Chapter 8
... • Soy protein in place of milk protein should be limited in its use • There is little scientific evidence for benefit of increase soy over milk-based • The use of soy formula is not recommended ...
... • Soy protein in place of milk protein should be limited in its use • There is little scientific evidence for benefit of increase soy over milk-based • The use of soy formula is not recommended ...
the content of magnesium, calcium, sodium and potassium in infant
... The level of some minerals in infant milk formulas can be much higher in comparison to mother’s milk, which is a result of their lower assimilability (Stolarczyk 2001). Some studies available in the literature have shown that infant and baby formulas have a carefully balanced mineral composition, bo ...
... The level of some minerals in infant milk formulas can be much higher in comparison to mother’s milk, which is a result of their lower assimilability (Stolarczyk 2001). Some studies available in the literature have shown that infant and baby formulas have a carefully balanced mineral composition, bo ...
Lecture 6 - Prenatal - 1 year
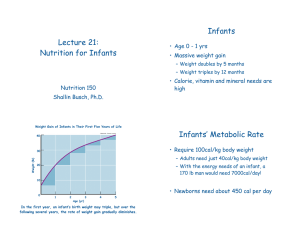
... How much a newborn sleep does compares to a 1 year old? What helps an infant establish good sleep patterns? What type of play does an infant (0 – 1 year) participate in? What is the goal of infant play? What are good toys for an infant (characteristics)? What safety measures should be implemented fo ...
... How much a newborn sleep does compares to a 1 year old? What helps an infant establish good sleep patterns? What type of play does an infant (0 – 1 year) participate in? What is the goal of infant play? What are good toys for an infant (characteristics)? What safety measures should be implemented fo ...
baby formula
... Advantages of breastfeeding include: (1) breast milk is nutritionally sound and easy to digest; (2) breastfeeding is believed to enhance a close mother-child relationship; and (3) breast milk contains infectionfighting antibodies (immunoglobulins) that ,diarrhea may reduce the frequency of ...
... Advantages of breastfeeding include: (1) breast milk is nutritionally sound and easy to digest; (2) breastfeeding is believed to enhance a close mother-child relationship; and (3) breast milk contains infectionfighting antibodies (immunoglobulins) that ,diarrhea may reduce the frequency of ...
2003-DEC-11: Oral Testimony on Soy
... the main classes of phytoestrogens and have been found to exert both oestrogenic and anti-oestrogenic effects on the central nervous system. The effects have not been limited to reproductive behaviour, but include effects on learning and anxiety and actions on the hypothalamo-pituitary axis.” Noting ...
... the main classes of phytoestrogens and have been found to exert both oestrogenic and anti-oestrogenic effects on the central nervous system. The effects have not been limited to reproductive behaviour, but include effects on learning and anxiety and actions on the hypothalamo-pituitary axis.” Noting ...
March Board Review - LSU School of Medicine
... • High in total protein, low in carbohydrate, and lower in fat than mature milk • After processing, cow milk and infant formula contain no cells, no enzymes, and no antibodies or other active protective agents – Do not support the maintenance of physiologic gut flora ...
... • High in total protein, low in carbohydrate, and lower in fat than mature milk • After processing, cow milk and infant formula contain no cells, no enzymes, and no antibodies or other active protective agents – Do not support the maintenance of physiologic gut flora ...
P1028 Infant Formula - Dietitians Association of Australia
... will mislead caregivers to believe that infant formula provides health benefits that are equal to or above that of breastmilk. This perception may also be exacerbated by such formula being priced above other formula. Women who are more comfortable with infant formula are less likely to breast feed4. ...
... will mislead caregivers to believe that infant formula provides health benefits that are equal to or above that of breastmilk. This perception may also be exacerbated by such formula being priced above other formula. Women who are more comfortable with infant formula are less likely to breast feed4. ...
Infant Feeding Through Year One
... meats, raw carrots, apples and popcorn are all foods that can get caught in a baby’s throat. ...
... meats, raw carrots, apples and popcorn are all foods that can get caught in a baby’s throat. ...
Slide 1
... Solid foods must be mashed or pureed in 1st year of life to avoid aspiration No honey until after 1 year Limit milk to 16-24 oz per day ...
... Solid foods must be mashed or pureed in 1st year of life to avoid aspiration No honey until after 1 year Limit milk to 16-24 oz per day ...
Infant Formula Basics - Intermountain Healthcare
... •• DHA and ARA. These are types of fat found in breast milk. Studies show that these fats aid in eye and brain development. •• Hydrolyzed whey protein. This protein is broken into smaller bits so your baby can digest it more easily. Studies say it may help prevent allergies in babies who have a fami ...
... •• DHA and ARA. These are types of fat found in breast milk. Studies show that these fats aid in eye and brain development. •• Hydrolyzed whey protein. This protein is broken into smaller bits so your baby can digest it more easily. Studies say it may help prevent allergies in babies who have a fami ...
DIAGNOSTIC TOOL - Nutricia Early Life Nutrition
... management of lactose intolerance, e.g. lactose free milk. IMPORTANT NOTICE: Breastfeeding is best for babies. Infant formula is suitable from birth when babies are not breastfed. Follow-on milk is only for babies over 6 months as part of a mixed diet, and should not be used as a breastmilk substitu ...
... management of lactose intolerance, e.g. lactose free milk. IMPORTANT NOTICE: Breastfeeding is best for babies. Infant formula is suitable from birth when babies are not breastfed. Follow-on milk is only for babies over 6 months as part of a mixed diet, and should not be used as a breastmilk substitu ...
Child and Adult Care Food Program ( CACFP )
... Infant meal times may vary from center meal times ...
... Infant meal times may vary from center meal times ...
NUTRITION FROM INFANCY THROUGH ADOLESCENCE
... 6. Minerals of special interest: a. Iron - Stores generally depleted by age 4 to 6 months - Infant > 6 months need dietary iron source b. Iodine and zinc generally met if energy needs met c. Fluoride supplement if water not fluoridated 7. Water: a. 700-800 ml (3 c) needed per day b. Human milk and f ...
... 6. Minerals of special interest: a. Iron - Stores generally depleted by age 4 to 6 months - Infant > 6 months need dietary iron source b. Iodine and zinc generally met if energy needs met c. Fluoride supplement if water not fluoridated 7. Water: a. 700-800 ml (3 c) needed per day b. Human milk and f ...
Infant and Child mortality rates
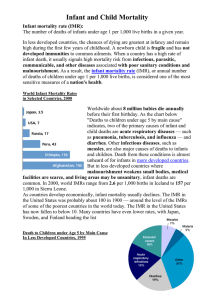
... Worldwide about 8 million babies die annually before their first birthday. As the chart below "Deaths to children under age 5 by main cause" indicates, two of the primary causes of infant and child deaths are acute respiratory diseases — such as pneumonia, tuberculosis, and influenza — and diarrhea. ...
... Worldwide about 8 million babies die annually before their first birthday. As the chart below "Deaths to children under age 5 by main cause" indicates, two of the primary causes of infant and child deaths are acute respiratory diseases — such as pneumonia, tuberculosis, and influenza — and diarrhea. ...
Feeding Infants Feeding Infants
... are often less constipated and gassy. It may lower the risk of sudden infant death syndrome in the first year of your baby's life. It may raise your child's intelligence. Studies show breastfed babies have higher levels of cognitive function. Decreased incidence of ear infections, UTI, gastroe ...
... are often less constipated and gassy. It may lower the risk of sudden infant death syndrome in the first year of your baby's life. It may raise your child's intelligence. Studies show breastfed babies have higher levels of cognitive function. Decreased incidence of ear infections, UTI, gastroe ...
Template Letter for Medical Necessity
... also help to preserve gut integrity4,5. The formula contains Prebio1™ blend, a unique prebiotic fiber blend to help support the growth of beneficial intestinal bacteria to support digestive health. Prebio1™ prebiotic fiber blend helps promote the growth of beneficial intestinal bacteria to help supp ...
... also help to preserve gut integrity4,5. The formula contains Prebio1™ blend, a unique prebiotic fiber blend to help support the growth of beneficial intestinal bacteria to support digestive health. Prebio1™ prebiotic fiber blend helps promote the growth of beneficial intestinal bacteria to help supp ...
BMA PARNUTs Sep09
... infant health. The Report of the Scientific Committee on Food on the Revision of Essential Requirements of Infant Formulae and Follow-on Formulae identified some of problems that have occurred with the introduction of modified infant formulae. Examples included reduced protein availability with imp ...
... infant health. The Report of the Scientific Committee on Food on the Revision of Essential Requirements of Infant Formulae and Follow-on Formulae identified some of problems that have occurred with the introduction of modified infant formulae. Examples included reduced protein availability with imp ...
Nestle Compleat Letter of Medical Necessity
... enteral feeding and/or for transitioning from or dual feeding with TPN. The product can be used as a complete tube feeding or oral supplement. Peptamen® 1.5 with Prebio1™ formula is a medical food for use under the supervision of a medical professional. Peptamen® 1.5 with Prebio1™ formula is designe ...
... enteral feeding and/or for transitioning from or dual feeding with TPN. The product can be used as a complete tube feeding or oral supplement. Peptamen® 1.5 with Prebio1™ formula is a medical food for use under the supervision of a medical professional. Peptamen® 1.5 with Prebio1™ formula is designe ...
Standard Operating Procedures on Donations
... 3. Infant formula should be manufactured and packaged in accordance with the Codex Alimentarius standards and have a shelf-life of at least 6 months on receipt of supply. 4. Labels of procured infant formula should be in an appropriate language and should adhere to the specific labeling requirements ...
... 3. Infant formula should be manufactured and packaged in accordance with the Codex Alimentarius standards and have a shelf-life of at least 6 months on receipt of supply. 4. Labels of procured infant formula should be in an appropriate language and should adhere to the specific labeling requirements ...
Nestle Compleat Letter of Medical Necessity
... feeding and/or for transitioning from or dual feeding with TPN. The product can be used as a complete tube feeding or oral supplement. Peptamen® 1.5 with Prebio1™ formula is a medical food for use under the supervision of a medical professional. Peptamen® 1.5 with Prebio1™ formula is designed to sup ...
... feeding and/or for transitioning from or dual feeding with TPN. The product can be used as a complete tube feeding or oral supplement. Peptamen® 1.5 with Prebio1™ formula is a medical food for use under the supervision of a medical professional. Peptamen® 1.5 with Prebio1™ formula is designed to sup ...
Case Study NIRMaster™ for Quality Control of Infant Formula
... with a portfolio of products manufactured in India and sold nationally under recognized brands including Farex, Protinex, Dexolac and Nusobee. These products are designed to provide the best nutrition at each stage of life of Indian people. All their sourcing and manufacturing processes aim for the ...
... with a portfolio of products manufactured in India and sold nationally under recognized brands including Farex, Protinex, Dexolac and Nusobee. These products are designed to provide the best nutrition at each stage of life of Indian people. All their sourcing and manufacturing processes aim for the ...
Nutritional intake and feeding practices in the first 1000
... increasing amount of solid foods, and yet, breastmilk remains the most appropriate liquid part of a progressively diversified diet. For babies not being breastfed, those under the age of 1 year can take infant formula, while those above 1 year can take full cream milh fermented milk or yogurt etc. C ...
... increasing amount of solid foods, and yet, breastmilk remains the most appropriate liquid part of a progressively diversified diet. For babies not being breastfed, those under the age of 1 year can take infant formula, while those above 1 year can take full cream milh fermented milk or yogurt etc. C ...
BIOL 103 Ch 11 Homework Answer Key
... 7. How much water does a breastfed or formula-fed infant need each day? Babies need approximately 0.7 liters of water each day in the first six months of life and 0.8 liters per day from age 7 months to 1 year. Breastfed and formula-fed infants do not need supplemental water; the breast milk and pr ...
... 7. How much water does a breastfed or formula-fed infant need each day? Babies need approximately 0.7 liters of water each day in the first six months of life and 0.8 liters per day from age 7 months to 1 year. Breastfed and formula-fed infants do not need supplemental water; the breast milk and pr ...
Infant formula

Infant formula is a manufactured food designed and marketed for feeding to babies and infants under 12 months of age, usually prepared for bottle-feeding or cup-feeding from powder (mixed with water) or liquid (with or without additional water). The U.S. Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act (FFDCA) defines infant formula as ""a food which purports to be or is represented for special dietary use solely as a food for infants by reason of its simulation of human milk or its suitability as a complete or partial substitute for human milk"".Manufacturers state that the composition of infant formula is designed to be roughly based on a human mother's milk at approximately one to three months postpartum; however, there are significant differences in the nutrient content of these products. The most commonly used infant formulas contain purified cow's milk whey and casein as a protein source, a blend of vegetable oils as a fat source, lactose as a carbohydrate source, a vitamin-mineral mix, and other ingredients depending on the manufacturer. In addition, there are infant formulas using soybean as a protein source in place of cow's milk (mostly in the United States and Great Britain) and formulas using protein hydrolysed into its component amino acids for infants who are allergic to other proteins. An upswing in breastfeeding in many countries has been accompanied by a deferment in the average age of introduction of baby foods (including cow's milk), resulting in both increased breastfeeding and increased use of infant formula between the ages of 3- and 12-months.A 2001 World Health Organization (WHO) report found that infant formula prepared in accordance with applicable Codex Alimentarius standards was a safe complementary food and a suitable breast milk substitute. In 2003, the WHO and UNICEF published their Global Strategy for Infant and Young Child Feeding, which restated that ""processed-food products for infants and young children should, when sold or otherwise distributed, meet applicable standards recommended by the Codex Alimentarius Commission"", and also warned that ""lack of breastfeeding—and especially lack of exclusive breastfeeding during the first half-year of life—are important risk factors for infant and childhood morbidity and mortality"". In particular, the use of infant formula in less economically developed countries is linked to poorer health outcomes because of the prevalence of unsanitary preparation conditions, including lack of clean water and lack of sanitizing equipment. UNICEF estimates that a formula-fed child living in unhygienic conditions is between 6 and 25 times more likely to die of diarrhea and four times more likely to die of pneumonia than a breastfed child. Rarely, use of powdered infant formula (PIF) has been associated with serious illness, and even death, due to infection with Enterobacter sakazakii and other microorganisms that can be introduced to PIF during its production. Although E. sakazakii can cause illness in all age groups, infants are believed to be at greatest risk of infection. Between 1958 and 2006, there have been several dozen reported cases of E. sakazakii infection worldwide. The WHO believes that such infections are under-reported.