Roman Social Classes and The Roman Republic
... • The Senate (300 powerful patricians who served for life) ...
... • The Senate (300 powerful patricians who served for life) ...
The Roman Republic - EDSS Ancient Civilizations
... The Roman Senate Council of most powerful men in Rome Controlled the state budget and foreign affairs Owned most of the land Chosen for life ...
... The Roman Senate Council of most powerful men in Rome Controlled the state budget and foreign affairs Owned most of the land Chosen for life ...
Forget Hump Day* How about a Snow Day?
... • If there is a split between the patricians and plebeians, what could possibly go wrong in Rome? ...
... • If there is a split between the patricians and plebeians, what could possibly go wrong in Rome? ...
Rome - Shasta Union High School District
... Roman Society was made of Plebeians and Patricians Rome’s Republic Senate: Finances, foreign ...
... Roman Society was made of Plebeians and Patricians Rome’s Republic Senate: Finances, foreign ...
The Patricians and the Plebeians
... elected senators to serve their interests. Senate is derived from a term meaning elder, because the Roman Senate consisted of the oldest and wisest of the patricians. The senate selected two people to rule together in place of the Etruscan king. The new patrician rulers were known as consuls. The pl ...
... elected senators to serve their interests. Senate is derived from a term meaning elder, because the Roman Senate consisted of the oldest and wisest of the patricians. The senate selected two people to rule together in place of the Etruscan king. The new patrician rulers were known as consuls. The pl ...
8:1 The Roman Republic
... Name: ___________________________________________________________________________ Period: _______ ...
... Name: ___________________________________________________________________________ Period: _______ ...
The Rise of the Roman Republic
... the people (which at first meant the patricians) – SENATE: Group of 300 patricians elected by the patricians; served for life – CONSULS: 2 patricians elected to share control of the army – DICTATOR: One who makes a decision in an emergency situation if consuls disagree ...
... the people (which at first meant the patricians) – SENATE: Group of 300 patricians elected by the patricians; served for life – CONSULS: 2 patricians elected to share control of the army – DICTATOR: One who makes a decision in an emergency situation if consuls disagree ...
Class Notes Chapter 7, Lesson 2 The Roman Republic
... They were born to a princess; left to drown by their jealous uncle and would survive to build the city of Rome (named after Romulus, its first king. This legend provides Rome with a noble, strong beginning. (2) The Birth of a Republic Between 600 and 509 B.C., Rome was ruled by seven different kings ...
... They were born to a princess; left to drown by their jealous uncle and would survive to build the city of Rome (named after Romulus, its first king. This legend provides Rome with a noble, strong beginning. (2) The Birth of a Republic Between 600 and 509 B.C., Rome was ruled by seven different kings ...
Document
... • In 450 BCE, plebeians forced patricians to have all laws written down • Laws displayed in the Roman Forum, the central square, on 12 large bronze ...
... • In 450 BCE, plebeians forced patricians to have all laws written down • Laws displayed in the Roman Forum, the central square, on 12 large bronze ...
Representative government of Rome:
... --Assembly of Centuries: (named for a military formation of 100 soldiers) elected officials of the executive branch; --the Senate: group of 300 patrician men who served for life (outweighed the Assembly of Centuries); advised the consuls-two officials that headed the executive branch; debated foreig ...
... --Assembly of Centuries: (named for a military formation of 100 soldiers) elected officials of the executive branch; --the Senate: group of 300 patrician men who served for life (outweighed the Assembly of Centuries); advised the consuls-two officials that headed the executive branch; debated foreig ...
ESS DEPASRTMENT Term III Name: Grade: 7 Date: / / The Roman
... 1. What three forms of government did Rome have between 600 B.C. and 44 B.C.? Monarchy, republic, dictatorship. ...
... 1. What three forms of government did Rome have between 600 B.C. and 44 B.C.? Monarchy, republic, dictatorship. ...
Questions
... Who were the Patricians? What role did Patricians serve in Rome between 616 and 509 B.C.E? ...
... Who were the Patricians? What role did Patricians serve in Rome between 616 and 509 B.C.E? ...
1. The Etruscans ruled Rome between 616 and 509 B.C.E. 2. The
... 2. Patricians held the power. They made the decisions and interpreted the laws to benefit ...
... 2. Patricians held the power. They made the decisions and interpreted the laws to benefit ...
Conflict Between Classes
... representatives, called the Council of the Plebs. The Council of the Plebs elected officials called tribunes (TRIH • byoonz). Tribunes voiced plebeian concerns to the government. Tribunes could also veto government decisions. Later, plebeians were even allowed to become consuls, and marriages betwee ...
... representatives, called the Council of the Plebs. The Council of the Plebs elected officials called tribunes (TRIH • byoonz). Tribunes voiced plebeian concerns to the government. Tribunes could also veto government decisions. Later, plebeians were even allowed to become consuls, and marriages betwee ...
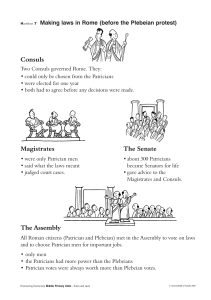
Handout 7
... All Roman citizens (Patrician and Plebeian) met in the Assembly to vote on laws and to choose Patrician men for important jobs. • only men • the Patricians had more power than the Plebeians • Patrician votes were always worth more than Plebeian votes. ...
... All Roman citizens (Patrician and Plebeian) met in the Assembly to vote on laws and to choose Patrician men for important jobs. • only men • the Patricians had more power than the Plebeians • Patrician votes were always worth more than Plebeian votes. ...