DNA Similarities
... Suppose you could compare the total DNA sequences of various organisms (some billions of base pairs). How much similarity would you expect between a whale and a fish? A whale and a dog? A dog and a shrimp? A shrimp and a bacterium? As always, there are two types of similarity to be considered: analo ...
... Suppose you could compare the total DNA sequences of various organisms (some billions of base pairs). How much similarity would you expect between a whale and a fish? A whale and a dog? A dog and a shrimp? A shrimp and a bacterium? As always, there are two types of similarity to be considered: analo ...
Section 1.1 Name:
... The process of copying DNA in a cell is called ____________________. In the first step, the twonucleotide chains separate. The point at which the two chains separate is called the _____________ _____________, and are separated by enzymes called ____________________. In the next step, enzymes called ...
... The process of copying DNA in a cell is called ____________________. In the first step, the twonucleotide chains separate. The point at which the two chains separate is called the _____________ _____________, and are separated by enzymes called ____________________. In the next step, enzymes called ...
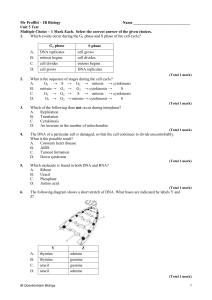
CHAPTER 10 - Protein Synthesis The DNA genotype is expressed
... of the cell or exported out of the cell Figure 10.20 • Summary of transcription and translation Review: The flow of genetic information in the cell is DNA→RNA→protein • The sequence of codons in DNA spells out the primary structure of a polypeptide – Polypeptides form proteins that cells and organis ...
... of the cell or exported out of the cell Figure 10.20 • Summary of transcription and translation Review: The flow of genetic information in the cell is DNA→RNA→protein • The sequence of codons in DNA spells out the primary structure of a polypeptide – Polypeptides form proteins that cells and organis ...
English Version
... 2. Profound grasp of the key knowledge of the structure and function of DNA and RNA. 3. Familiarity with the physio-chemical properties of DNA and the relation between these properties and the DNA structure. 4. To know the technique of isolation and purification of nucleic acids and DNA sequencing. ...
... 2. Profound grasp of the key knowledge of the structure and function of DNA and RNA. 3. Familiarity with the physio-chemical properties of DNA and the relation between these properties and the DNA structure. 4. To know the technique of isolation and purification of nucleic acids and DNA sequencing. ...
A. Nucleic Acid = polymer of nucleotides 1. nucleotide = molecule
... the next sugar molecule), at locations identified as recognition sequences which are approximately 6 base pairs long and enzyme specific! C. In a mixture of DNA and restriction enzymes, each enzyme causes the disruption of the DNA backbone within each of the recognition sequences that occur in that ...
... the next sugar molecule), at locations identified as recognition sequences which are approximately 6 base pairs long and enzyme specific! C. In a mixture of DNA and restriction enzymes, each enzyme causes the disruption of the DNA backbone within each of the recognition sequences that occur in that ...
BIOLOGY-DNA replication, transcription, translation (DOC 98KB)
... to the nitrogenous base and the type of bonds found between them. Give the students the following code sequence to build a model: 5’ ATGTTTAAGGTGGAGCCC 3’ ...
... to the nitrogenous base and the type of bonds found between them. Give the students the following code sequence to build a model: 5’ ATGTTTAAGGTGGAGCCC 3’ ...
Topic 3 The Chemistry of Life
... o Scientific truths are often pragmatic. We accept them as true because they give us predictive power, that is, they work. The German scientist Emil Fischer introduced the lock-and-key model for enzymes and their substrates in 1890. It was not until 1958 that Daniel Koshland in the United States sug ...
... o Scientific truths are often pragmatic. We accept them as true because they give us predictive power, that is, they work. The German scientist Emil Fischer introduced the lock-and-key model for enzymes and their substrates in 1890. It was not until 1958 that Daniel Koshland in the United States sug ...
1 Biology 437 Fall 2015 Syllabus Biology 437: LABORATORY ON
... Training rationale: You will learn to design, clone, and analyze the sequence for the mutations. This process is called genetic engineering and is critical for basic science, biotechnology, and biomedical research. Through this project you will gain hands on skills in DNA manipulation that will be t ...
... Training rationale: You will learn to design, clone, and analyze the sequence for the mutations. This process is called genetic engineering and is critical for basic science, biotechnology, and biomedical research. Through this project you will gain hands on skills in DNA manipulation that will be t ...
BOTANY-II (wef 2013-14)
... of Recombinant DNA Technology-Restriction Enzymes, Cloning Vectors, Competent Host (For Transformation with Recombinant DNA), Processes of Recombinant DNA Technology- Isolation of the Genetic Material (DNA), Cutting of DNA at Specific Locations, Separation and isolation of DNA fragments, Insertion o ...
... of Recombinant DNA Technology-Restriction Enzymes, Cloning Vectors, Competent Host (For Transformation with Recombinant DNA), Processes of Recombinant DNA Technology- Isolation of the Genetic Material (DNA), Cutting of DNA at Specific Locations, Separation and isolation of DNA fragments, Insertion o ...
HUMAN-CHIMP DNA
... only 13 nucleotides, a far larger number of changes than would be expected had the mutations been the result of drift rather than selection. The location of enhancer activity highlights the importance of the difference. Our hands, with their opposable thumbs*, our feet, evolved for bipedal locomotio ...
... only 13 nucleotides, a far larger number of changes than would be expected had the mutations been the result of drift rather than selection. The location of enhancer activity highlights the importance of the difference. Our hands, with their opposable thumbs*, our feet, evolved for bipedal locomotio ...
Mr Proffitt – IB Biology Name Unit 3 Test Multiple Choice – 1 Mark
... Short Answer – Various marks. Answer, to the best of your ability, the following questions. Be sure to pay attention to the number of marks available for each question! 15. The micrograph below shows an adult human stem cell. ...
... Short Answer – Various marks. Answer, to the best of your ability, the following questions. Be sure to pay attention to the number of marks available for each question! 15. The micrograph below shows an adult human stem cell. ...
RAJIV GANDHI UNIVERSITY OF HEALTH SCIENCES ANNEXURE
... Matrix metalloproteinases are a family of zinc dependent endo peptidases that are capable of degrading most components of the extra cellular matrix (ECM). Degeneration of matrix is a key invent in invasion and metastasis of malignant lesions of the head and neck. A polymorphism is a genetic variant ...
... Matrix metalloproteinases are a family of zinc dependent endo peptidases that are capable of degrading most components of the extra cellular matrix (ECM). Degeneration of matrix is a key invent in invasion and metastasis of malignant lesions of the head and neck. A polymorphism is a genetic variant ...
Class Outline 1. Understanding polynucleotide structure (Read) 2
... the sequence of the amino acids within proteins. The code is read by copying stretches of DNA into the related nucleic acid RNA in a process called transcription. Within cells, DNA is organized into long structures called chromosomes. During cell division these chromosomes are duplicated in the proc ...
... the sequence of the amino acids within proteins. The code is read by copying stretches of DNA into the related nucleic acid RNA in a process called transcription. Within cells, DNA is organized into long structures called chromosomes. During cell division these chromosomes are duplicated in the proc ...
Full Paper - Biotechniques.org
... reaction tubes were placed in the thermal cycler for 2 min at 94o, then at the following temperatures for 35 cycles: 94o x 30”, 58o x 30”, and 72o x 1’. 4l of stop solution was added to each reaction tube after cycling, then samples were denatured for 3 min. 3l of each sample was loaded onto the s ...
... reaction tubes were placed in the thermal cycler for 2 min at 94o, then at the following temperatures for 35 cycles: 94o x 30”, 58o x 30”, and 72o x 1’. 4l of stop solution was added to each reaction tube after cycling, then samples were denatured for 3 min. 3l of each sample was loaded onto the s ...
Group 6 - Purdue Genomics Wiki
... Matched orthologs in 5 other plant genomes. Image from: http://pdb.rcsb.org ...
... Matched orthologs in 5 other plant genomes. Image from: http://pdb.rcsb.org ...
Real-time polymerase chain reaction

A real-time polymerase chain reaction is a laboratory technique of molecular biology based on the polymerase chain reaction (PCR). It monitors the amplification of a targeted DNA molecule during the PCR, i.e. in real-time, and not at its end, as in conventional PCR. Real-time PCR can be used quantitatively (Quantitative real-time PCR), semi-quantitatively, i.e. above/below a certain amount of DNA molecules (Semi quantitative real-time PCR) or qualitatively (Qualitative real-time PCR).Two common methods for the detection of PCR products in real-time PCR are: (1) non-specific fluorescent dyes that intercalate with any double-stranded DNA, and (2) sequence-specific DNA probes consisting of oligonucleotides that are labelled with a fluorescent reporter which permits detection only after hybridization of the probe with its complementary sequence.The Minimum Information for Publication of Quantitative Real-Time PCR Experiments (MIQE) guidelines propose that the abbreviation qPCR be used for quantitative real-time PCR and that RT-qPCR be used for reverse transcription–qPCR [1]. The acronym ""RT-PCR"" commonly denotes reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction and not real-time PCR, but not all authors adhere to this convention.