its flat geometry. By uniformity we mean that when we look at the CMB in opposite directions in the sky, they have the same temperature (with small differences in ripples), but these two regions could never ha ...
... The original Big Bang theory did not explain the incredible uniformity of the Universe nor its flat geometry. By uniformity we mean that when we look at the CMB in opposite directions in the sky, they have the same temperature (with small differences in ripples), but these two regions could never ha ...
How the universe works – Answer Key Star dust is the building
... over 100 billion galaxies. There are more stars than there are grains of sand on earth. Every star can create the basic matter for everything in the universe, including us. Stars are balls of super-heated gas. You could fit a million earths inside the sun. Our sun is over a million km in diameter. T ...
... over 100 billion galaxies. There are more stars than there are grains of sand on earth. Every star can create the basic matter for everything in the universe, including us. Stars are balls of super-heated gas. You could fit a million earths inside the sun. Our sun is over a million km in diameter. T ...
Formation of the Solar System
... An advanced theory, called the condensation theory, includes the nebular theory but also incorporates interstellar dust as an essential ingredient in the formation of the planets. This theory claims that the dust grains of the interstellar medium helped cool the nebular cloud by radiating heat away, ...
... An advanced theory, called the condensation theory, includes the nebular theory but also incorporates interstellar dust as an essential ingredient in the formation of the planets. This theory claims that the dust grains of the interstellar medium helped cool the nebular cloud by radiating heat away, ...
Stellar Remnants
... • An object as big as the Sun with a onemonth rotation period will rotate more than 1000 times a second if squeezed down to the size of a neutron star – This happens when a massive star’s iron core collapses – magnetic field beams radiation energy in ...
... • An object as big as the Sun with a onemonth rotation period will rotate more than 1000 times a second if squeezed down to the size of a neutron star – This happens when a massive star’s iron core collapses – magnetic field beams radiation energy in ...
Cosmic Distance Ladder
... • Edwin Hubble determined a Cepheid Variable in Andromeda Galaxy. • Used Leavitt’s method to find the distance. • Conclusion: Andromeda is much distant than the estimated size of our galaxy! ...
... • Edwin Hubble determined a Cepheid Variable in Andromeda Galaxy. • Used Leavitt’s method to find the distance. • Conclusion: Andromeda is much distant than the estimated size of our galaxy! ...
The Milky Way
... Spiral arms are patterns • According to the density-wave theory, spiral arms are waves of high density that sweep around the Galaxy • The gravitational field of the density wave causes stars and gas to slow down near the arm • This compresses the interstellar clouds, triggering the formation of sta ...
... Spiral arms are patterns • According to the density-wave theory, spiral arms are waves of high density that sweep around the Galaxy • The gravitational field of the density wave causes stars and gas to slow down near the arm • This compresses the interstellar clouds, triggering the formation of sta ...
Carbon monoxide in clouds at low metallicity in the dwarf irregular
... where stars form, but it has never been detected in galaxies in which the oxygen abundance relative to hydrogen is less than 20 per cent of that of the Sun, even though such ‘low-metallicity’ galaxies often form stars. This raises the question of whether stars can form in dense gas without molecules ...
... where stars form, but it has never been detected in galaxies in which the oxygen abundance relative to hydrogen is less than 20 per cent of that of the Sun, even though such ‘low-metallicity’ galaxies often form stars. This raises the question of whether stars can form in dense gas without molecules ...
The Night Sky September 2016 - Bridgend Astronomical Society
... times more than the Sun and is about 50 times brighter. It is thus burning up its nuclear fuel at a greater rate than the Sun and so will shine for a correspondingly shorter time. Vega is much younger than the Sun, perhaps only a few hundred million years old, and is surrounded by a cold, dark disc ...
... times more than the Sun and is about 50 times brighter. It is thus burning up its nuclear fuel at a greater rate than the Sun and so will shine for a correspondingly shorter time. Vega is much younger than the Sun, perhaps only a few hundred million years old, and is surrounded by a cold, dark disc ...
Star Formation
... Shock Waves and Star Formation Shock waves from nearby star formation can be the trigger needed to start the collapse process in an interstellar cloud ...
... Shock Waves and Star Formation Shock waves from nearby star formation can be the trigger needed to start the collapse process in an interstellar cloud ...
Galaxies - Stockton University
... Actual proof of the Milky Way consisting of many stars came in 1610 when Galileo Galilei used a telescope to study the Milky Way and discovered that it was composed of a huge number of faint stars ...
... Actual proof of the Milky Way consisting of many stars came in 1610 when Galileo Galilei used a telescope to study the Milky Way and discovered that it was composed of a huge number of faint stars ...
Stellar Physics - University of Reading
... Classical Mechanics and Optics Thermodynamics and Statistical Mechanics Atomic and Molecular Physics Ideas from Observational Astronomy ...
... Classical Mechanics and Optics Thermodynamics and Statistical Mechanics Atomic and Molecular Physics Ideas from Observational Astronomy ...
Ch 28 Class Notes
... whose cycles of brightness range from about 1 day to 50 days (5 is average). The absolute magnitude of a Cepheid is related to the length of time between its periods of maximum brightness. The slower the cycle, the greater the luminosity of the star. By ___________________ a ________________________ ...
... whose cycles of brightness range from about 1 day to 50 days (5 is average). The absolute magnitude of a Cepheid is related to the length of time between its periods of maximum brightness. The slower the cycle, the greater the luminosity of the star. By ___________________ a ________________________ ...
a new isotopic abundance anomaly in chemically peculiar stars
... stars. Wavelengths of the infrared triplet were available for several of them. Interestingly, the Ca II lines in the most peculiar of their stars, the notorious Przybylski’s star, appeared to show the 48Ca shifts. When another spectrum of the same star, obtained with a different spectrograph also in ...
... stars. Wavelengths of the infrared triplet were available for several of them. Interestingly, the Ca II lines in the most peculiar of their stars, the notorious Przybylski’s star, appeared to show the 48Ca shifts. When another spectrum of the same star, obtained with a different spectrograph also in ...
Directed Reading A
... a. They are explosions in which a massive star collapses. b. They are explosions that occur at the beginning of a star’s life. c. They can be brighter than an entire galaxy for several days. d. They are explosions in which a star throws its outer layers into space. 27. A star that has collapsed unde ...
... a. They are explosions in which a massive star collapses. b. They are explosions that occur at the beginning of a star’s life. c. They can be brighter than an entire galaxy for several days. d. They are explosions in which a star throws its outer layers into space. 27. A star that has collapsed unde ...
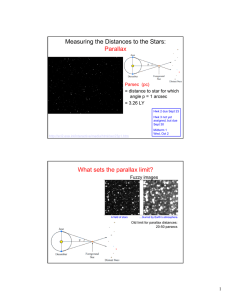
Measuring the Distances to the Stars: Parallax What sets the parallax limit?
... R0 are from tangent point method. • Beyond R0 most data points are young objects with known distances & motions. • But Merrifield used variation of apparent thickness of H I disk with longitude (complicated). ...
... R0 are from tangent point method. • Beyond R0 most data points are young objects with known distances & motions. • But Merrifield used variation of apparent thickness of H I disk with longitude (complicated). ...
The Family of Stars
... Polaris has just about the same spectral type (and surface temperature) as our sun, but it is 10,000 times brighter. Thus, Polaris’ radius is … the sun’s radius. ...
... Polaris has just about the same spectral type (and surface temperature) as our sun, but it is 10,000 times brighter. Thus, Polaris’ radius is … the sun’s radius. ...
Word doc - UC-HiPACC - University of California, Santa Cruz
... Today, the highest-mass stars top out at about 100 solar masses (Eta Carinae, one of the most massive stars in our Milky Way galaxy, is about 90). But recent cosmological simulations suggest the possibility that in the early universe truly gargantuan stars could exist. So Chen began exploring this w ...
... Today, the highest-mass stars top out at about 100 solar masses (Eta Carinae, one of the most massive stars in our Milky Way galaxy, is about 90). But recent cosmological simulations suggest the possibility that in the early universe truly gargantuan stars could exist. So Chen began exploring this w ...
H II region

An H II region is a large, low-density cloud of partially ionized gas in which star formation has recently taken place. The short-lived blue stars forged in these regions emit copious amounts of ultraviolet light that ionize the surrounding gas. H II regions—sometimes several hundred light-years across—are often associated with giant molecular clouds. The first known H II region was the Orion Nebula, which was discovered in 1610 by Nicolas-Claude Fabri de Peiresc.H II regions are named for the large amount of ionised atomic hydrogen they contain, referred to as H II, pronounced H-two by astronomers (an H I region being neutral atomic hydrogen, and H2 being molecular hydrogen). Such regions have extremely diverse shapes, because the distribution of the stars and gas inside them is irregular. They often appear clumpy and filamentary, sometimes showing bizarre shapes such as the Horsehead Nebula. H II regions may give birth to thousands of stars over a period of several million years. In the end, supernova explosions and strong stellar winds from the most massive stars in the resulting star cluster will disperse the gases of the H II region, leaving behind a cluster of birthed stars such as the Pleiades.H II regions can be seen to considerable distances in the universe, and the study of extragalactic H II regions is important in determining the distance and chemical composition of other galaxies. Spiral and irregular galaxies contain many H II regions, while elliptical galaxies are almost devoid of them. In the spiral galaxies, including the Milky Way, H II regions are concentrated in the spiral arms, while in the irregular galaxies they are distributed chaotically. Some galaxies contain huge H II regions, which may contain tens of thousands of stars. Examples include the 30 Doradus region in the Large Magellanic Cloud and NGC 604 in the Triangulum Galaxy.