Variation in Pattern of Rectus Sheath and Rectus Abdominis muscle
... yology is the study of muscles. More than 600 skeletal muscles make up the muscular system, and technically each one is an organ—it is composed of skeletal muscle tissue, connective tissue, and nervous tissue. Each muscle also has a particular function, such as moving a finger or blinking an eyelid. ...
... yology is the study of muscles. More than 600 skeletal muscles make up the muscular system, and technically each one is an organ—it is composed of skeletal muscle tissue, connective tissue, and nervous tissue. Each muscle also has a particular function, such as moving a finger or blinking an eyelid. ...
OMM-PPC Lecture 08 – TMJ Evaluation and Treatment – Block 7
... OMM-PPC Lecture 08 – TMJ Evaluation and Treatment – Block 7 TMJ anatomy – Capsule Synovial joint Differs from other joints: o Covered by fibrocartilage rather than hyaline cartilage o Joint cavity is divided into two separate compartments by an articular disc or meniscus More like 2 joints ins ...
... OMM-PPC Lecture 08 – TMJ Evaluation and Treatment – Block 7 TMJ anatomy – Capsule Synovial joint Differs from other joints: o Covered by fibrocartilage rather than hyaline cartilage o Joint cavity is divided into two separate compartments by an articular disc or meniscus More like 2 joints ins ...
World Journal of Surgical, Medical and Radiation
... the total blood loss but also because after a small blood vessel is divided in a few minutes it contracts and stops bleeding but may, when the patient rewarms after operation, dilate and start bleeding again. In a compartment resection, which includes the vastus lateralis as one tries to stay outsid ...
... the total blood loss but also because after a small blood vessel is divided in a few minutes it contracts and stops bleeding but may, when the patient rewarms after operation, dilate and start bleeding again. In a compartment resection, which includes the vastus lateralis as one tries to stay outsid ...
Transcripts/2_6 8
... in it. Those have their cell bodies in the trigeminal ganglion. The fibers initially leading into the trigeminal ganglion where the cell bodies are located most of those fibers are sensory so they are called central processes of the cell bodies. Peripheral processes from this single cell body, these ...
... in it. Those have their cell bodies in the trigeminal ganglion. The fibers initially leading into the trigeminal ganglion where the cell bodies are located most of those fibers are sensory so they are called central processes of the cell bodies. Peripheral processes from this single cell body, these ...
1. The gastroesophageal junction occurs at - NYCC SP-01
... 28. The deltoid muscle nerve supply comes from which nerve: a) axillary b)musculocutaneous c) Radial nerve d) ulnar nerve 29. The rotator cuff muscles are supplied by all of the following nerves EXCEPT: a) axillary b) subscapular c) suprascapular d)dorsal scapular 30. Which artery travels through th ...
... 28. The deltoid muscle nerve supply comes from which nerve: a) axillary b)musculocutaneous c) Radial nerve d) ulnar nerve 29. The rotator cuff muscles are supplied by all of the following nerves EXCEPT: a) axillary b) subscapular c) suprascapular d)dorsal scapular 30. Which artery travels through th ...
Review slides 14 - Zill Anatomy Web Pages
... 4. Accessory nerve (CNXI) 5. Vagus nerve (CNX) 6. Piriform recess (popcorn 2, lateral to laryngeal inlet) 7. A. Stylopharyngeus, B. Branchiomotor 8. Suboccipital nerve (dorsal ramus C1) 9. Vertebral artery 10. Pedicle of vertebra 11. Extend C1-Occipital bone, Rotate C1-C2 12. Obliquus Capitis Inferi ...
... 4. Accessory nerve (CNXI) 5. Vagus nerve (CNX) 6. Piriform recess (popcorn 2, lateral to laryngeal inlet) 7. A. Stylopharyngeus, B. Branchiomotor 8. Suboccipital nerve (dorsal ramus C1) 9. Vertebral artery 10. Pedicle of vertebra 11. Extend C1-Occipital bone, Rotate C1-C2 12. Obliquus Capitis Inferi ...
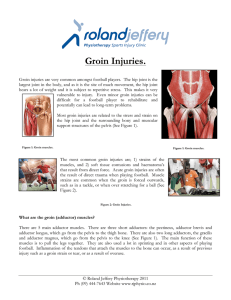
Groin Injuries. - Roland Jeffery Physiotherapy
... largest joint in the body, and as it is the site of much movement, the hip joint bears a lot of weight and it is subject to repetitive stress. This makes it very vulnerable to injury. Even minor groin injuries can be difficult for a football player to rehabilitate and potentially can lead to long-te ...
... largest joint in the body, and as it is the site of much movement, the hip joint bears a lot of weight and it is subject to repetitive stress. This makes it very vulnerable to injury. Even minor groin injuries can be difficult for a football player to rehabilitate and potentially can lead to long-te ...
TOTAL LARyNGECTOMy
... border will be the apron flap. The size of the stoma should approximate the size of the patient’s thumb to facilitate the use of a voice prosthesis, or be about 1.5 times the diameter of the trachea. The lower border of the stoma should be 2 cm above the upper border of the manubrium. It is importan ...
... border will be the apron flap. The size of the stoma should approximate the size of the patient’s thumb to facilitate the use of a voice prosthesis, or be about 1.5 times the diameter of the trachea. The lower border of the stoma should be 2 cm above the upper border of the manubrium. It is importan ...
Brachium and Cubital Fossa
... Don’t 1. Cut the biceps muscle just mobilize it Do 2. Follow the cords and tubes from known to unknown as you clean them Do 3. Remove the duplicated deep veins but save the unpaired superficial veins Do 4. Follow the radial nerve to the spiral groove and palpate it rather than cutting the triceps mu ...
... Don’t 1. Cut the biceps muscle just mobilize it Do 2. Follow the cords and tubes from known to unknown as you clean them Do 3. Remove the duplicated deep veins but save the unpaired superficial veins Do 4. Follow the radial nerve to the spiral groove and palpate it rather than cutting the triceps mu ...
Neck dissection using the fascial planes technique - Vula
... from the underlying vascular, glandular, neural, and muscular structures. Anatomical basis The basic understanding of fascial planes in the neck is that there are two distinct fascial layers, the superficial cervical fascia, and the deep cervical fascia (Figures 1A-C). Superficial cervical fascia Th ...
... from the underlying vascular, glandular, neural, and muscular structures. Anatomical basis The basic understanding of fascial planes in the neck is that there are two distinct fascial layers, the superficial cervical fascia, and the deep cervical fascia (Figures 1A-C). Superficial cervical fascia Th ...
The central compartment of the sole
... corresponding nerve. At the medial side of the fifth metatarsal bone the artery sinks deeply, on reaching the base of the 5th metatarsal bone the artery curve medially across the proximal ends of the second, third and fourth metatarsal bones to form the planter arch. ...
... corresponding nerve. At the medial side of the fifth metatarsal bone the artery sinks deeply, on reaching the base of the 5th metatarsal bone the artery curve medially across the proximal ends of the second, third and fourth metatarsal bones to form the planter arch. ...
Muscles of the face
... and supplies the buccinator muscle and the muscles of the upper lip and nostril . The mandibular branch emerges from the anterior border of the glang and supplies the muscles of the lower lip. The cervical branch emerges from the lower of the gland and passes forward in the neck below the mandib ...
... and supplies the buccinator muscle and the muscles of the upper lip and nostril . The mandibular branch emerges from the anterior border of the glang and supplies the muscles of the lower lip. The cervical branch emerges from the lower of the gland and passes forward in the neck below the mandib ...
5. upper extremity neuroanatomy
... named based on Brachial plexus their relationship to the axillary artery (as this The brachial plexus is formed from the five roots neurovascular bundle passes in its sheath into (anterior rami) of C5–T1. Occasionally contributions to the axilla). the brachial plexus come from C4 (prefixed plexus) o ...
... named based on Brachial plexus their relationship to the axillary artery (as this The brachial plexus is formed from the five roots neurovascular bundle passes in its sheath into (anterior rami) of C5–T1. Occasionally contributions to the axilla). the brachial plexus come from C4 (prefixed plexus) o ...
8. The Larynx - UCLA Linguistics
... vocal folds are abducted by moving the vocal folds apart. This is principally achieved by using the posterior cricoarytenoid muscles to separate the arytenoid cartilages. (b) Lengthening/Shortening vocal folds. The pitch of voiced sounds is largely controlled by varying the length of the vocal folds ...
... vocal folds are abducted by moving the vocal folds apart. This is principally achieved by using the posterior cricoarytenoid muscles to separate the arytenoid cartilages. (b) Lengthening/Shortening vocal folds. The pitch of voiced sounds is largely controlled by varying the length of the vocal folds ...
biceps tendonitis (long head of biceps tendonitis)
... As mentioned above, this condition often occurs as a result of overuse. It can be caused by excessive overhead motions such as throwing or swimming. With these types of activities, there is excessive wear on the tendon, but other factors may contribute to the problem. The long head of biceps tendon ...
... As mentioned above, this condition often occurs as a result of overuse. It can be caused by excessive overhead motions such as throwing or swimming. With these types of activities, there is excessive wear on the tendon, but other factors may contribute to the problem. The long head of biceps tendon ...
BNG-345: Lecture 13 The Spine Anatomy Test on Friday Learning
... fibrocartilaginous joint that allows slight movement between vertebrae ...
... fibrocartilaginous joint that allows slight movement between vertebrae ...
Muscle

Muscle is a soft tissue found in most animals. Muscle cells contain protein filaments of actin and myosin that slide past one another, producing a contraction that changes both the length and the shape of the cell. Muscles function to produce force and motion. They are primarily responsible for maintaining and changing posture, locomotion, as well as movement of internal organs, such as the contraction of the heart and the movement of food through the digestive system via peristalsis.Muscle tissues are derived from the mesodermal layer of embryonic germ cells in a process known as myogenesis. There are three types of muscle, skeletal or striated, cardiac, and smooth. Muscle action can be classified as being either voluntary or involuntary. Cardiac and smooth muscles contract without conscious thought and are termed involuntary, whereas the skeletal muscles contract upon command. Skeletal muscles in turn can be divided into fast and slow twitch fibers.Muscles are predominantly powered by the oxidation of fats and carbohydrates, but anaerobic chemical reactions are also used, particularly by fast twitch fibers. These chemical reactions produce adenosine triphosphate (ATP) molecules that are used to power the movement of the myosin heads.The term muscle is derived from the Latin musculus meaning ""little mouse"" perhaps because of the shape of certain muscles or because contracting muscles look like mice moving under the skin.