NAME_________________________________________ DATE
... We tend to think of this biome as being hot, but it may be very cold. Plants must be adapted to store moisture and withstand the drying winds. Most rain falls during the short summers in this biome. Plants must tolerate the nutrient poor, acidic soils. Although the soil freezes in the winter, it is ...
... We tend to think of this biome as being hot, but it may be very cold. Plants must be adapted to store moisture and withstand the drying winds. Most rain falls during the short summers in this biome. Plants must tolerate the nutrient poor, acidic soils. Although the soil freezes in the winter, it is ...
Weathering and Soil Formation *** Practice Test
... Describe how freezing and thawing of water causes mechanical weathering. Water seeps into cracks in the rocks and then freezes causing expansion which causes the rock to crack more and allow more water into the rock. ...
... Describe how freezing and thawing of water causes mechanical weathering. Water seeps into cracks in the rocks and then freezes causing expansion which causes the rock to crack more and allow more water into the rock. ...
chapter 8
... Slide: the downslope movement of a relatively coherent unit of rock or soil along a well-defined surface. Slump: a slide that has moved a short distance. Soil slumps often display a rotational movement. Flow: the downslope movement of a material in a chaotic fashion with mixing of particles within t ...
... Slide: the downslope movement of a relatively coherent unit of rock or soil along a well-defined surface. Slump: a slide that has moved a short distance. Soil slumps often display a rotational movement. Flow: the downslope movement of a material in a chaotic fashion with mixing of particles within t ...
Emerging aspects in Microbial Geotechnology and Ground
... • Increasing the resistance to petroleum borehole degradation during drilling and extraction. • Increasing the resistance of offshore structures to erosion of sediment within or beneath gravity foundations and pipelines. • Stabilising pollutants from soil by the binding. • Controlling erosion in ...
... • Increasing the resistance to petroleum borehole degradation during drilling and extraction. • Increasing the resistance of offshore structures to erosion of sediment within or beneath gravity foundations and pipelines. • Stabilising pollutants from soil by the binding. • Controlling erosion in ...
chapter 8
... Slide: the downslope movement of a relatively coherent unit of rock or soil along a well-defined surface. Slump: a slide that has moved a short distance. Soil slumps often display a rotational movement. Flow: the downslope movement of a material in a chaotic fashion with mixing of particles within t ...
... Slide: the downslope movement of a relatively coherent unit of rock or soil along a well-defined surface. Slump: a slide that has moved a short distance. Soil slumps often display a rotational movement. Flow: the downslope movement of a material in a chaotic fashion with mixing of particles within t ...
mass movements
... c. the weight of surface vegetation. d. reduction in soil moisture. 10. The rate of motion of a landslide is commonly related to a. the weight of the material. b. the proportion of moisture within the material. c. the distance the material travels. d. the chemical composition of the material. 11. Sc ...
... c. the weight of surface vegetation. d. reduction in soil moisture. 10. The rate of motion of a landslide is commonly related to a. the weight of the material. b. the proportion of moisture within the material. c. the distance the material travels. d. the chemical composition of the material. 11. Sc ...
Soil, sand, pollen
... Characteristics for identification—size, density, color, luster, fracture, streak, or ...
... Characteristics for identification—size, density, color, luster, fracture, streak, or ...
Discovery and microbial content of the driest site of
... (MES) (Fig. 1). MES, located 275 km northeast of Yungay, was the driest site among them (Fig. 2A). The mean atmospheric RH at Yungay was 28.8%, whereas at the same period at MES, it was only 17.3%. Previous reports had shown even higher mean atmospheric RH values (36.9%) at Yungay (de los Ríos et al ...
... (MES) (Fig. 1). MES, located 275 km northeast of Yungay, was the driest site among them (Fig. 2A). The mean atmospheric RH at Yungay was 28.8%, whereas at the same period at MES, it was only 17.3%. Previous reports had shown even higher mean atmospheric RH values (36.9%) at Yungay (de los Ríos et al ...
SOIL 4400 Soil Ecology
... it a very thin layer of the agar surface. If the colony is thick and woolly, it may not be necessary to take the agar, but in the more appressed type it is essential. 3. Place the piece of colony in the mounting medium, and, with a second needle, tease it out so that the filaments are well spread. A ...
... it a very thin layer of the agar surface. If the colony is thick and woolly, it may not be necessary to take the agar, but in the more appressed type it is essential. 3. Place the piece of colony in the mounting medium, and, with a second needle, tease it out so that the filaments are well spread. A ...
Earthworms: ecofriendly environmental engineers
... microorganisms from the gut of earthworms. Earthworms have been used for land recovery, reclamation and rehabilitation of sub-optimal soils such as poor mineral soils, polder soils, open cast mining sites, closed landfill sites and cutover peat [4, 5]. Within the soil environment, an earthworm’s sph ...
... microorganisms from the gut of earthworms. Earthworms have been used for land recovery, reclamation and rehabilitation of sub-optimal soils such as poor mineral soils, polder soils, open cast mining sites, closed landfill sites and cutover peat [4, 5]. Within the soil environment, an earthworm’s sph ...
The Chemical Fertility of Soils: Soil Nutrients and Plant Nutrition
... The makeup of a soil, its acidity or alkalinity, and its ambient temperature are just a sample of the many factors that will determine the extent to which nutrients are available to plants. The relative importance of these factors depends upon the nutrient, the plant and the soil. Most importantly, ...
... The makeup of a soil, its acidity or alkalinity, and its ambient temperature are just a sample of the many factors that will determine the extent to which nutrients are available to plants. The relative importance of these factors depends upon the nutrient, the plant and the soil. Most importantly, ...
Soil test reports by AAT
... micronutrients (10) in soil so as to provide the farmer the information he requires for maintaining the health of the soil. The present methods that are available require sophisticated, costly and equipment. Depending on the information required, the cost of testing a single soil sample could vary b ...
... micronutrients (10) in soil so as to provide the farmer the information he requires for maintaining the health of the soil. The present methods that are available require sophisticated, costly and equipment. Depending on the information required, the cost of testing a single soil sample could vary b ...
Thermal signatures of land mines buried in mineral and organic soils
... ½1 þ ðahÞn Soil heat capacity and soil heat conductivity may be calculated using a statistical model described elsewhere [2]. ...
... ½1 þ ðahÞn Soil heat capacity and soil heat conductivity may be calculated using a statistical model described elsewhere [2]. ...
Lecture 2 — Earth Materials and Igneous Rocks
... General familiarity, Expansive soils Be aware of where clays occur geologically ...
... General familiarity, Expansive soils Be aware of where clays occur geologically ...
2 «Schwarze Kiefern», ФРГ - G-global www.group
... Based on these results we analyzed the results, showing the level of heavy metals in soil samples. The dynamics of health indicators, shown in the background of the general trend to reduce soil pollution that in the Oktyabrsky district recorded 66.6% of non-standard samples in the zone of influence ...
... Based on these results we analyzed the results, showing the level of heavy metals in soil samples. The dynamics of health indicators, shown in the background of the general trend to reduce soil pollution that in the Oktyabrsky district recorded 66.6% of non-standard samples in the zone of influence ...
Disposal Of Dairy Sludge
... In 2000 Developed a wetland system to treat dairy wastes produced The objective of the plan was to create ecological affect and to reduce various organic pollutants. Monitoring of the system was done over a 3 year period. ...
... In 2000 Developed a wetland system to treat dairy wastes produced The objective of the plan was to create ecological affect and to reduce various organic pollutants. Monitoring of the system was done over a 3 year period. ...
Agronomy – definition – meaning and scope. Agro
... coastal areas on the East and mountains in the West. This zone comprises Sivagangai, Ramanathapuram, Virudunagar, Tuticorin and Tirunelveli districts and Natham and Dindigul taluks of Dindigul district, Melur, Tirumangalam, Madurai South and Madurai North taluks of Madurai district and Pudukkottai d ...
... coastal areas on the East and mountains in the West. This zone comprises Sivagangai, Ramanathapuram, Virudunagar, Tuticorin and Tirunelveli districts and Natham and Dindigul taluks of Dindigul district, Melur, Tirumangalam, Madurai South and Madurai North taluks of Madurai district and Pudukkottai d ...
Soil of Atlas Europe
... • Mid January = Agreement on regional text boxes and other map texts • End January = all text and graphical elements with LJ • End February = production of final draft and dispatch for comments • Mid March = deadline for comments – factual or errors only • End March = Final check and OK to produce f ...
... • Mid January = Agreement on regional text boxes and other map texts • End January = all text and graphical elements with LJ • End February = production of final draft and dispatch for comments • Mid March = deadline for comments – factual or errors only • End March = Final check and OK to produce f ...
Weathering and Erosion 2013
... Sand from lower right towards the upper left portion of the triangle . The intersection of the three sizes on the triangle give the texture class. For instance, if you have a soil with 20% clay, 60% silt, and 20% sand it falls in the "silt ...
... Sand from lower right towards the upper left portion of the triangle . The intersection of the three sizes on the triangle give the texture class. For instance, if you have a soil with 20% clay, 60% silt, and 20% sand it falls in the "silt ...
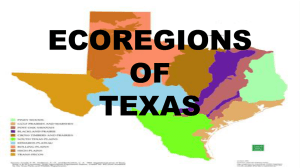
Texas eco regions 2016
... ground has left most of the region with very shallow soils (less than 10 inches) ...
... ground has left most of the region with very shallow soils (less than 10 inches) ...
Foliar Fertilization Improves Nutrient Use Efficiency
... esearch has shattered the belief that only roots absorb nutrients. The use of radioactive and isotopically tagged nutrients has confirmed that plants can be fed through their leaves. Foliar N, in particular, is absorbed through other green tissue and soft woody tissue including stems, buds, blossoms ...
... esearch has shattered the belief that only roots absorb nutrients. The use of radioactive and isotopically tagged nutrients has confirmed that plants can be fed through their leaves. Foliar N, in particular, is absorbed through other green tissue and soft woody tissue including stems, buds, blossoms ...
Soil Carbon Sequestration – for climate, food security and
... Linking science, policies and action on soil carbon sequestration Building bridges between science, policy and action is urgently needed. Although almost all of our calories come from use of soils, soil issues are not on top of the agenda in the present policy framework. Soils are overlooked and ta ...
... Linking science, policies and action on soil carbon sequestration Building bridges between science, policy and action is urgently needed. Although almost all of our calories come from use of soils, soil issues are not on top of the agenda in the present policy framework. Soils are overlooked and ta ...
Weathering and Soil Formation
... Soil Properties • Soil Texture and Soil Structure Soil texture is the soil quality that is based on the proportions of soil particles. Soil structure is the arrangement of soil particles. ...
... Soil Properties • Soil Texture and Soil Structure Soil texture is the soil quality that is based on the proportions of soil particles. Soil structure is the arrangement of soil particles. ...
T07_15
... earlier. Moreover, the numerous existing structures are also needed to be treated for their foundation problems such as low bearing capacity of soil, etc. as they were built on soil with poor geotechnical properties. For this purpose, stabilization of soil needs to be carried out. Although many diff ...
... earlier. Moreover, the numerous existing structures are also needed to be treated for their foundation problems such as low bearing capacity of soil, etc. as they were built on soil with poor geotechnical properties. For this purpose, stabilization of soil needs to be carried out. Although many diff ...
EFFECT OF SOIL COMPOSITION ON ELECTROKINETIC GROUTING
... earlier. Moreover, the numerous existing structures are also needed to be treated for their foundation problems such as low bearing capacity of soil, etc. as they were built on soil with poor geotechnical properties. For this purpose, stabilization of soil needs to be carried out. Although many diff ...
... earlier. Moreover, the numerous existing structures are also needed to be treated for their foundation problems such as low bearing capacity of soil, etc. as they were built on soil with poor geotechnical properties. For this purpose, stabilization of soil needs to be carried out. Although many diff ...