Characteristics of stars powerpoint
... • The brightness a star would have if it was a standard distance from Earth • This requires an astronomer to determine both the apparent magnitude and distance from Earth • Ex: calculating absolute magnitude by making all stars 1 light-year away ...
... • The brightness a star would have if it was a standard distance from Earth • This requires an astronomer to determine both the apparent magnitude and distance from Earth • Ex: calculating absolute magnitude by making all stars 1 light-year away ...
Answers Universe Cornell Notes Chapter 8, Sec 2
... and size. Supergiant star, giant star, medium-sized star, white dwarf star, neutron star A star’s color reveals its temperature. Red, yellow - white, blue - white Brightness depends on the star’s size and temperature. It’s brightness as seen from Earth. Apparent brightness is how bright it appears t ...
... and size. Supergiant star, giant star, medium-sized star, white dwarf star, neutron star A star’s color reveals its temperature. Red, yellow - white, blue - white Brightness depends on the star’s size and temperature. It’s brightness as seen from Earth. Apparent brightness is how bright it appears t ...
Main Sequence Star
... a) Size of giants depends on the initial mass b) Could be a super red giant like Betelgeuse ...
... a) Size of giants depends on the initial mass b) Could be a super red giant like Betelgeuse ...
Chapter 21
... The sun is a medium-sized star. Stars that are much larger than the sun are called ______________ or __________________. Composition – The chemical composition of most stars is about 73 % ______________ and 25 % ____________________. How can astronomers infer which elements are found in stars? ___ ...
... The sun is a medium-sized star. Stars that are much larger than the sun are called ______________ or __________________. Composition – The chemical composition of most stars is about 73 % ______________ and 25 % ____________________. How can astronomers infer which elements are found in stars? ___ ...
Astronomy I Ex.2
... 1. Convert the following distances into distances in cm: a) 1 Lyr. b) 50 Mpc. c) 100,000 AU. 2. H0 ' 70 secKm M pc What is the (approximate) age of the universe in Gyr? 3. Convert the following distances in cm to distances in AU: a) Approximate distance from the earth to the sun: 1.44 × 1013 cm b) A ...
... 1. Convert the following distances into distances in cm: a) 1 Lyr. b) 50 Mpc. c) 100,000 AU. 2. H0 ' 70 secKm M pc What is the (approximate) age of the universe in Gyr? 3. Convert the following distances in cm to distances in AU: a) Approximate distance from the earth to the sun: 1.44 × 1013 cm b) A ...
ASTR2050 Spring 2005 •
... Depending on circumstances, it may be more or less convenient to express the type of radiation in terms of either its frequency or its wavelength. ...
... Depending on circumstances, it may be more or less convenient to express the type of radiation in terms of either its frequency or its wavelength. ...
Pistol Star of the Pistol Nebula
... With a diameter larger than Earth's orbit around the Sun, it radiates as much as more than 10 million times more light than Sol (L= 10^6.3) and appears to have more than 150 Solar-masses, having been resolved as a single star down to a projected separation of 110 AUs (Figer et al, 1998). Indeed, the ...
... With a diameter larger than Earth's orbit around the Sun, it radiates as much as more than 10 million times more light than Sol (L= 10^6.3) and appears to have more than 150 Solar-masses, having been resolved as a single star down to a projected separation of 110 AUs (Figer et al, 1998). Indeed, the ...
Chapter 11 - USD Home Pages
... properties of stars? a. speed; b. rotation rates; c. distances; d. colors; e. temperatures. c. distance. The only direct way to determine distance. 3. Measurements of binary star systems are required to determine what property of stars? : a. luminosity; b. apparent magnitude; c. distance; d. mass; e ...
... properties of stars? a. speed; b. rotation rates; c. distances; d. colors; e. temperatures. c. distance. The only direct way to determine distance. 3. Measurements of binary star systems are required to determine what property of stars? : a. luminosity; b. apparent magnitude; c. distance; d. mass; e ...
Understanding Stars
... – The same kinds of stars are equally bright, • Brighter means closer for stars of the same type – different kinds of stars can be different brightnesses regardless of their distances • The actual brightness depends on the star’s diameter ...
... – The same kinds of stars are equally bright, • Brighter means closer for stars of the same type – different kinds of stars can be different brightnesses regardless of their distances • The actual brightness depends on the star’s diameter ...
LT 5: I can describe how astronomers determine the composition
... – May revolve around another star – May move away from or toward our solar system ...
... – May revolve around another star – May move away from or toward our solar system ...
REVIEW: STAR`S TEST
... The apparent magnitude of a star tells you how bright the star is as viewed from A nebula is a huge cloud of gas, primarily composed of ...
... The apparent magnitude of a star tells you how bright the star is as viewed from A nebula is a huge cloud of gas, primarily composed of ...
Astronomy Chapter 13 Name
... M. The region in the H-R diagram in which most stars are located N. A dense star whose radius is approximately equal to Earth’s but whose mass is comparable to the Sun’s O. Two stars in orbit around each other, held together by their mutual gravity P. A pair of stars held together by their mutual gr ...
... M. The region in the H-R diagram in which most stars are located N. A dense star whose radius is approximately equal to Earth’s but whose mass is comparable to the Sun’s O. Two stars in orbit around each other, held together by their mutual gravity P. A pair of stars held together by their mutual gr ...
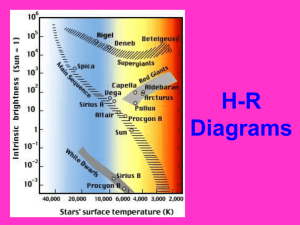
H-R Diagrams
... TEMPERATURE – It also shows color since color is related to temperature – It was made by two astronomers who plotted the data for thousands of stars and noticed some trends. ...
... TEMPERATURE – It also shows color since color is related to temperature – It was made by two astronomers who plotted the data for thousands of stars and noticed some trends. ...
Characteristics of Stars
... the lower right when plotted according to luminosity and surface temperature on the Hertzprung-Russell Diagram ...
... the lower right when plotted according to luminosity and surface temperature on the Hertzprung-Russell Diagram ...
STARS and GALAXIES
... • A large ball of gas held together by gravity that produces tremendous amounts of heat and light. • Some stars are very old and the size of planets or moons, and some no longer ...
... • A large ball of gas held together by gravity that produces tremendous amounts of heat and light. • Some stars are very old and the size of planets or moons, and some no longer ...
Chapter 18 Study Guide
... Name __________________________________________ Class ____________ Date ___________ Earth Science Study Guide: Chapter 18- Stars Complete each question or statement with as much information as we covered in class. 1. What is a star? 2. Describe the process of star formation in 5 steps. ...
... Name __________________________________________ Class ____________ Date ___________ Earth Science Study Guide: Chapter 18- Stars Complete each question or statement with as much information as we covered in class. 1. What is a star? 2. Describe the process of star formation in 5 steps. ...
Stars: Other Suns
... • Inverse relation: Smaller parallax, greater the distance • Hipparcos satellite measured over 100,000 stars precisely (±1 mas), over 1 million with less precision ...
... • Inverse relation: Smaller parallax, greater the distance • Hipparcos satellite measured over 100,000 stars precisely (±1 mas), over 1 million with less precision ...
Astronomy - Shelbyville Central Schools
... White dwarf – outer layer contracts (about size of Earth) Neutron star – only neutrons can exist in the dense core Black hole – gravity is so strong that nothing can escape, not even light ...
... White dwarf – outer layer contracts (about size of Earth) Neutron star – only neutrons can exist in the dense core Black hole – gravity is so strong that nothing can escape, not even light ...
18-3 constellations RG
... 13. When a star or galaxy moves quickly away from an observer, the light it emits appears redder than it usually would, this effect is called _____________________________________________. 14. When a star or galaxy moves quickly toward an observer, the light it emits appears bluer than it usually w ...
... 13. When a star or galaxy moves quickly away from an observer, the light it emits appears redder than it usually would, this effect is called _____________________________________________. 14. When a star or galaxy moves quickly toward an observer, the light it emits appears bluer than it usually w ...
Chapter 24 Test:Stars/Galaxies
... plasma precipitation called _____. (a) prominences, (b) photospheres, (c) solar flares, (d) corona. ...
... plasma precipitation called _____. (a) prominences, (b) photospheres, (c) solar flares, (d) corona. ...
ppt
... If star wobbles with amplitude of 1 arc-second (1/3600th of a degree), then it is at distance of 1 parsec (definition of parsec). 1 pc = 3.26 light years. In general, ...
... If star wobbles with amplitude of 1 arc-second (1/3600th of a degree), then it is at distance of 1 parsec (definition of parsec). 1 pc = 3.26 light years. In general, ...
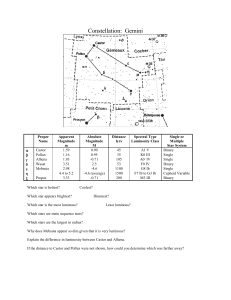
Gemini
... corresponds to a linear diameter of about 24 light years; its central density is about 6.21 stars per cubic parsec. Some authors have estimated a larger diameter of up to 46' (H. Shapley in 1930). With about 100 million years (WEBDA gives a value 95, the Sky Catalogue 2000.0 of 110 million years), i ...
... corresponds to a linear diameter of about 24 light years; its central density is about 6.21 stars per cubic parsec. Some authors have estimated a larger diameter of up to 46' (H. Shapley in 1930). With about 100 million years (WEBDA gives a value 95, the Sky Catalogue 2000.0 of 110 million years), i ...
Malmquist bias
The Malmquist bias is an effect in observational astronomy which leads to the preferential detection of intrinsically bright objects. It was first described in 1922 by Swedish astronomer Gunnar Malmquist (1893–1982), who then greatly elaborated upon this work in 1925. In statistics, this bias is referred to as a selection bias and affects the survey results in a brightness limited survey, where stars below a certain apparent brightness are not included. Since observed stars and galaxies appear dimmer when farther away, the brightness that is measured will fall off with distance until their brightness falls below the observational threshold. Objects which are more luminous, or intrinsically brighter, can be observed at a greater distance, creating a false trend of increasing intrinsic brightness, and other related quantities, with distance. This effect has led to many spurious claims in the field of astronomy. Properly correcting for these effects has become an area of great focus.