
Pluto and the Dwarf Planets
... Pluto was discovered by Clyde Tombaugh in 1930 by comparing one image of the sky taken one night with an image taken 6 nights later. ...
... Pluto was discovered by Clyde Tombaugh in 1930 by comparing one image of the sky taken one night with an image taken 6 nights later. ...
File
... predict motion, and explain how celestial bodies move through the universe. Newton was the first to show mathematically that the force of gravity extend outside of the earth (think of the visual of Newton sitting under a tree and apple hits him on the head because of gravity). He use math to show th ...
... predict motion, and explain how celestial bodies move through the universe. Newton was the first to show mathematically that the force of gravity extend outside of the earth (think of the visual of Newton sitting under a tree and apple hits him on the head because of gravity). He use math to show th ...
Lab 1: Introduction to Astronomy
... clue is worth one point. If you have trouble, feel free to ask your TA for help! The total lab is out of 30 points, so there are two points of extra credit available! Across 2: This object is Roman Vulcan’s home in our Solar System 3: First seen by Galileo around the 6th planet, these are mostly icy ...
... clue is worth one point. If you have trouble, feel free to ask your TA for help! The total lab is out of 30 points, so there are two points of extra credit available! Across 2: This object is Roman Vulcan’s home in our Solar System 3: First seen by Galileo around the 6th planet, these are mostly icy ...
Mon Nov 18, 2013 THE MOON`S TIDAL LOCK The old gibbous
... Edwin Hubble on this date, November 20th, in 1889. Both these men made remarkable discoveries about our Universe. Shapley discovered that our sun and solar system were not at the center of the Milky Way Galaxy, but instead a little over halfway out, and that the Milky Way was much larger than anyone ...
... Edwin Hubble on this date, November 20th, in 1889. Both these men made remarkable discoveries about our Universe. Shapley discovered that our sun and solar system were not at the center of the Milky Way Galaxy, but instead a little over halfway out, and that the Milky Way was much larger than anyone ...
Astronomy 103: First Exam Name
... (d) the gasses get added to the gas giants (e) none of these 40. Which planet has the most extreme seasons? (a) Venus (b) Earth (c) Jupiter (d) Uranus (e) Pluto 41. In what way is Pluto more like a comet then a planet (a) It is made of rock and ice. (b) It sometimes enters the inner solar system. (c ...
... (d) the gasses get added to the gas giants (e) none of these 40. Which planet has the most extreme seasons? (a) Venus (b) Earth (c) Jupiter (d) Uranus (e) Pluto 41. In what way is Pluto more like a comet then a planet (a) It is made of rock and ice. (b) It sometimes enters the inner solar system. (c ...
Ancient Civilizations Ancient Greek Astronomers Ancient Greek
... because they were based on wrong “first principles”, believed to be “obvious” and not questioned: 1. Geocentric Universe: Earth at the Center of the Universe. 2. “Perfect Heavens”: Motions of all celestial bodies described by motions involving objects of “perfect” shape, i.e., spheres or circles. ...
... because they were based on wrong “first principles”, believed to be “obvious” and not questioned: 1. Geocentric Universe: Earth at the Center of the Universe. 2. “Perfect Heavens”: Motions of all celestial bodies described by motions involving objects of “perfect” shape, i.e., spheres or circles. ...
Integrative Studies 410 Our Place in the Universe
... – Argued that the planets move on spheres around the Earth (“geocentric” model) – Argues that the earth is spherical based on the shape of its shadow on the moon during lunar eclipses ...
... – Argued that the planets move on spheres around the Earth (“geocentric” model) – Argues that the earth is spherical based on the shape of its shadow on the moon during lunar eclipses ...
PowerPoint 演示文稿
... 100,000 light-years across. It is about 14 billion years old and takes 225 million years or so to rotate(旋转) once. Like all spirals, it contains plenty of gas and dust, from which new stars are formed. The dense nucleus(核心) is the oldest part and has no gas left for new star. ...
... 100,000 light-years across. It is about 14 billion years old and takes 225 million years or so to rotate(旋转) once. Like all spirals, it contains plenty of gas and dust, from which new stars are formed. The dense nucleus(核心) is the oldest part and has no gas left for new star. ...
Final Study Guide copy
... the sky; in ancient times this included the sun, moon, and 5 classical planets (Mercury, Venus, Mars, Jupiter, and Saturn) Geocentric Model – A model or understanding of the universe where the Earth is at the center, and the sun, moon, planets and stars revolve around the Earth Heliocentric Model – ...
... the sky; in ancient times this included the sun, moon, and 5 classical planets (Mercury, Venus, Mars, Jupiter, and Saturn) Geocentric Model – A model or understanding of the universe where the Earth is at the center, and the sun, moon, planets and stars revolve around the Earth Heliocentric Model – ...
The Solar System - Belle Vernon Area School District
... temperatures do not allow for liquid or gaseous water to exist on the surface • There are indications in the land that look like the result of running water, but are more likely the result of the seasonal dust/wind ...
... temperatures do not allow for liquid or gaseous water to exist on the surface • There are indications in the land that look like the result of running water, but are more likely the result of the seasonal dust/wind ...
July 2013 - Joliet Junior College
... below Arcturus and to the left of another bright star -Spica. On July 16th the moon will be close below Saturn. Mercury, Jupiter and Mars all rise before the sun and are in the early morning sky. On July 22nd, Jupiter will be within one degree of Mars. The pair will rise at 3:45 am. Earth will be at ...
... below Arcturus and to the left of another bright star -Spica. On July 16th the moon will be close below Saturn. Mercury, Jupiter and Mars all rise before the sun and are in the early morning sky. On July 22nd, Jupiter will be within one degree of Mars. The pair will rise at 3:45 am. Earth will be at ...
(Lecture 3). The Solar System in the Night Sky (cont)
... count 365 days, and exactly 365 mean solar days later, as the Sun crosses the Meridian, we celebrate the start of the new year. The trouble is, the Sun has not returned to the same place relative to the stars. It is still 0.25 days away from that point. After the next year, it is half a day, and the ...
... count 365 days, and exactly 365 mean solar days later, as the Sun crosses the Meridian, we celebrate the start of the new year. The trouble is, the Sun has not returned to the same place relative to the stars. It is still 0.25 days away from that point. After the next year, it is half a day, and the ...
Astronomy Review
... and revolution. Earth’s rotation on its axis causes the length of one day to be approximately 24 hours. This rotation also causes the Sun and Moon to appear to rise along the eastern horizon and to set along the western horizon. Earth’s revolution around the Sun defines the length of the year to be ...
... and revolution. Earth’s rotation on its axis causes the length of one day to be approximately 24 hours. This rotation also causes the Sun and Moon to appear to rise along the eastern horizon and to set along the western horizon. Earth’s revolution around the Sun defines the length of the year to be ...
Astronomy Study Guide
... and revolution. Earth’s rotation on its axis causes the length of one day to be approximately 24 hours. This rotation also causes the Sun and Moon to appear to rise along the eastern horizon and to set along the western horizon. Earth’s revolution around the Sun defines the length of the year to be ...
... and revolution. Earth’s rotation on its axis causes the length of one day to be approximately 24 hours. This rotation also causes the Sun and Moon to appear to rise along the eastern horizon and to set along the western horizon. Earth’s revolution around the Sun defines the length of the year to be ...
Astronomy
... Pluto • No longer considered a planet; dwarf planet • No rings and thin atmosphere • One moon • Crosses Neptune’s orbit part of the time • Rotates once every 6 days • Revolves once every 248 years. ...
... Pluto • No longer considered a planet; dwarf planet • No rings and thin atmosphere • One moon • Crosses Neptune’s orbit part of the time • Rotates once every 6 days • Revolves once every 248 years. ...
6, 19, 24, 37, 47 and 65
... 19. At what altitude above Earth’s surface would the gravitational acceleration be 4.9 m/s2? Answer: 2.6 ...
... 19. At what altitude above Earth’s surface would the gravitational acceleration be 4.9 m/s2? Answer: 2.6 ...
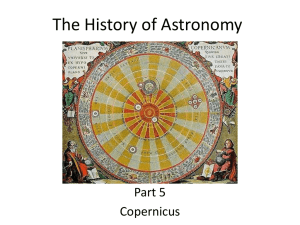
The History of Astronomy
... • He even got the relative distances from the sun correct (see chart on page 49). • Moon orbits Earth To avoid religious persecution he published his work “de revolutionibus orbium coelestium” posthumusly. ...
... • He even got the relative distances from the sun correct (see chart on page 49). • Moon orbits Earth To avoid religious persecution he published his work “de revolutionibus orbium coelestium” posthumusly. ...
1. Match the following items [a] 1. when a planet seems to reverse its
... *a. Remains stationary - Polaris lines up exactly with the Earth's axis, so it does not appear to move. b. Remains stationary - Polaris moves in synchronous rotation with Earth, so it does not appear to move c. Apparent motion - The Earth rotates so our perspective of Polaris changes and it appears ...
... *a. Remains stationary - Polaris lines up exactly with the Earth's axis, so it does not appear to move. b. Remains stationary - Polaris moves in synchronous rotation with Earth, so it does not appear to move c. Apparent motion - The Earth rotates so our perspective of Polaris changes and it appears ...
What part of the sun can we see only during a solar eclipse?
... A piece of an asteroid which breaks off due to collision is known as… ...
... A piece of an asteroid which breaks off due to collision is known as… ...
The solar system - Secondary Education
... • Both planets and dwarf planets orbit the Sun, not other planets (in which case we call them moons). Both must be large enough that their own gravity pulls them into the shapes of ...
... • Both planets and dwarf planets orbit the Sun, not other planets (in which case we call them moons). Both must be large enough that their own gravity pulls them into the shapes of ...
Homework #1 10 points Question #1 (2 pts) Even in ancient times
... Even in ancient times, astronomers knew that planets vary in brightness over the course of several months or even years. Explain, why this observation can not be used to rule out the geocentric model, in which all planets and the Sun orbit the Earth on circular orbits. Ignore the epicycles, i.e. ass ...
... Even in ancient times, astronomers knew that planets vary in brightness over the course of several months or even years. Explain, why this observation can not be used to rule out the geocentric model, in which all planets and the Sun orbit the Earth on circular orbits. Ignore the epicycles, i.e. ass ...
AP Physics - Universal Gravitation
... the projectile is to rise to a height of 2R above the surface of the planet? Disregard any dissipative effects of the atmosphere. A) B) C) D) E) 6. What is the kinetic energy of a 200-kg satellite as it follows a circular orbit of radius 8.0 × 106 m around the Earth? (Mass of Earth = 6.0 × 1024 kg.) ...
... the projectile is to rise to a height of 2R above the surface of the planet? Disregard any dissipative effects of the atmosphere. A) B) C) D) E) 6. What is the kinetic energy of a 200-kg satellite as it follows a circular orbit of radius 8.0 × 106 m around the Earth? (Mass of Earth = 6.0 × 1024 kg.) ...
Chapter-08
... If you double the distance between m1 and m2, the gravitational force on m2 1. Increases by 2 2. Increases by 4 3. Decreases by 1/2 4. Decreases by 1/4 5. Stays the same ...
... If you double the distance between m1 and m2, the gravitational force on m2 1. Increases by 2 2. Increases by 4 3. Decreases by 1/2 4. Decreases by 1/4 5. Stays the same ...
Document
... Not only did early humans navigate by means of the sky, but the motions of objects in the sky predicted the changing of the seasons, etc. ...
... Not only did early humans navigate by means of the sky, but the motions of objects in the sky predicted the changing of the seasons, etc. ...
Satellite system (astronomy)

A satellite system is a set of gravitationally bound objects in orbit around a planetary mass object or minor planet. Generally speaking, it is a set of natural satellites (moons), although such systems may also consist of bodies such as circumplanetary disks, ring systems, moonlets, minor-planet moons and artificial satellites any of which may themselves have satellite systems of their own. Some satellite systems have complex interactions with both their parent and other moons, including magnetic, tidal, atmospheric and orbital interactions such as orbital resonances and libration. Individually major satellite objects are designated in Roman numerals. Satellite systems are referred to either by the possessive adjectives of their primary (e.g. ""Jovian system""), or less commonly by the name of their primary (e.g. ""Jupiter system""). Where only one satellite is known, or it is a binary orbiting a common centre of gravity, it may be referred to using the hyphenated names of the primary and major satellite (e.g. the ""Earth-Moon system"").Many Solar System objects are known to possess satellite systems, though their origin is still unclear. Notable examples include the largest satellite system, the Jovian system, with 67 known moons (including the large Galilean moons) and the Saturnian System with 62 known moons (and the most visible ring system in the Solar System). Both satellite systems are large and diverse. In fact all of the giant planets of the Solar System possess large satellite systems as well as planetary rings, and it is inferred that this is a general pattern. Several objects farther from the Sun also have satellite systems consisting of multiple moons, including the complex Plutonian system where multiple objects orbit a common center of mass, as well as many asteroids and plutinos. Apart from the Earth-Moon system and Mars' system of two tiny natural satellites, the other terrestrial planets are generally not considered satellite systems, although some have been orbited by artificial satellites originating from Earth.Little is known of satellite systems beyond the Solar System, although it is inferred that natural satellites are common. J1407b is an example of an extrasolar satellite system. It is also theorised that Rogue planets ejected from their planetary system could retain a system of satellites.















![1. Match the following items [a] 1. when a planet seems to reverse its](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/009818644_1-b9fd1766950aed5f7aaf96271f95fc41-300x300.png)






