Link State Routing
... • The Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) protocol is an intra-domain routing protocol based on link state routing • Its domain is also an autonomous system • OSPF does not use a TCP/IP transport protocol (UDP, TCP), but is encapsulated directly in IP datagrams with protocol number 89 • This is in contr ...
... • The Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) protocol is an intra-domain routing protocol based on link state routing • Its domain is also an autonomous system • OSPF does not use a TCP/IP transport protocol (UDP, TCP), but is encapsulated directly in IP datagrams with protocol number 89 • This is in contr ...
IntroductionToUnix_S14 - Silicon Valley University
... 4) Supporting protocols used for routing application data from one host to another in a LAN/internetwork. 5) Supporting protocols for transporting data from a process on a host to a process on another host on LAN/internetwork. 6) Supporting protocols used by network-based software for specific appli ...
... 4) Supporting protocols used for routing application data from one host to another in a LAN/internetwork. 5) Supporting protocols for transporting data from a process on a host to a process on another host on LAN/internetwork. 6) Supporting protocols used by network-based software for specific appli ...
Understanding Network Access Control
... devices, but this compatibility is also one of the main problems. Many vendors deliver imprecise or faulty information via SNMP where a correct outcome cannot be assured. In addition, authentication via SMNP does not conform to any standards and is not real-time capable since SNMP requests are sent ...
... devices, but this compatibility is also one of the main problems. Many vendors deliver imprecise or faulty information via SNMP where a correct outcome cannot be assured. In addition, authentication via SMNP does not conform to any standards and is not real-time capable since SNMP requests are sent ...
(IP) dan Subnet Mask
... Because broadcast traffic is used to send packets to all hosts in the network, a packet uses a special broadcast address. When a host receives a packet with the broadcast address as the destination, it processes the packet as it would a packet to its unicast address. Broadcast transmission is used f ...
... Because broadcast traffic is used to send packets to all hosts in the network, a packet uses a special broadcast address. When a host receives a packet with the broadcast address as the destination, it processes the packet as it would a packet to its unicast address. Broadcast transmission is used f ...
MultiCast Sockets
... distributed filesystems parallel computing multiperson conferencing database replication name services and directory services ...
... distributed filesystems parallel computing multiperson conferencing database replication name services and directory services ...
Chapter 1 - Prof J. Noorul Ameen ME
... different transport streams that are part of a single application ...
... different transport streams that are part of a single application ...
Plant Floor Network Levels
... Install a free TFTP server on your network Download and copy the upgrade file to the TFTP server Go to the “firmware download” section of the 2572-A web server interface Enter the IP address of the TFTP server Complete information in Appendix F of the user ...
... Install a free TFTP server on your network Download and copy the upgrade file to the TFTP server Go to the “firmware download” section of the 2572-A web server interface Enter the IP address of the TFTP server Complete information in Appendix F of the user ...
ppt
... • Active networks makes such applications easy to develop and deploy © Srinivasan Seshan, 2002 ...
... • Active networks makes such applications easy to develop and deploy © Srinivasan Seshan, 2002 ...
Magnum Network Software – DX
... translated and passed to the private network, just as you would normally do if you were only using NAT. 2. The addressing scheme used on the private network (i.e. the network “behind” the NAT) is still hidden by the DX NAT functionality. Hosts at the “outside”, e.g. at the remote VPN location, must ...
... translated and passed to the private network, just as you would normally do if you were only using NAT. 2. The addressing scheme used on the private network (i.e. the network “behind” the NAT) is still hidden by the DX NAT functionality. Hosts at the “outside”, e.g. at the remote VPN location, must ...
Lecture 9 – Mobility Management and Mobile Application Part (MAP)
... In our description, at first, we will ignore number portability that is a recent addition to the original design. The discussion in the previous section shows that in order to achieve scalability, the problem of mobility management must be broken down into smaller problems. GSM does this in several ...
... In our description, at first, we will ignore number portability that is a recent addition to the original design. The discussion in the previous section shows that in order to achieve scalability, the problem of mobility management must be broken down into smaller problems. GSM does this in several ...
Ethernet Passive Optical Network (EPON)
... In the Figure 4, the data broadcasted downstream from OLT to multiple ONUs in variable-length packets of up to 1,518 bytes, according to IEEE 802.3 protocol. Each packet carries a header that uniquely identifies it as data intended for ONU-1, ONU-2 or ONU-3.At the splitter the traffic is divided int ...
... In the Figure 4, the data broadcasted downstream from OLT to multiple ONUs in variable-length packets of up to 1,518 bytes, according to IEEE 802.3 protocol. Each packet carries a header that uniquely identifies it as data intended for ONU-1, ONU-2 or ONU-3.At the splitter the traffic is divided int ...
Address Resolution Protocol
... Proxy ARP is a method that allows hosts on different LANs to successfully transmit packets across an internetworking environment. Suppose that Host A has an IP packet addressed to Host D. According to the normal ARP process, it might send a request to all other hosts physically connected to its netw ...
... Proxy ARP is a method that allows hosts on different LANs to successfully transmit packets across an internetworking environment. Suppose that Host A has an IP packet addressed to Host D. According to the normal ARP process, it might send a request to all other hosts physically connected to its netw ...
Authentication
... be protected in accordance with best practice appropriate for that device.” “Network address servers and those used to resolve addresses shall be protected in accordance with best practice appropriate for that device.” ...
... be protected in accordance with best practice appropriate for that device.” “Network address servers and those used to resolve addresses shall be protected in accordance with best practice appropriate for that device.” ...
Addressing the Network – IPv4
... Explain which types of addresses should be assigned to devices other than end user devices ...
... Explain which types of addresses should be assigned to devices other than end user devices ...
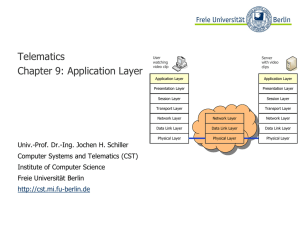
Application Layer - Freie Universität Berlin
... ● File Transfer Protocol (FTP) ● World Wide Web ● HTTP ● HTML ...
... ● File Transfer Protocol (FTP) ● World Wide Web ● HTTP ● HTML ...
18-MidIIRev_1 - Computer Science Division
... Flow control: regulates how much data can a sender send without overflowing the receiver Congestion control: regulates how much data can a sender send without congesting the ...
... Flow control: regulates how much data can a sender send without overflowing the receiver Congestion control: regulates how much data can a sender send without congesting the ...
GPRS - School of Electrical and Computer Engineering at Georgia
... The location is updated with a routing update procedure: 1. When an MS changes a routing area (RA), it sends an RA update request containing cell identity and the identity of the previous routing area, to the new SGSN. 2.The new SGSN asks the old SGSN to provide the routing context (GGSN address and ...
... The location is updated with a routing update procedure: 1. When an MS changes a routing area (RA), it sends an RA update request containing cell identity and the identity of the previous routing area, to the new SGSN. 2.The new SGSN asks the old SGSN to provide the routing context (GGSN address and ...
Class Seven
... Hold-Down Timer—Rule states that when a router receives information about a network that is unreachable, the router must ignore all subsequent information about that network for a configurable amount of time. ...
... Hold-Down Timer—Rule states that when a router receives information about a network that is unreachable, the router must ignore all subsequent information about that network for a configurable amount of time. ...
Addressing the Network – IPv4
... Explain which types of addresses should be assigned to devices other than end user devices ...
... Explain which types of addresses should be assigned to devices other than end user devices ...
module11a
... 3. Each router maintains a database of all received LSAs (topological database or link state database), which describes the network has a graph with weighted edges 4. Each router uses its link state database to run a shortest path algorithm (Dijikstra’s algorithm) to produce the shortest path to eac ...
... 3. Each router maintains a database of all received LSAs (topological database or link state database), which describes the network has a graph with weighted edges 4. Each router uses its link state database to run a shortest path algorithm (Dijikstra’s algorithm) to produce the shortest path to eac ...
RIP/OSPF
... Open Shortest Path First OSPF uses a different algorithm to perform routing decisions. OSPF working group was organized in 1988 because RIP had several shortcomings when dealing with interior routing in a large heterogeneous network. ...
... Open Shortest Path First OSPF uses a different algorithm to perform routing decisions. OSPF working group was organized in 1988 because RIP had several shortcomings when dealing with interior routing in a large heterogeneous network. ...
California Fault Lines: Understanding the Causes and
... of a failure, but at the same time it is generated by non-deterministic social processes and, thus, only reflects failures that are of a subjectively sufficient magnitude and duration to warrant a broader notice. However, this duality allows such announcement data to serve two distinct purposes: as ...
... of a failure, but at the same time it is generated by non-deterministic social processes and, thus, only reflects failures that are of a subjectively sufficient magnitude and duration to warrant a broader notice. However, this duality allows such announcement data to serve two distinct purposes: as ...
Assignment 1.1 - Network access testing and trouble shooting
... (paketförmedling) paradigm. Also distinguish between datagram and virtual circuit packet switching. Describe their differences and give examples of networks using the types. Which gives constant bit rate and constant delay? Which requires a connection phase? In which may packets travel different pat ...
... (paketförmedling) paradigm. Also distinguish between datagram and virtual circuit packet switching. Describe their differences and give examples of networks using the types. Which gives constant bit rate and constant delay? Which requires a connection phase? In which may packets travel different pat ...
IBM Presentation - Telecom SudParis
... • Then: Yes. • Do existing access control devices comply with these conditions ? Respect of the QoS has to be insured through other means Basic Idea: Using a non blocking access control process The Access Control decision is taken independently from the flows transported over the network. IBM Zurich ...
... • Then: Yes. • Do existing access control devices comply with these conditions ? Respect of the QoS has to be insured through other means Basic Idea: Using a non blocking access control process The Access Control decision is taken independently from the flows transported over the network. IBM Zurich ...
Recursive InterNetwork Architecture (RINA)

The Recursive InterNetwork Architecture (RINA) is a computer network architecture that unifies distributed computing and telecommunications. RINA's fundamental principle is that computer networking is just Inter-Process Communication or IPC. RINA reconstructs the overall structure of the Internet, forming a model that comprises a single repeating layer, the DIF (Distributed IPC Facility), which is the minimal set of components required to allow distributed IPC between application processes. RINA inherently supports mobility, multi-homing and Quality of Service without the need for extra mechanisms, provides a secure and programmable environment, motivates for a more competitive marketplace, and allows for a seamless adoption.