PH19510 Lecture 12
... over telephone line Originally acoustic coupling Must be in audio (400Hz-4Khz) range Encode 1 & 0 as tones Nowadays up to 56kbps over conventional phone system ...
... over telephone line Originally acoustic coupling Must be in audio (400Hz-4Khz) range Encode 1 & 0 as tones Nowadays up to 56kbps over conventional phone system ...
NET331_Ch1
... A network is a set of devices (often referred to as nodes) connected by communication links. A node can be a computer, printer, or any other device capable of sending and/or receiving data generated by other nodes on the network. ...
... A network is a set of devices (often referred to as nodes) connected by communication links. A node can be a computer, printer, or any other device capable of sending and/or receiving data generated by other nodes on the network. ...
Local-area network
... been used to administer LANs – Ring topology A configuration that connects all nodes in a closed loop on which messages travel in one direction – Star topology A configuration that centers around one node to which all others are connected and through which all messages are sent – Bus topology All no ...
... been used to administer LANs – Ring topology A configuration that connects all nodes in a closed loop on which messages travel in one direction – Star topology A configuration that centers around one node to which all others are connected and through which all messages are sent – Bus topology All no ...
Networks
... The connections between computers in a network are either made using physical wires/cables or they can be wireless Networks can be classified into: • Local-Area network (LAN): A network connecting a small number of computers + devices in a close geographic area • Wide-Area network (WAN): A network c ...
... The connections between computers in a network are either made using physical wires/cables or they can be wireless Networks can be classified into: • Local-Area network (LAN): A network connecting a small number of computers + devices in a close geographic area • Wide-Area network (WAN): A network c ...
The Internet is a global communication network which acts as a
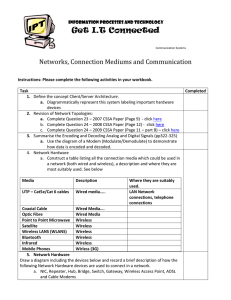
... 3. Summarise the Encoding and Decoding Analog and Digital Signals (pp322-325) a. Use the diagram of a Modem (Modulate/Demodulate) to demonstrate how data is encoded and decoded. 4. Network Hardware a. Construct a table listing all the connection media which could be used in a network (both wired and ...
... 3. Summarise the Encoding and Decoding Analog and Digital Signals (pp322-325) a. Use the diagram of a Modem (Modulate/Demodulate) to demonstrate how data is encoded and decoded. 4. Network Hardware a. Construct a table listing all the connection media which could be used in a network (both wired and ...
ppt - CSE
... Install, test and commission voice and data communications networks in medium to large enterprises using Next Generation Networks (NGN) technologies Cover local area networks (LAN) and wide area networks (WAN), IP based protocol networks, 3G/4G cellular mobile networks, microwave systems, wireless a ...
... Install, test and commission voice and data communications networks in medium to large enterprises using Next Generation Networks (NGN) technologies Cover local area networks (LAN) and wide area networks (WAN), IP based protocol networks, 3G/4G cellular mobile networks, microwave systems, wireless a ...
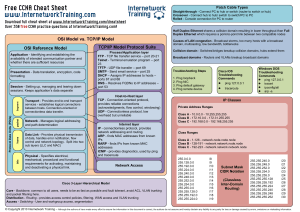
CCNA cheat sheet - Internetwork Training
... Cisco 3-Layer Hierarchical Model Core - Backbone, common to all users, needs to be as fast as possible and fault tolerant, avoid ACL, VLAN trunking and packet filtering here. Distribution - Routing - provides access control policies, filtering, WAN access and VLAN trunking Access - Switching - User ...
... Cisco 3-Layer Hierarchical Model Core - Backbone, common to all users, needs to be as fast as possible and fault tolerant, avoid ACL, VLAN trunking and packet filtering here. Distribution - Routing - provides access control policies, filtering, WAN access and VLAN trunking Access - Switching - User ...
Network interface cards (NIC)
... • A type of communications where a channel or circuit is established for the duration of the call. • That circuit is dedicated to the two end nodes using it. • 1950’s/60’s the networks were analog, circuit switched networks. • Telephony companies invested millions/billions of dollars in equipment ov ...
... • A type of communications where a channel or circuit is established for the duration of the call. • That circuit is dedicated to the two end nodes using it. • 1950’s/60’s the networks were analog, circuit switched networks. • Telephony companies invested millions/billions of dollars in equipment ov ...
Chapter1R_v2
... To interconnect local workstations To access local shared resources (printers, storage, servers) ...
... To interconnect local workstations To access local shared resources (printers, storage, servers) ...
Pres 1 Protocol Architectures
... • Logic needed to support various applications • Each type of application (file transfer, remote access) requires different software on this layer ...
... • Logic needed to support various applications • Each type of application (file transfer, remote access) requires different software on this layer ...
Chapter07 - College of Business, UNR
... Switches receive data and forward it to the correct device ...
... Switches receive data and forward it to the correct device ...
44_ExploringNetworkProperties
... Define client and protocol and explain the purpose of each. Explain the purpose of the NetBEUI, IPX/SPX, and TCP/IP protocols. Change the client, services, and protocol of a local area network connection in a Windows XP Pro computer. ...
... Define client and protocol and explain the purpose of each. Explain the purpose of the NetBEUI, IPX/SPX, and TCP/IP protocols. Change the client, services, and protocol of a local area network connection in a Windows XP Pro computer. ...
Class_3_-_Subarea_V
... – Ring Network is a decentralized parallel network in which each node is connected to the node on either side of it. A failure in one node will be dealt with by re-routing information elsewhere around the ring. ...
... – Ring Network is a decentralized parallel network in which each node is connected to the node on either side of it. A failure in one node will be dealt with by re-routing information elsewhere around the ring. ...
Networking | computer Network | TCP/IP
... • Traffic data rate, pattern (bursty or constant bit rate), target (multipoint or single destination, mobile or fixed) • Delay and loss sensitivity • Other application-support services • Overlays, Active Networks, Data-oriented, … ...
... • Traffic data rate, pattern (bursty or constant bit rate), target (multipoint or single destination, mobile or fixed) • Delay and loss sensitivity • Other application-support services • Overlays, Active Networks, Data-oriented, … ...
Chapter 8 Slides
... • Widely used interior protocol to TCP/IP networks • Computes a route through the network that incurs the least cost • User can configure the cost as a function of: -delay -data rate -cost ...
... • Widely used interior protocol to TCP/IP networks • Computes a route through the network that incurs the least cost • User can configure the cost as a function of: -delay -data rate -cost ...