R1L5 Soil Composition - School Garden Project
... do two other 10 minute rotations depending on what you’re wanting to focus on. The soil bingo game is really great for younger students (K-4) but I would cut it out for older students (5-8). 2) You could also make the WAMO explanation another rotation for short sessions, skipping a big group intro a ...
... do two other 10 minute rotations depending on what you’re wanting to focus on. The soil bingo game is really great for younger students (K-4) but I would cut it out for older students (5-8). 2) You could also make the WAMO explanation another rotation for short sessions, skipping a big group intro a ...
Growing Garlic - University of Minnesota Extension
... Garlic does not compete well against weeds. Use of mulch will help control weeds. Frequent, shallow cultivation will kill weeds before they become a problem. The roots of garlic are very close to the surface of the soil, so it is important not to cultivate too deeply. Cultivate just deeply enough t ...
... Garlic does not compete well against weeds. Use of mulch will help control weeds. Frequent, shallow cultivation will kill weeds before they become a problem. The roots of garlic are very close to the surface of the soil, so it is important not to cultivate too deeply. Cultivate just deeply enough t ...
Soils
... found in the soil. These vary in amount depending on the type of soil. The amounts of sand, silt, and clay also determine the soils ability to hold water and provide nutrients. ...
... found in the soil. These vary in amount depending on the type of soil. The amounts of sand, silt, and clay also determine the soils ability to hold water and provide nutrients. ...
Types of measuring soil moisture
... matter content and many other factors it addition to moisture content. Therefore all systems need to be calibrated and readings evaluated in order to be helpful in irrigation scheduling. Used in conjunction with a scheduling program these systems can be an important component to efficient water use ...
... matter content and many other factors it addition to moisture content. Therefore all systems need to be calibrated and readings evaluated in order to be helpful in irrigation scheduling. Used in conjunction with a scheduling program these systems can be an important component to efficient water use ...
CHAPTER 9 Weathering and Formation of Soil
... Weathering is the process that changes solid rock into sediments. Sediments were described in the Rocks chapter. With weathering, rock is disintegrated. It breaks into pieces. Once these sediments are separated from the rocks, erosion is the process that moves the sediments. Erosion is the next chap ...
... Weathering is the process that changes solid rock into sediments. Sediments were described in the Rocks chapter. With weathering, rock is disintegrated. It breaks into pieces. Once these sediments are separated from the rocks, erosion is the process that moves the sediments. Erosion is the next chap ...
Kempen_3D kartering SOM_extabstract - Wageningen UR E
... horizons and the properties of soil horizons. Hence, soil type maps can be considered discrete, threedimensional models of soil properties. When such maps are available, then these might very well be used for three-dimensional mapping of soil properties. Soil horizons then act as carriers of soil pr ...
... horizons and the properties of soil horizons. Hence, soil type maps can be considered discrete, threedimensional models of soil properties. When such maps are available, then these might very well be used for three-dimensional mapping of soil properties. Soil horizons then act as carriers of soil pr ...
NH_4e_CRS_Ch08
... b) Construct buildings on a compacted fill layer c) Installation of injection wells d) Restoration of drained organic soils or collapsed soils e) Stop all mining ...
... b) Construct buildings on a compacted fill layer c) Installation of injection wells d) Restoration of drained organic soils or collapsed soils e) Stop all mining ...
Good Fruit Grower, April 2016
... Although the information provided by SoilWeb isn’t a substitute for a soil test, the program can deliver preliminary data in the form of geographic, system-positioned soil pro㊱묩les in an instant. Originally, it was a standalone mobile app. “Mobile operating systems were changing so quickly we had tr ...
... Although the information provided by SoilWeb isn’t a substitute for a soil test, the program can deliver preliminary data in the form of geographic, system-positioned soil pro㊱묩les in an instant. Originally, it was a standalone mobile app. “Mobile operating systems were changing so quickly we had tr ...
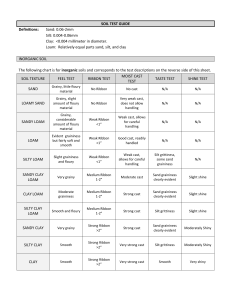
SOIL TEST GUIDE Definitions: Sand
... Ribbon Test: Roll a handful of moist soil into a 1/8“ cylinder and squeeze it out between the thumb and forefinger to make the longest ribbon possible. When it breaks off, measure the length and compare to the above chart. Moist Cast Test: Squeeze moist soil in your hand and attempt to form a ball. ...
... Ribbon Test: Roll a handful of moist soil into a 1/8“ cylinder and squeeze it out between the thumb and forefinger to make the longest ribbon possible. When it breaks off, measure the length and compare to the above chart. Moist Cast Test: Squeeze moist soil in your hand and attempt to form a ball. ...
746.29 kb Phosphorus Management Northern Region Fact
... subsequent rainfall allowed a good seedbed to ensure crop establishment. as often occurs in other regions with different soils. In some locations in the northern grains region, benefits are still being recorded six cropping seasons after deep application. These excellent residual effects mean P can ...
... subsequent rainfall allowed a good seedbed to ensure crop establishment. as often occurs in other regions with different soils. In some locations in the northern grains region, benefits are still being recorded six cropping seasons after deep application. These excellent residual effects mean P can ...
pertanian dan lingkungan – prinsip dasar
... • Once applied may decompose in place or be carried by wind and water – Breakdown products can also be toxic – Eventually fully decompose but can take a very long time ...
... • Once applied may decompose in place or be carried by wind and water – Breakdown products can also be toxic – Eventually fully decompose but can take a very long time ...
Revisiting agro-ecological sub-regions of India – a
... similar in soil bioclimate and length of moisture availability period related to crop production, are known as agro-ecological regions (AERs)7. FAO’s exercises concentrated on creation of broad crop feasibility zones based on length of moisture availability period superimposed on FAO/UNESCO global s ...
... similar in soil bioclimate and length of moisture availability period related to crop production, are known as agro-ecological regions (AERs)7. FAO’s exercises concentrated on creation of broad crop feasibility zones based on length of moisture availability period superimposed on FAO/UNESCO global s ...
Weathering, Erosion, and Deposition: Trans Pecos/Chihuahuan
... The South Texas Plains is largely covered with materials carried out from the erosion of the Edwards Plateau. The area adjacent to the Balcones Escarpment, is characterized by black soils that extend from Austin to San Antonio and westward. The area closer to the coastal comprises the low, flat coun ...
... The South Texas Plains is largely covered with materials carried out from the erosion of the Edwards Plateau. The area adjacent to the Balcones Escarpment, is characterized by black soils that extend from Austin to San Antonio and westward. The area closer to the coastal comprises the low, flat coun ...
Permafrost Engineering
... • A. Suprapermafrost - Water above the permafrost (in the active layer). In the Arctic region, the active layer is 1~6 feet. Very little water accumulates in this layer, and what does is often contaminated and is frozen in winter. • B. Intrapermafrost- Water within the permafrost layer- In order to ...
... • A. Suprapermafrost - Water above the permafrost (in the active layer). In the Arctic region, the active layer is 1~6 feet. Very little water accumulates in this layer, and what does is often contaminated and is frozen in winter. • B. Intrapermafrost- Water within the permafrost layer- In order to ...
Weathering and Soil Formation
... Sand from lower right towards the upper left portion of the triangle . The intersection of the three sizes on the triangle give the texture class. For instance, if you have a soil with 20% clay, 60% silt, and 20% sand it falls in the "silt ...
... Sand from lower right towards the upper left portion of the triangle . The intersection of the three sizes on the triangle give the texture class. For instance, if you have a soil with 20% clay, 60% silt, and 20% sand it falls in the "silt ...
Eastern Cascades Incised Volcanoes and Flows Volcanoes are
... channels throughout is the key difference from the younger or less degraded Volcanoes and Flows. The volcanoes are typically of the cinder cone type and these have a near summit depression that sometimes open out onto the landscape and become part of the integrated drainage system. Volcano summits a ...
... channels throughout is the key difference from the younger or less degraded Volcanoes and Flows. The volcanoes are typically of the cinder cone type and these have a near summit depression that sometimes open out onto the landscape and become part of the integrated drainage system. Volcano summits a ...
Age Old Organics
... resulting in stronger, healthier plants and higher yields. Soil applications of Humic acid are used to release nutrients that are in the soil, but not readily available to the plant. It is also used to reclaim soils damaged by chemicals. (Available in: 12 x 32 oz, 4 x 1 Gallon, 2 x 2 1/2 Gallon case ...
... resulting in stronger, healthier plants and higher yields. Soil applications of Humic acid are used to release nutrients that are in the soil, but not readily available to the plant. It is also used to reclaim soils damaged by chemicals. (Available in: 12 x 32 oz, 4 x 1 Gallon, 2 x 2 1/2 Gallon case ...
essential guide
... Organic matter consists of living organisms and is very important to soil function and plant growth as it influences soil structure (and hence aeration, drainage and root growth), water-holding capacity and soil fertility. It binds mineral particles into granular or crumb structures and the proporti ...
... Organic matter consists of living organisms and is very important to soil function and plant growth as it influences soil structure (and hence aeration, drainage and root growth), water-holding capacity and soil fertility. It binds mineral particles into granular or crumb structures and the proporti ...
COURSE TITLE (COURSE CODE)
... On completing the course, students should be able to: p.1 Practice solving engineering problems. p.2 Show field techniques of investigation of physical properties of soil, and hydraulic soil properties. p.3 Calculate Stress distribution within the soil mass, Stresses under point, Compressibility and ...
... On completing the course, students should be able to: p.1 Practice solving engineering problems. p.2 Show field techniques of investigation of physical properties of soil, and hydraulic soil properties. p.3 Calculate Stress distribution within the soil mass, Stresses under point, Compressibility and ...
Water on the Earth
... and the ecological collapse of entire areas. If erosion happens at a pace faster than the land can regenerate itself, this can render the land desert‐like and incapable of supporting life. Believe it or not, soil is actually a valuable and nonrenewable resource, as it contains nutrients and minerals ...
... and the ecological collapse of entire areas. If erosion happens at a pace faster than the land can regenerate itself, this can render the land desert‐like and incapable of supporting life. Believe it or not, soil is actually a valuable and nonrenewable resource, as it contains nutrients and minerals ...
Soil Invertebrates and Abiotic Factors
... ground; yet the essential requirements do not differ. Like organisms that live outside the soil, life in the soil requires living space, oxygen, food, and water. Without the presence and intense activity of living organisms, soil development could not proceed. Soil inhabitants from bacteria and fung ...
... ground; yet the essential requirements do not differ. Like organisms that live outside the soil, life in the soil requires living space, oxygen, food, and water. Without the presence and intense activity of living organisms, soil development could not proceed. Soil inhabitants from bacteria and fung ...
Soil and the LAw UNCCD Side Event September 2013
... manner that preserves the balance between the processes of soil formation and soil degradation, while maintaining the ecological functions and needs of soil”.7 The achievement of land degradation neutrality, whereby LD is either avoided or off set by land restoration and promoting the ZNLD target wo ...
... manner that preserves the balance between the processes of soil formation and soil degradation, while maintaining the ecological functions and needs of soil”.7 The achievement of land degradation neutrality, whereby LD is either avoided or off set by land restoration and promoting the ZNLD target wo ...
Evolution of Groundwater Chemistry
... Organic Compound Properties • In general, not very soluble in water • Uncharged or weakly charged • Can exist as dissolved, solid, or gaseous phases • Organic matter in water is composed of an almost infinite variety of compounds – Most dissolved organic matter in groundwater are humic acids – Very ...
... Organic Compound Properties • In general, not very soluble in water • Uncharged or weakly charged • Can exist as dissolved, solid, or gaseous phases • Organic matter in water is composed of an almost infinite variety of compounds – Most dissolved organic matter in groundwater are humic acids – Very ...
Water Balance in Small Piedmont Watersheds
... ‘Mapping first –order controls on streamflow from drainage basins…’ (Buttle, 2006) – ...
... ‘Mapping first –order controls on streamflow from drainage basins…’ (Buttle, 2006) – ...