Cellular respiration
... Although there is a theoretical yield of 36-38 ATP molecules per glucose during cellular respiration, such conditions are generally not realized due to losses such as the cost of moving pyruvate (from glycolysis), phosphate, and ADP (substrates for ATP synthesis) into the mitochondria. All are activ ...
... Although there is a theoretical yield of 36-38 ATP molecules per glucose during cellular respiration, such conditions are generally not realized due to losses such as the cost of moving pyruvate (from glycolysis), phosphate, and ADP (substrates for ATP synthesis) into the mitochondria. All are activ ...
Chapter 9 - Cellular Respiration
... • In muscle tissues during rapid and vigorous exercise, muscle cells may be depleted of oxygen. • Muscles then switch from respiration to lacticacid fermentation. ...
... • In muscle tissues during rapid and vigorous exercise, muscle cells may be depleted of oxygen. • Muscles then switch from respiration to lacticacid fermentation. ...
A Rice Plastidial Nucleotide Sugar Epimerase Is Involved in
... novel chloroplast-localized UDP-glucose epimerase (UGE), which is conserved in the plant kingdom. The chloroplast localization of PHD1 was confirmed by immunoblots, immunocytochemistry, and UGE activity in isolated chloroplasts, which was approximately 50% lower in the phd1-1 mutant than in the wild ...
... novel chloroplast-localized UDP-glucose epimerase (UGE), which is conserved in the plant kingdom. The chloroplast localization of PHD1 was confirmed by immunoblots, immunocytochemistry, and UGE activity in isolated chloroplasts, which was approximately 50% lower in the phd1-1 mutant than in the wild ...
General Medicine Pharmacotherapy Card
... treatment as the side effect will usually clear in a few days. 2. If a patient has been on regular opioids and develops drowsiness or confusion, assess patient for other causes (e.g. delirium, changes in metabolic function, underlying illnesses, other sedating medications). Also consider opioid toxi ...
... treatment as the side effect will usually clear in a few days. 2. If a patient has been on regular opioids and develops drowsiness or confusion, assess patient for other causes (e.g. delirium, changes in metabolic function, underlying illnesses, other sedating medications). Also consider opioid toxi ...
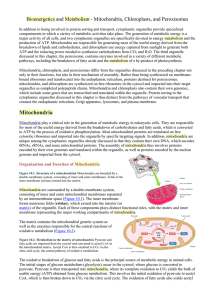
Mitochondria, Chloroplasts, and Peroxisomes
... molecular oxygen is coupled to the transfer of protons from the mitochondrial matrix to the intermembrane space. Since protons are charged particles, this transfer establishes an electric potential across the inner membrane, with the matrix being negative. During protein import, this electric potent ...
... molecular oxygen is coupled to the transfer of protons from the mitochondrial matrix to the intermembrane space. Since protons are charged particles, this transfer establishes an electric potential across the inner membrane, with the matrix being negative. During protein import, this electric potent ...
Electron Transport Chain - Dr-Manar-KSU
... 4-the net yield of ATP by substrate level phosphorylation during citric acid cycle for each glucose molecule is two. 5- FADH2 is an electron carrier in glycolysis. ...
... 4-the net yield of ATP by substrate level phosphorylation during citric acid cycle for each glucose molecule is two. 5- FADH2 is an electron carrier in glycolysis. ...
eprint_1_29837_493
... Enzymes are biological catalysts which bring about chemical are present in very small amounts in various cells . Almost all the functions of the body such as digestion , breathing , synthesis and breakdown of carbohydrates m fats and proteins are catalysed and controlled by specific enzymes . Most c ...
... Enzymes are biological catalysts which bring about chemical are present in very small amounts in various cells . Almost all the functions of the body such as digestion , breathing , synthesis and breakdown of carbohydrates m fats and proteins are catalysed and controlled by specific enzymes . Most c ...
The three main functions of stems are : a.)Conduction, asexual
... Which of the following statements is correct about cork cell a.)Contain only cells that do not differentiate b.)Are active centers of cell growth throughout the life of the plant c.) Are deed cell d. )Are either apical or lateral e. )Occur in both roots and shoots Secondary growth, an increase in t ...
... Which of the following statements is correct about cork cell a.)Contain only cells that do not differentiate b.)Are active centers of cell growth throughout the life of the plant c.) Are deed cell d. )Are either apical or lateral e. )Occur in both roots and shoots Secondary growth, an increase in t ...
Regulation of Glycolysis
... is therefore considered an allosteric activator. The activity of PFK-1 is dependent on the ATP, ADP and AMP concentrations which are all functions of the cellular energy status. ...
... is therefore considered an allosteric activator. The activity of PFK-1 is dependent on the ATP, ADP and AMP concentrations which are all functions of the cellular energy status. ...
Unit 4 Notes - heckgrammar.co.uk
... good thing, as these small packets of easily-released energy are more useful to cells and can be used to do simple common jobs, as the next paragraph shows. An analogy would be that small change (ATP) is often more useful than large bank notes (glucose). What is the energy in ATP used for? The proce ...
... good thing, as these small packets of easily-released energy are more useful to cells and can be used to do simple common jobs, as the next paragraph shows. An analogy would be that small change (ATP) is often more useful than large bank notes (glucose). What is the energy in ATP used for? The proce ...
Acid/Base Homeostasis - Interactive Physiology
... their shape is crucial for their function. • The protein shown is an enzyme. Enzymes have active sites with a specific shape. If for some reason the shape of the protein changes, this enzyme would no longer be able to function. • Because this enzyme functions within the cytoplasm of the cell, it ope ...
... their shape is crucial for their function. • The protein shown is an enzyme. Enzymes have active sites with a specific shape. If for some reason the shape of the protein changes, this enzyme would no longer be able to function. • Because this enzyme functions within the cytoplasm of the cell, it ope ...
Cellular Respiration
... • Glucose and other fuels are broken down gradually in a series of steps, each catalyzed by a specific enzyme • At key steps, H atoms are stripped from glucose and passed first to a coenzyme, ...
... • Glucose and other fuels are broken down gradually in a series of steps, each catalyzed by a specific enzyme • At key steps, H atoms are stripped from glucose and passed first to a coenzyme, ...
Cellular Respiration
... • Glucose and other fuels are broken down gradually in a series of steps, each catalyzed by a specific enzyme • At key steps, H atoms are stripped from glucose and passed first to a coenzyme, ...
... • Glucose and other fuels are broken down gradually in a series of steps, each catalyzed by a specific enzyme • At key steps, H atoms are stripped from glucose and passed first to a coenzyme, ...
MS Word Version - Interactive Physiology
... their shape is crucial for their function. • The protein shown is an enzyme. Enzymes have active sites with a specific shape. If for some reason the shape of the protein changes, this enzyme would no longer be able to function. • Because this enzyme functions within the cytoplasm of the cell, it ope ...
... their shape is crucial for their function. • The protein shown is an enzyme. Enzymes have active sites with a specific shape. If for some reason the shape of the protein changes, this enzyme would no longer be able to function. • Because this enzyme functions within the cytoplasm of the cell, it ope ...
MS Word Version
... their shape is crucial for their function. • The protein shown is an enzyme. Enzymes have active sites with a specific shape. If for some reason the shape of the protein changes, this enzyme would no longer be able to function. • Because this enzyme functions within the cytoplasm of the cell, it ope ...
... their shape is crucial for their function. • The protein shown is an enzyme. Enzymes have active sites with a specific shape. If for some reason the shape of the protein changes, this enzyme would no longer be able to function. • Because this enzyme functions within the cytoplasm of the cell, it ope ...
REAL Health Solutions!
... word ─ LIFE. Without systemic enzymes, LIFE itself is not possible, not for people, plants, or animals.** Enzymes are the single most important essential for every reaction taking place in a living organism because every second of everyday life changes and renews itself. Restoring proper levels of s ...
... word ─ LIFE. Without systemic enzymes, LIFE itself is not possible, not for people, plants, or animals.** Enzymes are the single most important essential for every reaction taking place in a living organism because every second of everyday life changes and renews itself. Restoring proper levels of s ...
Rusnak_Rosenzweig_2000 - Vanderbilt University School of Medicine
... metal ions are linked by a bridging solvent molecule and a µ-1,1 aspartic acid. Additional ligands include a histidine and an aspartic acid to the first metal ion and two histidines and an asparagine to the second metal ion. The locations of other conserved residues in the phosphoesterase motif are ...
... metal ions are linked by a bridging solvent molecule and a µ-1,1 aspartic acid. Additional ligands include a histidine and an aspartic acid to the first metal ion and two histidines and an asparagine to the second metal ion. The locations of other conserved residues in the phosphoesterase motif are ...
Chapter 8 – an introduction to metabolism
... 26. Describe the evidence that suggests that glycolysis is an ancient metabolic pathway. 27. Describe how food molecules other than glucose can be oxidized to make ATP. 28. Explain how glycolysis and the citric acid cycle can contribute to anabolic pathways. 29. Explain how ATP production is control ...
... 26. Describe the evidence that suggests that glycolysis is an ancient metabolic pathway. 27. Describe how food molecules other than glucose can be oxidized to make ATP. 28. Explain how glycolysis and the citric acid cycle can contribute to anabolic pathways. 29. Explain how ATP production is control ...
H +
... Where is this process taking place? How do the electrons get shuttled down the ETC? How is electronegativity involved? What molecule is the final acceptor of the electrons? What is the byproduct that is generated during the ETC? The ETC does not generate ATP. What is it’s purpose? ...
... Where is this process taking place? How do the electrons get shuttled down the ETC? How is electronegativity involved? What molecule is the final acceptor of the electrons? What is the byproduct that is generated during the ETC? The ETC does not generate ATP. What is it’s purpose? ...
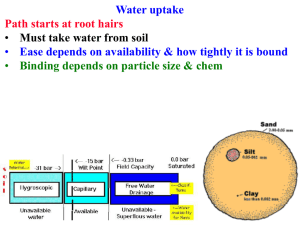
Vascular tissue - Cloudfront.net
... nutrients from the soil Most water and minerals enter a plant through the tiny root hairs Water moves into the cortex, through the cells of the endodermis, and into the vascular cylinder Finally, water reaches the xylem, where it is transported throughout the plant Cells in the endodermis are made w ...
... nutrients from the soil Most water and minerals enter a plant through the tiny root hairs Water moves into the cortex, through the cells of the endodermis, and into the vascular cylinder Finally, water reaches the xylem, where it is transported throughout the plant Cells in the endodermis are made w ...
Cellular Respiration
... from NADH for its continuous role in glycolysis During anaerobic cellular respiration only 2 ATP are produced from one initial glucose molecule ...
... from NADH for its continuous role in glycolysis During anaerobic cellular respiration only 2 ATP are produced from one initial glucose molecule ...
1st Semester Final Exam Study Guide (excluding DNA/protein
... b) They are usually coupled with anabolic pathways to which they supply energy in the form of ATP. c) They are endergonic. d) They are spontaneous and do not need enzyme catalysis. e) They build up complex molecules such as protein from simpler compounds. 42. A type of protein critical to all cells ...
... b) They are usually coupled with anabolic pathways to which they supply energy in the form of ATP. c) They are endergonic. d) They are spontaneous and do not need enzyme catalysis. e) They build up complex molecules such as protein from simpler compounds. 42. A type of protein critical to all cells ...
Document
... •Animals get energy second- or third-hand from ____ or other ____________ •Regardless, the energy is converted to the chemical bond energy of ____ ...
... •Animals get energy second- or third-hand from ____ or other ____________ •Regardless, the energy is converted to the chemical bond energy of ____ ...
Bio 226: Cell and Molecular Biology
... Alternative: presenting another good plant/stressor response to study and why we should choose it over the ones already presented. ...
... Alternative: presenting another good plant/stressor response to study and why we should choose it over the ones already presented. ...
Application for the removal of "Antacids" from the WHO Model List of
... effects are probably not important in the treatment of peptic ulcers. With larger doses than those used for the antacid effect, magnesium hydroxide (magnesia) and magnesium oxide antacids produce a laxative effect. Antacids have been used for decades, mainly as OTC medicines, in the treatment of pat ...
... effects are probably not important in the treatment of peptic ulcers. With larger doses than those used for the antacid effect, magnesium hydroxide (magnesia) and magnesium oxide antacids produce a laxative effect. Antacids have been used for decades, mainly as OTC medicines, in the treatment of pat ...
Magnesium in biology

Magnesium is an essential element in biological systems. Magnesium occurs typically as the Mg2+ ion. It is an essential mineral nutrient (i.e., element) for life and is present in every cell type in every organism. For example, ATP (adenosine triphosphate), the main source of energy in cells, must be bound to a magnesium ion in order to be biologically active. What is called ATP is often actually Mg-ATP. As such, magnesium plays a role in the stability of all polyphosphate compounds in the cells, including those associated with the synthesis of DNA and RNA.Over 300 enzymes require the presence of magnesium ions for their catalytic action, including all enzymes utilizing or synthesizing ATP, or those that use other nucleotides to synthesize DNA and RNA.In plants, magnesium is necessary for synthesis of chlorophyll and photosynthesis.