Switches
... Higher-layer switches may also be called routing switches or application switches ...
... Higher-layer switches may also be called routing switches or application switches ...
When Failure is NOT an Option
... ERPS (Ethernet Ring Protection Switching) ITU-T G.8032/Y.1344 ERPS (Ethernet Ring Protection Switching) was introduced in 2008 by the International Telecommunication Union (ITU). ERPS defines the automatic protection switching (APS) protocol and protection switching mechanisms for ETH layer Ethernet ...
... ERPS (Ethernet Ring Protection Switching) ITU-T G.8032/Y.1344 ERPS (Ethernet Ring Protection Switching) was introduced in 2008 by the International Telecommunication Union (ITU). ERPS defines the automatic protection switching (APS) protocol and protection switching mechanisms for ETH layer Ethernet ...
ppt
... n nodes, k member infected, Anybody can infect anyone else with equal probability. What is the probability Pinfect(k, n) that a particular uninfected member is infected in a round if k are already infected? ...
... n nodes, k member infected, Anybody can infect anyone else with equal probability. What is the probability Pinfect(k, n) that a particular uninfected member is infected in a round if k are already infected? ...
Lecture 1 to 5 - Spartans Fall-14
... 1984, StarLAN showed the potential of simple unshielded twisted pair by using Cat3 cable—the same simple cable used for telephone systems. This led to the development of 10BASE-T and its successors 100BASE-TX and 1000BASE-T, supporting speeds of 10, 100 and 1000 Mbit/s respectively. Often the higher ...
... 1984, StarLAN showed the potential of simple unshielded twisted pair by using Cat3 cable—the same simple cable used for telephone systems. This led to the development of 10BASE-T and its successors 100BASE-TX and 1000BASE-T, supporting speeds of 10, 100 and 1000 Mbit/s respectively. Often the higher ...
An integrated approach based on cross
... with the segment. For example, the MAC layer can use segments of very small size to transport a small number of control information bits. In fact, even a single information bit can be transported with little overhead. The segment need not contain any extensive training sequences because of the natu ...
... with the segment. For example, the MAC layer can use segments of very small size to transport a small number of control information bits. In fact, even a single information bit can be transported with little overhead. The segment need not contain any extensive training sequences because of the natu ...
Circuits and Pathways Presentation from May 2013 meeting
... Approved Fire Alarm Pathway For decades, smart systems have been sold as an improvement over conventional fire alarm systems. AHJs can see the obvious improvement that communication with each device provides. Yet, minimum Code requirements do not require operational capability of each device to be ...
... Approved Fire Alarm Pathway For decades, smart systems have been sold as an improvement over conventional fire alarm systems. AHJs can see the obvious improvement that communication with each device provides. Yet, minimum Code requirements do not require operational capability of each device to be ...
Distance Vector Multicast Routing Protocol
... • When a multicast datagram is received at the router – Look up the source network in the routing table – RPF check – Forwarding cache entry created ...
... • When a multicast datagram is received at the router – Look up the source network in the routing table – RPF check – Forwarding cache entry created ...
Lecture note 13
... If these access points use the same frequency channel, when a mobile node move from one cell into another cell, its used frequency channel need not be changed. However, it packet transmission or reception may be interfered by neighboring access points when it is at the cell ...
... If these access points use the same frequency channel, when a mobile node move from one cell into another cell, its used frequency channel need not be changed. However, it packet transmission or reception may be interfered by neighboring access points when it is at the cell ...
TCP/IP Discussion Related to Essay Question on Final
... With smask, the computer can determine which IP addresses are part of its subnet ...
... With smask, the computer can determine which IP addresses are part of its subnet ...
Helvetica is a Good Font
... • The learned model can predict normal, anomaly, or known intrusion subclass • Experiments were performed on increasing subsets of known intrusion subclasses in the training data (simulates identified intrusions over time). ...
... • The learned model can predict normal, anomaly, or known intrusion subclass • Experiments were performed on increasing subsets of known intrusion subclasses in the training data (simulates identified intrusions over time). ...
Introduction
... Covered a “ton” of material! q Internet overview q what’s a protocol? q network edge, core, access network v packet-switching versus circuit-switching v Internet structure q performance: loss, delay, throughput q layering, service models q history ...
... Covered a “ton” of material! q Internet overview q what’s a protocol? q network edge, core, access network v packet-switching versus circuit-switching v Internet structure q performance: loss, delay, throughput q layering, service models q history ...
International Telecommunication Union
... OA&M for mobile networks (Access / Core / Control) Converged Management of fixed and mobile networks Self-Organizing Networks (SON) Objective: decrease OPEX/CAPEX related to network configuration, ...
... OA&M for mobile networks (Access / Core / Control) Converged Management of fixed and mobile networks Self-Organizing Networks (SON) Objective: decrease OPEX/CAPEX related to network configuration, ...
Tier 1 ISP
... store and forward: entire packet must arrive at router before it can be transmitted on next link delay = 3L/R (assuming zero propagation delay) ...
... store and forward: entire packet must arrive at router before it can be transmitted on next link delay = 3L/R (assuming zero propagation delay) ...
CMPT 371: Chapter 1 - Simon Fraser University
... dtrans = transmission delay = L/R, significant for low-speed links dprop = propagation delay a few microsecs to hundreds of msecs ...
... dtrans = transmission delay = L/R, significant for low-speed links dprop = propagation delay a few microsecs to hundreds of msecs ...
4th Edition: Chapter 1
... If you use these slides (e.g., in a class) in substantially unaltered form, that you mention their source (after all, we’d like people to use our book!) If you post any slides in substantially unaltered form on a www site, that you note that they are adapted from (or perhaps identical to) our sl ...
... If you use these slides (e.g., in a class) in substantially unaltered form, that you mention their source (after all, we’d like people to use our book!) If you post any slides in substantially unaltered form on a www site, that you note that they are adapted from (or perhaps identical to) our sl ...
NAME: Computer Science 461 Midterm Exam March 30, 2009
... client sends a very small amount of data using the send() function, and the server receives the data with a recv() call. Each of the following scenarios shows a different order in which the socket calls are called on both the client and the server. Assume all system calls are blocking, and there may ...
... client sends a very small amount of data using the send() function, and the server receives the data with a recv() call. Each of the following scenarios shows a different order in which the socket calls are called on both the client and the server. Assume all system calls are blocking, and there may ...
802.1Qau Flow ID choices
... The Regions choose which NNI (shown by a heavy red line) is used for each service. Each Node in the Buffer Network, whether real or virtual, must exist, so that data can be reliably delivered from NNI to NNI. ...
... The Regions choose which NNI (shown by a heavy red line) is used for each service. Each Node in the Buffer Network, whether real or virtual, must exist, so that data can be reliably delivered from NNI to NNI. ...
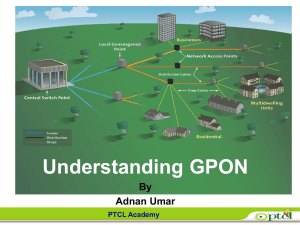
GPON 1
... First Passive optical network standard. Used primarily for business applications was based on ATM (Asynchronous Transfer Mode) Initial offering 155.52 Mbps Downstream, 155.52 Mbps upstream. ...
... First Passive optical network standard. Used primarily for business applications was based on ATM (Asynchronous Transfer Mode) Initial offering 155.52 Mbps Downstream, 155.52 Mbps upstream. ...
Module 4 Data Link Layer
... • first widely used LAN technology! • simpler, cheaper than token LANs and ATM! • kept up with speed race: 10 Mbps – 10 Gbps ! Metcalfe s Ethernet! ...
... • first widely used LAN technology! • simpler, cheaper than token LANs and ATM! • kept up with speed race: 10 Mbps – 10 Gbps ! Metcalfe s Ethernet! ...
CQ24604607
... input to the modulator is the data signal from PRBS generator. This generator generates the logical signal and this logical signal is converted into the electrical signal by the NRZ driver as shown in the diagram. So this electrical signal is then fed into the electrical input if the modulator. The ...
... input to the modulator is the data signal from PRBS generator. This generator generates the logical signal and this logical signal is converted into the electrical signal by the NRZ driver as shown in the diagram. So this electrical signal is then fed into the electrical input if the modulator. The ...
What Is the Purpose of the Components Required for Successful
... Communications technologies include blogs, chat rooms, e-mail, fax, FTP, instant messaging, newsgroups, RSS, video conferencing, VoIP, Web, Web folders, and wikis. Users can send and receive wireless messages to and from smart phones, cell phones, handheld game consoles, and other mobile devices usi ...
... Communications technologies include blogs, chat rooms, e-mail, fax, FTP, instant messaging, newsgroups, RSS, video conferencing, VoIP, Web, Web folders, and wikis. Users can send and receive wireless messages to and from smart phones, cell phones, handheld game consoles, and other mobile devices usi ...
Week_One_ppt - Computing Sciences
... Bridges is a device for connecting two segments of a network and transmitting packets between them. Both segments must use identical protocols to communicate. Their purpose is to filter, send, or flood any incoming frame, based on the MAC address of that particular frame. Broadcast domain is a group ...
... Bridges is a device for connecting two segments of a network and transmitting packets between them. Both segments must use identical protocols to communicate. Their purpose is to filter, send, or flood any incoming frame, based on the MAC address of that particular frame. Broadcast domain is a group ...