IP Addressing Power Point for
... • Subnets can be freely assigned within the organization • Internally, subnets are treated as separate networks • Subnet structure is not visible outside the organization COMP680E by M. Hamdi ...
... • Subnets can be freely assigned within the organization • Internally, subnets are treated as separate networks • Subnet structure is not visible outside the organization COMP680E by M. Hamdi ...
What are Active Networks
... Protection and resource management issues What’s beyond active networks … ...
... Protection and resource management issues What’s beyond active networks … ...
Lecture Topics
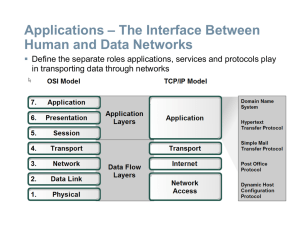
... Lecture 5 Outline - The OSI Model: The "Data-Link Layer" (Layer 2) and the "Network Layer" (Layer 3): Repeaters, Concentrators, Bridges, Switches, and Routers.) ...
... Lecture 5 Outline - The OSI Model: The "Data-Link Layer" (Layer 2) and the "Network Layer" (Layer 3): Repeaters, Concentrators, Bridges, Switches, and Routers.) ...
... to access WAN via wired connection. Mobile node access the outer network via home agent. Home agent creates a secure connection with MN so that packet monitoring will not work for it and the user data gets secure. By implanting advanced routing technique, MN can move from one network to another netw ...
Readme x4 1
... logout process. If they still have another open session of the browser, other people cannot login to the Nomadix gateway with different IP addresses. This issue only occurs when admin concurrency has been enabled. ...
... logout process. If they still have another open session of the browser, other people cannot login to the Nomadix gateway with different IP addresses. This issue only occurs when admin concurrency has been enabled. ...
WiSense Seminar #49 M. Ebada, Multipath Routing for Wireless
... • Adjustments made to Multipath Finding Protocol and Traffic Splitting Protocol resulted in significant savings in network power • Hybrid Routing Protocol combines the advantages of Source Routing Protocol and Diffusion Routing Protocol • The cut off value used in Hybrid Routing Protocol provides a ...
... • Adjustments made to Multipath Finding Protocol and Traffic Splitting Protocol resulted in significant savings in network power • Hybrid Routing Protocol combines the advantages of Source Routing Protocol and Diffusion Routing Protocol • The cut off value used in Hybrid Routing Protocol provides a ...
Network Layer
... fragment the datagram. If it cannot pass the datagram though any available physical network, it discards the datagram and sends and ICMP error message to the source host. If the value is 0, this means that whenever required the datagram can be fragmented according to the requirement of the physical ...
... fragment the datagram. If it cannot pass the datagram though any available physical network, it discards the datagram and sends and ICMP error message to the source host. If the value is 0, this means that whenever required the datagram can be fragmented according to the requirement of the physical ...
A Combined Routing+Queueing Approach to Improving
... way of reducing congestion, and consequently queueing delay, is to use QoS routing. In this method, packets are routed along the fastest and not necessarily the shortest path. Although attractive, QoS routing is computationally expensive to be implemented as a dynamic protocol but becomes much more ...
... way of reducing congestion, and consequently queueing delay, is to use QoS routing. In this method, packets are routed along the fastest and not necessarily the shortest path. Although attractive, QoS routing is computationally expensive to be implemented as a dynamic protocol but becomes much more ...
Chapter Questions Chapter 1 1. The network card, the monitor
... 1) Stored in ROM until they are sent out 2) Flows from RAM and the CPU, via the bus and expansion slots, to the interfaces 3) Flows from RAM to some form of storage device 4) After they are loaded, they are stored in RAM temporarily 5) Stored in RAM as long as the application is being used ...
... 1) Stored in ROM until they are sent out 2) Flows from RAM and the CPU, via the bus and expansion slots, to the interfaces 3) Flows from RAM to some form of storage device 4) After they are loaded, they are stored in RAM temporarily 5) Stored in RAM as long as the application is being used ...
Unit 3 - NIST NACOL
... It is suitable for small sized private owned networks such as personal network in home, school, and cyber cafe. Each workstation or computer connected in the network has unique address for its identification. When a message is to be sent from one computer to another computer in the network, the addr ...
... It is suitable for small sized private owned networks such as personal network in home, school, and cyber cafe. Each workstation or computer connected in the network has unique address for its identification. When a message is to be sent from one computer to another computer in the network, the addr ...
Introduction
... • No notion of a connection between users of peer protocol entities • CL service interface promises best effort delivery of data from one user to the other, data may or may not reach the peer user and may or may not be delivered in order sent • AGAIN NOTE that this says nothing about the implementat ...
... • No notion of a connection between users of peer protocol entities • CL service interface promises best effort delivery of data from one user to the other, data may or may not reach the peer user and may or may not be delivered in order sent • AGAIN NOTE that this says nothing about the implementat ...
Wireless Communication Systems
... TCP sends an acknowledgement only after receiving a packet If a sender receives several acknowledgements for the same packet, this is ...
... TCP sends an acknowledgement only after receiving a packet If a sender receives several acknowledgements for the same packet, this is ...
net-transport
... Rate control to extract max capacity from available SINR Power control for spatial reuse & energy savings – topology control TDMA scheduling, multi-channel use, encryption security … and many more ...
... Rate control to extract max capacity from available SINR Power control for spatial reuse & energy savings – topology control TDMA scheduling, multi-channel use, encryption security … and many more ...
Slide 1
... • Short for Media Access Control address, a hardware address that uniquely identifies each node of a network. In IEEE 802 networks, the Data Link Control (DLC) layer of the OSI Reference Model is divided into two sublayers: the Logical Link Control (LLC) layer and the Media Access Control (MAC) laye ...
... • Short for Media Access Control address, a hardware address that uniquely identifies each node of a network. In IEEE 802 networks, the Data Link Control (DLC) layer of the OSI Reference Model is divided into two sublayers: the Logical Link Control (LLC) layer and the Media Access Control (MAC) laye ...
Introduction of IMS for 3G Voice Services and Migration
... – provide netwok value added services using the IMS. – Service Enabler Network(SEN) concept. ...
... – provide netwok value added services using the IMS. – Service Enabler Network(SEN) concept. ...
HWBA54G Manual
... The Hi-Speed 54G Wireless AP/Bridge utilizes the highest wireless security standards (WPA) to protect your network from outside intruders. The unique multi-function feature of the HWBA54G puts three solutions into one compact unit, saving you time and money. You may setup your HWBA54G as a Wireless ...
... The Hi-Speed 54G Wireless AP/Bridge utilizes the highest wireless security standards (WPA) to protect your network from outside intruders. The unique multi-function feature of the HWBA54G puts three solutions into one compact unit, saving you time and money. You may setup your HWBA54G as a Wireless ...
Application Layer Functionality and Protocols
... Compare and contrast client server networking with peer-to-peer networking and peer-to-peer applications ...
... Compare and contrast client server networking with peer-to-peer networking and peer-to-peer applications ...
DHCP and NAT
... allocate addresses to devices in local network without notifying outside world can change ISP without changing addresses of devices in local network devices inside local net not explicitly addressable, visible by outside world (a security plus). widespread use Private IP addresses: ...
... allocate addresses to devices in local network without notifying outside world can change ISP without changing addresses of devices in local network devices inside local net not explicitly addressable, visible by outside world (a security plus). widespread use Private IP addresses: ...
CCNA2 3.1-06 Routed & Routing Protocols
... • The process that a router uses to forward packets toward the destination network. • A router makes this decision based on the destination IP address • If dynamic routing is used, routers have to learn routes from other routers. • If static routing is used, the administrator configures this informa ...
... • The process that a router uses to forward packets toward the destination network. • A router makes this decision based on the destination IP address • If dynamic routing is used, routers have to learn routes from other routers. • If static routing is used, the administrator configures this informa ...
20088-2 CCNA3 3.1-01 Questions Scaling IP Addresses
... An additional subnet is required for a new Ethernet link between Router1 and Router2 as shown in the diagram. Which of the following subnet addresses can be configured in this network to provide a maximum of 14 useable addresses for this link while wasting the fewest addresses? ...
... An additional subnet is required for a new Ethernet link between Router1 and Router2 as shown in the diagram. Which of the following subnet addresses can be configured in this network to provide a maximum of 14 useable addresses for this link while wasting the fewest addresses? ...
cdma450 Core Network - CDMA Development Group
... accesses. It may support 802.1x and/or 802.11i. The topology of the WLAN is outside the scope of a 3GPP2 specification. ...
... accesses. It may support 802.1x and/or 802.11i. The topology of the WLAN is outside the scope of a 3GPP2 specification. ...
Wake-on-LAN
Wake-on-LAN (WoL) is an Ethernet or Token ring computer networking standard that allows a computer to be turned on or awakened by a network message.The message is usually sent by a program executed on another computer on the same local area network. It is also possible to initiate the message from another network by using subnet directed broadcasts or a WOL gateway service. Equivalent terms include wake on WAN, remote wake-up, power on by LAN, power up by LAN, resume by LAN, resume on LAN and wake up on LAN. In case the computer being awakened is communicating via Wi-Fi, a supplementary standard called Wake on Wireless LAN (WoWLAN) must be employed.The WOL and WoWLAN standards are often supplemented by vendors to provide protocol-transparent on-demand services, for example in the Apple Bonjour wake-on-demand (Sleep Proxy) feature.