Discovering Devices using HP Web Jetadmin
... Discovery settings .................................................................................................................. 4 Network device discovery vs. PC-connected discovery............................................................... 4 Network discovery specifics ................... ...
... Discovery settings .................................................................................................................. 4 Network device discovery vs. PC-connected discovery............................................................... 4 Network discovery specifics ................... ...
2011-02-3.presentation
... The attacker will send a fake LSP on behalf of other router with seq. number of SequenceModulus. The victim will try to activate the “fight-back” mechanism but it needs to wait MaxAge+ZeroAgeLifetime seconds (≈ 21 minutes) before sending a new LSP with S.N = 1. During this period, the fake LSP will ...
... The attacker will send a fake LSP on behalf of other router with seq. number of SequenceModulus. The victim will try to activate the “fight-back” mechanism but it needs to wait MaxAge+ZeroAgeLifetime seconds (≈ 21 minutes) before sending a new LSP with S.N = 1. During this period, the fake LSP will ...
CDD-564A/L CDD-562AL-IP
... A Vipersat powered network integrates these advanced demodulators with a powerful network management tool, the Vipersat Management System (VMS). In addition to the traditional Monitoring and Control of the CDM-570A/L-IP modems and the CDD-564A/L and CDD-562AL demodulators, the VMS allows these devic ...
... A Vipersat powered network integrates these advanced demodulators with a powerful network management tool, the Vipersat Management System (VMS). In addition to the traditional Monitoring and Control of the CDM-570A/L-IP modems and the CDD-564A/L and CDD-562AL demodulators, the VMS allows these devic ...
Slides - SIGMOBILE
... • Benefits of REfactor approach • How REfactor works • Challenges & design innovations • Additional scenarios • Evaluation results ...
... • Benefits of REfactor approach • How REfactor works • Challenges & design innovations • Additional scenarios • Evaluation results ...
Information-centric networking – Ready for the real world?
... Numerous research problems remain open, some of which (such as naming content) may find different (optimal) solutions in different deployments while others are more fundamental in nature and could affect the performance of all deployments. The latter include the performance benefits achievable throu ...
... Numerous research problems remain open, some of which (such as naming content) may find different (optimal) solutions in different deployments while others are more fundamental in nature and could affect the performance of all deployments. The latter include the performance benefits achievable throu ...
PRP - EPFL
... - the sender inserts the same sequence counter into both frames of a pair, and increments it by one for each frame sent. - the receiver keeps track of the sequence counter for each for each source MAC address it receives frames from. Frames with the same source and counter value coming from differen ...
... - the sender inserts the same sequence counter into both frames of a pair, and increments it by one for each frame sent. - the receiver keeps track of the sequence counter for each for each source MAC address it receives frames from. Frames with the same source and counter value coming from differen ...
Signaling and Network Control - GUC
... redundancy. Under normal operation, the mated pair shares the load. If one of the STPs fails or isolation occurs because of signaling link failure, the other STP takes the full load until the problem with its mate has been rectified. Integrated STP (SP with STP): combine the functionality of an SSP ...
... redundancy. Under normal operation, the mated pair shares the load. If one of the STPs fails or isolation occurs because of signaling link failure, the other STP takes the full load until the problem with its mate has been rectified. Integrated STP (SP with STP): combine the functionality of an SSP ...
Link Layer - Gordon College
... Channel Partitioning MAC protocols: FDMA FDMA: frequency division multiple access channel spectrum divided into frequency bands each station assigned fixed frequency band unused transmission time in frequency bands go idle example: 6-station LAN, 1,3,4 have pkt, frequency ...
... Channel Partitioning MAC protocols: FDMA FDMA: frequency division multiple access channel spectrum divided into frequency bands each station assigned fixed frequency band unused transmission time in frequency bands go idle example: 6-station LAN, 1,3,4 have pkt, frequency ...
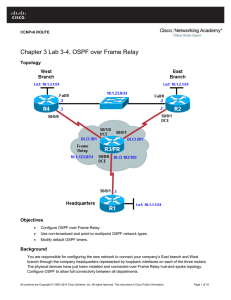
Chapter 3 Lab 3-4, OSPF over Frame Relay
... nonbroadcast. You can change this by adding neighbor statements. Configure neighbor statements on HQ pointing toward EAST and WEST. Only the router starting the exchange needs the statements (HQ in this case). However, it is considered best practice to also specify HQ as a neighbor on the EAST and W ...
... nonbroadcast. You can change this by adding neighbor statements. Configure neighbor statements on HQ pointing toward EAST and WEST. Only the router starting the exchange needs the statements (HQ in this case). However, it is considered best practice to also specify HQ as a neighbor on the EAST and W ...
Link Layer - Department of Computer and Information Science and
... “Taking Turns” MAC protocols channel partitioning MAC protocols: share channel efficiently and fairly at high load inefficient at low load: delay in channel access, 1/N bandwidth allocated even if only 1 active node! Random access MAC protocols efficient at low load: single node can fully uti ...
... “Taking Turns” MAC protocols channel partitioning MAC protocols: share channel efficiently and fairly at high load inefficient at low load: delay in channel access, 1/N bandwidth allocated even if only 1 active node! Random access MAC protocols efficient at low load: single node can fully uti ...
IEEE C802.16ppc-10/0043
... IEEE 802.16p shall support small burst transmission which implies that transmitted data bursts are extremely small in size. IEEE 802.16p shall support transmission of small data bursts with very low overhead. 6.6 High Reliability IEEE 802.16p shall support high reliability which implies that wheneve ...
... IEEE 802.16p shall support small burst transmission which implies that transmitted data bursts are extremely small in size. IEEE 802.16p shall support transmission of small data bursts with very low overhead. 6.6 High Reliability IEEE 802.16p shall support high reliability which implies that wheneve ...
Wireless LANs - College of DuPage
... –For example, the Linksys WRT300N used is really three devices in one box. •First, there is the wireless access point, which performs the typical functions of an access point. •A built-in four-port, full-duplex, 10/100 switch provides connectivity to wired devices. •Finally, the router function prov ...
... –For example, the Linksys WRT300N used is really three devices in one box. •First, there is the wireless access point, which performs the typical functions of an access point. •A built-in four-port, full-duplex, 10/100 switch provides connectivity to wired devices. •Finally, the router function prov ...
IPv6 Multicasting
... Although the basic notion of multicasting is common to IPv4 and IPv6, several new characteristics are introduced in IPv6 multicasting. In IPv4,multicasting was extension of the basic specification, while specifications of IPv6 require that all IPv6 nodes support multicasting. IPv6 explicitly limits ...
... Although the basic notion of multicasting is common to IPv4 and IPv6, several new characteristics are introduced in IPv6 multicasting. In IPv4,multicasting was extension of the basic specification, while specifications of IPv6 require that all IPv6 nodes support multicasting. IPv6 explicitly limits ...
Exploiting Route Redundancy via Structured Peer to Peer Overlays
... Streaming media, VoIP, B2B transactions Low tolerance of delay, jitter and faults Our work: transparent resilient routing infrastructure that adapts to faults in not seconds, but milliseconds ...
... Streaming media, VoIP, B2B transactions Low tolerance of delay, jitter and faults Our work: transparent resilient routing infrastructure that adapts to faults in not seconds, but milliseconds ...
Approximate Server Selection Algorithms in Content Distribution
... The remainder of the paper is organized as follows. In Section II we give a brief overview of previous research work on server selection algorithms. The proposed transformation technique is introduced in Section III, while the simulation results are illustrated in Section IV. Finally, Section V conc ...
... The remainder of the paper is organized as follows. In Section II we give a brief overview of previous research work on server selection algorithms. The proposed transformation technique is introduced in Section III, while the simulation results are illustrated in Section IV. Finally, Section V conc ...
Module 2 -IOS Running Config
... • Different types of network media (e.g. twisted-pair copper cables, fiber-optic cables, coaxial cables, or wireless) have different features and benefits. • Ethernet is the most common local area network (LAN) technology. • Cisco IOS Layer 2 switches have physical ports for devices to connect. Thes ...
... • Different types of network media (e.g. twisted-pair copper cables, fiber-optic cables, coaxial cables, or wireless) have different features and benefits. • Ethernet is the most common local area network (LAN) technology. • Cisco IOS Layer 2 switches have physical ports for devices to connect. Thes ...
3rd Edition, Chapter 5
... “Taking Turns” MAC protocols channel partitioning MAC protocols: share channel efficiently and fairly at high load inefficient at low load: delay in channel access, 1/N bandwidth allocated even if only 1 active node! Random access MAC protocols efficient at low load: single node can fully uti ...
... “Taking Turns” MAC protocols channel partitioning MAC protocols: share channel efficiently and fairly at high load inefficient at low load: delay in channel access, 1/N bandwidth allocated even if only 1 active node! Random access MAC protocols efficient at low load: single node can fully uti ...
FIREWALLS
... and server on the premises network with strong security features, such as intrusion protection, this may not be sufficient and in some cases is not cost-effective. Consider a network with hundreds or even thousands of systems, running various operating systems, such as different versions of UNIX and ...
... and server on the premises network with strong security features, such as intrusion protection, this may not be sufficient and in some cases is not cost-effective. Consider a network with hundreds or even thousands of systems, running various operating systems, such as different versions of UNIX and ...
3rd Edition, Chapter 5
... “Taking Turns” MAC protocols channel partitioning MAC protocols: share channel efficiently and fairly at high load inefficient at low load: delay in channel access, 1/N bandwidth allocated even if only 1 active node! Random access MAC protocols efficient at low load: single node can fully uti ...
... “Taking Turns” MAC protocols channel partitioning MAC protocols: share channel efficiently and fairly at high load inefficient at low load: delay in channel access, 1/N bandwidth allocated even if only 1 active node! Random access MAC protocols efficient at low load: single node can fully uti ...
Chapter 5 - Department of Computer Engineering
... “Taking Turns” MAC protocols channel partitioning MAC protocols: share channel efficiently and fairly at high load inefficient at low load: delay in channel access, 1/N bandwidth allocated even if only 1 active node! Random access MAC protocols efficient at low load: single node can fully uti ...
... “Taking Turns” MAC protocols channel partitioning MAC protocols: share channel efficiently and fairly at high load inefficient at low load: delay in channel access, 1/N bandwidth allocated even if only 1 active node! Random access MAC protocols efficient at low load: single node can fully uti ...
3rd Edition, Chapter 5
... “Taking Turns” MAC protocols channel partitioning MAC protocols: share channel efficiently and fairly at high load inefficient at low load: delay in channel access, 1/N bandwidth allocated even if only 1 active node! Random access MAC protocols efficient at low load: single node can fully uti ...
... “Taking Turns” MAC protocols channel partitioning MAC protocols: share channel efficiently and fairly at high load inefficient at low load: delay in channel access, 1/N bandwidth allocated even if only 1 active node! Random access MAC protocols efficient at low load: single node can fully uti ...
Linux and Shell Programming
... Consequences of routing based on next hop and destination network address All traffic destined for a given network takes the same path without regard to the delay or throughput of the physical network Only the final router along the path can determine whether the destination host exists or is oper ...
... Consequences of routing based on next hop and destination network address All traffic destined for a given network takes the same path without regard to the delay or throughput of the physical network Only the final router along the path can determine whether the destination host exists or is oper ...
3rd Edition: Chapter 3
... acknowledgements (ACKs): receiver explicitly tells sender that pkt received OK negative acknowledgements (NAKs): receiver explicitly tells sender that pkt had errors sender retransmits pkt on receipt of NAK ...
... acknowledgements (ACKs): receiver explicitly tells sender that pkt received OK negative acknowledgements (NAKs): receiver explicitly tells sender that pkt had errors sender retransmits pkt on receipt of NAK ...