Interference-Aware Node Disjoint Multi-Path Dynamic Source
... 5] multi-path routing protocols such as AOMDV [6], SR-MPOLSR [7], MP-OLSR [8] were purposed. These protocols did not address the problem of interference from source to destination. Hence interference plays an important role for the network performance such as data loss, conflict, retransmission of p ...
... 5] multi-path routing protocols such as AOMDV [6], SR-MPOLSR [7], MP-OLSR [8] were purposed. These protocols did not address the problem of interference from source to destination. Hence interference plays an important role for the network performance such as data loss, conflict, retransmission of p ...
Document
... The intelligent network concept: intelligence is taken out of exchanges and placed in computer nodes that are distributed throughout the network. Intelligence => access to various databases This provides the network operator with the means to develop and control services more efficiently. New capabi ...
... The intelligent network concept: intelligence is taken out of exchanges and placed in computer nodes that are distributed throughout the network. Intelligence => access to various databases This provides the network operator with the means to develop and control services more efficiently. New capabi ...
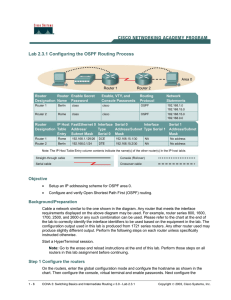
Lab 2.3.1 Configuring the OSPF Routing Process Objective
... FastEthernet 0/1 (FA0/1) Serial 0/0 (S0/0) Serial 0/1 (S0/1) (FA0/0) In order to find out exactly how the router is configured, look at the interfaces. This will identify what type and how many interfaces the router has. There is no way to effectively list all of the combinations of configurations f ...
... FastEthernet 0/1 (FA0/1) Serial 0/0 (S0/0) Serial 0/1 (S0/1) (FA0/0) In order to find out exactly how the router is configured, look at the interfaces. This will identify what type and how many interfaces the router has. There is no way to effectively list all of the combinations of configurations f ...
High field breakdown characteristics of carbon nanotube
... reliability and breakdown behavior of CN-TFTs as well. The variation in the breakdown behavior for a given TFT geometry can lead to instability and/or unreliability during the operation of CN-TFTs. Thus, it is very important to understand how the geometrical parameters affect the high field operatio ...
... reliability and breakdown behavior of CN-TFTs as well. The variation in the breakdown behavior for a given TFT geometry can lead to instability and/or unreliability during the operation of CN-TFTs. Thus, it is very important to understand how the geometrical parameters affect the high field operatio ...
Part2.3Internetworki..
... Although universal service is highly desirable, incompatibilities among network hardware and physical addressing prevent an organization from building a bridged network that includes arbitrary technologies ...
... Although universal service is highly desirable, incompatibilities among network hardware and physical addressing prevent an organization from building a bridged network that includes arbitrary technologies ...
yun-MPLS - KEMT FEI TUKE
... MPLS Advantages Improves packet-forwarding performance in the network Supports QoS and CoS for service ...
... MPLS Advantages Improves packet-forwarding performance in the network Supports QoS and CoS for service ...
Powerpoint - Purdue University
... Call, e.g., admission control Packet, e.g., scheduling, packet discard Performance concerns become on-line High speed = propagation delay much higher than packet transmission time Number of packets in the “pipe” is high Open loop Router-based Reservation Backpressure Sonia Fahmy ...
... Call, e.g., admission control Packet, e.g., scheduling, packet discard Performance concerns become on-line High speed = propagation delay much higher than packet transmission time Number of packets in the “pipe” is high Open loop Router-based Reservation Backpressure Sonia Fahmy ...
njit-etd2005-146 - New Jersey Institute of Technology
... The scalability problem of routing algorithms in Mobile Ad-hoc networks (MANET) has conventionally been addressed by introducing hierarchical architectures, clusters, and neighborhood zones. In all of these approaches, some nodes are assigned different routing related roles than others. Examples inc ...
... The scalability problem of routing algorithms in Mobile Ad-hoc networks (MANET) has conventionally been addressed by introducing hierarchical architectures, clusters, and neighborhood zones. In all of these approaches, some nodes are assigned different routing related roles than others. Examples inc ...
15245Chapter_5_V6.01
... encapsulate datagram into frame, adding header, trailer channel access if shared medium “MAC” addresses used in frame headers to identify source, dest • different from IP address! ...
... encapsulate datagram into frame, adding header, trailer channel access if shared medium “MAC” addresses used in frame headers to identify source, dest • different from IP address! ...
about this guide - CVS Caremark Online Applications
... Please feel free to call Caremark to discuss connectivity. A telecommunications analyst is available to assist you Monday through Friday, 6:00 am to 4:00 PM, ...
... Please feel free to call Caremark to discuss connectivity. A telecommunications analyst is available to assist you Monday through Friday, 6:00 am to 4:00 PM, ...
NetLayer
... storage. • To make a request of the data link layer, it needs the physical (MAC - Media Access Control) address of the gateway. • The same mapping would be needed if the target is on the same LAN COMT 625 ...
... storage. • To make a request of the data link layer, it needs the physical (MAC - Media Access Control) address of the gateway. • The same mapping would be needed if the target is on the same LAN COMT 625 ...
Chapter 1 FAILURE LOCATION IN WDM NETWORKS
... as the manifestation of the fault. For example, if the ventilator in a laser stops, and if the temperature increases and overpasses an accepted temperature limit, the fault is the stopped ventilator and the failure is the temperature of the laser, which is too high. Because both terms are closely re ...
... as the manifestation of the fault. For example, if the ventilator in a laser stops, and if the temperature increases and overpasses an accepted temperature limit, the fault is the stopped ventilator and the failure is the temperature of the laser, which is too high. Because both terms are closely re ...
MidoNet Troubleshooting Guide
... This change applies immediately and does not require a Cluster restart. ...
... This change applies immediately and does not require a Cluster restart. ...
NetFlow's limitations
... having to administer traffic reporting through the device: 1. Access to device administration is limited in most enterprises. 2. The targeting capabilities of NetFlow/sFlow are limited; NetFlow, for example, allows you to specify only two target collectors. By making a distributed probe the target, ...
... having to administer traffic reporting through the device: 1. Access to device administration is limited in most enterprises. 2. The targeting capabilities of NetFlow/sFlow are limited; NetFlow, for example, allows you to specify only two target collectors. By making a distributed probe the target, ...
Lecture 1: Course Introduction and Overview
... – 90-92: NSFNET moves to 45 Mbps, 16 mid-level networks – 94: NSF backbone dismantled, multiple private backbones; Introduction of Commercial Internet ...
... – 90-92: NSFNET moves to 45 Mbps, 16 mid-level networks – 94: NSF backbone dismantled, multiple private backbones; Introduction of Commercial Internet ...
p2p_3
... nodeId = pastryInit(Credentials, Application)make the local node join/create a Pastry network. Credentials are used for authorization. An object used for callbacks is passed through the Application parameter route(msg, key): routes a message to the live node D with nodeId numerically closest to the ...
... nodeId = pastryInit(Credentials, Application)make the local node join/create a Pastry network. Credentials are used for authorization. An object used for callbacks is passed through the Application parameter route(msg, key): routes a message to the live node D with nodeId numerically closest to the ...
H04L - Cooperative Patent Classification
... of TFCI explicit signalling (H04L 1/0046, H04L 27/0012 and H04L 25/0262 take precedence)} {by using forward error control (H04L 1/0618 takes precedence; coding, decoding or code conversion, for error detection or correction H03M 13/00)} . {Arrangements at the transmitter end} . . {Encoding specially ...
... of TFCI explicit signalling (H04L 1/0046, H04L 27/0012 and H04L 25/0262 take precedence)} {by using forward error control (H04L 1/0618 takes precedence; coding, decoding or code conversion, for error detection or correction H03M 13/00)} . {Arrangements at the transmitter end} . . {Encoding specially ...
Managing the Mobility of a Mobile Sensor Network Using Network
... formulate network dynamics involves a centralized controller with knowledge of each device’s position and the ability to communicate its directives to each mobile device. In practice, however, such a formulation ...
... formulate network dynamics involves a centralized controller with knowledge of each device’s position and the ability to communicate its directives to each mobile device. In practice, however, such a formulation ...
COS 420 day 16
... to packet forwarding Uses array lookup instead of destination address lookup Often associated with Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM) ...
... to packet forwarding Uses array lookup instead of destination address lookup Often associated with Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM) ...
2 Need for coexistence - IEEE 802 LAN/MAN Standards Committee
... networks do not cause unacceptable interference to one another. Since the devices in these networks are unlicensed, like the 2.4 GHz ISM band,,none of the network operators own the spectrum and they cannot prohibit use by any network owned or operated by other operators. In this case, the network op ...
... networks do not cause unacceptable interference to one another. Since the devices in these networks are unlicensed, like the 2.4 GHz ISM band,,none of the network operators own the spectrum and they cannot prohibit use by any network owned or operated by other operators. In this case, the network op ...
Inter-Process Communication Networks CS 217 • Mechanism by which two processes exchange
... • Mechanism by which two processes exchange information and coordinate activities Computer ...
... • Mechanism by which two processes exchange information and coordinate activities Computer ...
A Platform for Unobtrusive Measurements on PlanetLab Rob Sherwood Neil Spring Abstract
... Figure 1: Sidecar is a platform for unobtrusive measurements that provides an event-driven interface and connecInternet measurement is key to optimizing performance, tion tracking to higher-level tools, e.g., artrat, sideping. building overlay topologies, developing improved transport protocols, und ...
... Figure 1: Sidecar is a platform for unobtrusive measurements that provides an event-driven interface and connecInternet measurement is key to optimizing performance, tion tracking to higher-level tools, e.g., artrat, sideping. building overlay topologies, developing improved transport protocols, und ...