Soil Study Guide
... plants and animals. 4. Rocks are made of minerals. 5. Silt is fine particles of soil that are carried along by flowing water and settle at the bottom of a lake or river. 6. Loam is the best soil for plants to grow in, especially vegetables. 7. Sandy soil has large grains and does not hold water well ...
... plants and animals. 4. Rocks are made of minerals. 5. Silt is fine particles of soil that are carried along by flowing water and settle at the bottom of a lake or river. 6. Loam is the best soil for plants to grow in, especially vegetables. 7. Sandy soil has large grains and does not hold water well ...
SOIL COVER IN FLOODPLAINS OF SMALL RIVERS IN THE
... The reserve territory has several protected areas which are especially protected and prohibited for entrance (buffer), open for visits (tourist excursion zone), for recreational use (security zone) and the rest infrastructure. Our studies were carried out in Kaltat river valleys (the left tributary ...
... The reserve territory has several protected areas which are especially protected and prohibited for entrance (buffer), open for visits (tourist excursion zone), for recreational use (security zone) and the rest infrastructure. Our studies were carried out in Kaltat river valleys (the left tributary ...
Loss of Topsoil - Teacher Demonstration File
... 1. The energetic water movement and carried debris will uproot plants and damage them. Floodwater also exposes plant roots by carrying away precious topsoil. 2. They cannot access oxygen for respiration (energy production) because of the barrier of covering water. 3. They cannot access carbon dioxid ...
... 1. The energetic water movement and carried debris will uproot plants and damage them. Floodwater also exposes plant roots by carrying away precious topsoil. 2. They cannot access oxygen for respiration (energy production) because of the barrier of covering water. 3. They cannot access carbon dioxid ...
Chapter 2-section 3 geology notes
... III. How does conservation plowing help conserve soil? The previous year’s crop residue protects the soil. A. Contour plowing- farmers plow their fields along the curves of a slope t o slow runoff of excess rainfall. B. Conservation plowing- farmers disturb the soil and plant cover as little as poss ...
... III. How does conservation plowing help conserve soil? The previous year’s crop residue protects the soil. A. Contour plowing- farmers plow their fields along the curves of a slope t o slow runoff of excess rainfall. B. Conservation plowing- farmers disturb the soil and plant cover as little as poss ...
Lindsey`s Basic Guide to the Soil Orders of Canada Disclaimer: This
... Lindsey’s Basic Guide to the Soil Orders of Canada Disclaimer: This is an extreme generalization of soil orders of Canada. More information about each order can be found in the Canadian System of Soil Classification and the Soil Management Guide. However, I have found that these resources can be dif ...
... Lindsey’s Basic Guide to the Soil Orders of Canada Disclaimer: This is an extreme generalization of soil orders of Canada. More information about each order can be found in the Canadian System of Soil Classification and the Soil Management Guide. However, I have found that these resources can be dif ...
handout
... which bacteria and fungi inhabit it, what ingredients you have put inside, and environmental factors such as light, temperature and moisture. The first decomposing organisms that go to work attack the most available food molecules, such as sugars, carbohydrates and proteins. As they grow, these firs ...
... which bacteria and fungi inhabit it, what ingredients you have put inside, and environmental factors such as light, temperature and moisture. The first decomposing organisms that go to work attack the most available food molecules, such as sugars, carbohydrates and proteins. As they grow, these firs ...
Identification of exogenous growth stimulants or N
... beneficial relationship with Wheat. Previous studies by ADAS/University of Notting ham (CE0153) indicated that inoculation of wheat with A.caulinodans may offer the potential to supply agriculturally useful quantities of nitrogen to the cropping system as well as providing hormonal stimulation to ro ...
... beneficial relationship with Wheat. Previous studies by ADAS/University of Notting ham (CE0153) indicated that inoculation of wheat with A.caulinodans may offer the potential to supply agriculturally useful quantities of nitrogen to the cropping system as well as providing hormonal stimulation to ro ...
Soil Notes PowerPoint
... Clay - < .002 mm in size. Water clings to tiny particles holding larger soil particles together forming clumps called aggregates. Aggregates like gravel provide drainage channels for water. Water will not drain in soils with a lot of clay. Clay is easily compacted, crushing air and water pore space. ...
... Clay - < .002 mm in size. Water clings to tiny particles holding larger soil particles together forming clumps called aggregates. Aggregates like gravel provide drainage channels for water. Water will not drain in soils with a lot of clay. Clay is easily compacted, crushing air and water pore space. ...
Abiotic Factors Lesson Quiz A Multiple Choice 1.
... C. insects 2. Which object is a part of climate? A. river B. bacteria C. moisture 3. How does the atmosphere benefit life on Earth? A. It provides light to Earth. B. It breaks down dead plants and animals. C. It filters out certain harmful rays from the Sun. ...
... C. insects 2. Which object is a part of climate? A. river B. bacteria C. moisture 3. How does the atmosphere benefit life on Earth? A. It provides light to Earth. B. It breaks down dead plants and animals. C. It filters out certain harmful rays from the Sun. ...
Soil formation
... some sea molluscs produce acid substances that dig holes in the rock and use them as a shelter ...
... some sea molluscs produce acid substances that dig holes in the rock and use them as a shelter ...
Nitrifying bacteria Nitrifying bacteria Nitrogen fixing bacteria De
... • All organisms need nitrogen to make proteins. • Nitrogen gas makes up 78% of our air but it cannot be used directly by most organisms. • Organisms get nitrogen from substances that contain nitrogen. Examples? ...
... • All organisms need nitrogen to make proteins. • Nitrogen gas makes up 78% of our air but it cannot be used directly by most organisms. • Organisms get nitrogen from substances that contain nitrogen. Examples? ...
Soil Stories
... Soil: A complex mixture of minerals, air, water, and microorganisms that supports life on Earth. Soils modify the atmosphere by emitting and absorbing dust and gases. They process and recycle nutrients, including carbon, so that living things can use them over and over again. ...
... Soil: A complex mixture of minerals, air, water, and microorganisms that supports life on Earth. Soils modify the atmosphere by emitting and absorbing dust and gases. They process and recycle nutrients, including carbon, so that living things can use them over and over again. ...
GLACIAL EROSIONAL FEATURES
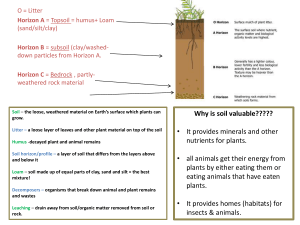
... Soil Profile = Pedon – vertical cuts made into the soil to expose its layers or horizons Soil Zones (Horizons) = the soil profile; many of the horizons may have subdivisions 1) O (organic) horizon - surface-litter layer; consists of fresh & decaying organic matter (freshly fallen leaves, twigs, anim ...
... Soil Profile = Pedon – vertical cuts made into the soil to expose its layers or horizons Soil Zones (Horizons) = the soil profile; many of the horizons may have subdivisions 1) O (organic) horizon - surface-litter layer; consists of fresh & decaying organic matter (freshly fallen leaves, twigs, anim ...
HYDROTHERMAL VENT PPT
... • Sulfur bacteria serve as the primary producers. They harvest energy from hydrogen sulfide discharged from cracks in Earth’s crust. This process is called chemosynthesis. • Animals of the vent communities feed on these bacteria. Some animals consume them directly. ...
... • Sulfur bacteria serve as the primary producers. They harvest energy from hydrogen sulfide discharged from cracks in Earth’s crust. This process is called chemosynthesis. • Animals of the vent communities feed on these bacteria. Some animals consume them directly. ...
CHOOSING LANDSCAPE PLANTS FOR MOIST AREAS
... downspout, near a garden pond, or a naturally occurring low spot in the yard to name a few. Planting most types of trees or shrubs in these areas results in a condition knows as “wet feet.” The saturated soil has less oxygen, the roots of the plant become damaged, and root rot takes place. It may ta ...
... downspout, near a garden pond, or a naturally occurring low spot in the yard to name a few. Planting most types of trees or shrubs in these areas results in a condition knows as “wet feet.” The saturated soil has less oxygen, the roots of the plant become damaged, and root rot takes place. It may ta ...
Composition of Soil
... The amount of water in the soil is closely linked with the climate and other characteristics of the region. The amount of water in the soil is one thing that can affect the amount of air. Very wet soil like you would find in a wetland probably has very little air. The composition of the soil affect ...
... The amount of water in the soil is closely linked with the climate and other characteristics of the region. The amount of water in the soil is one thing that can affect the amount of air. Very wet soil like you would find in a wetland probably has very little air. The composition of the soil affect ...
F2- Microbes and the Environment
... chlorophyll to trap sunlight • Chemosynthetic bacteria use chemical energy • Change inorganic molecules into organic molecules that can be used by other organisms for food ...
... chlorophyll to trap sunlight • Chemosynthetic bacteria use chemical energy • Change inorganic molecules into organic molecules that can be used by other organisms for food ...
Bloomington Community Orchard Fertility and Species Apple – also
... rugosa annulata may be the best, cheapest, and wisest way to manage long-‐term other nutrient needs. If we aim to use legumes such as clover for perennial nitrogen needs, molybdenum (Mo) is key to ...
... rugosa annulata may be the best, cheapest, and wisest way to manage long-‐term other nutrient needs. If we aim to use legumes such as clover for perennial nitrogen needs, molybdenum (Mo) is key to ...
CLASSIFICATION
... – expanded to include new and different living things – will continue to grow as human knowledge grows ...
... – expanded to include new and different living things – will continue to grow as human knowledge grows ...
soil study guide 2015
... Conservation of soil - a method to maintain the fertility of the soil by protecting the soil from erosion and nutrient loss. Contour plowing - forms ridges, slows the water flow and helps save precious topsoil. Terraced farming - uses "steps" that are built into the side of a mountain or hill. Good ...
... Conservation of soil - a method to maintain the fertility of the soil by protecting the soil from erosion and nutrient loss. Contour plowing - forms ridges, slows the water flow and helps save precious topsoil. Terraced farming - uses "steps" that are built into the side of a mountain or hill. Good ...
PS Final Project
... After watering, measuring, and recording data about our plants over a period of time, we found results and came to a conclusion. We averaged the heights of the plants and stalks of each category, with the categories being control group, plants with worms in the soil, plants with bacteria added to th ...
... After watering, measuring, and recording data about our plants over a period of time, we found results and came to a conclusion. We averaged the heights of the plants and stalks of each category, with the categories being control group, plants with worms in the soil, plants with bacteria added to th ...
Photosynthesizers
... Fungi Importance • Food production: improved yield due to symbiosis (plants and fungi mycorrhizae), leavened bread (yeast) • Recycling nutrients (through decomposition) • Industrial enzymes (bioremediation) • Plant growth hormones • Antibiotics (penicillin) • Lichens = symbiosis between fungi and ...
... Fungi Importance • Food production: improved yield due to symbiosis (plants and fungi mycorrhizae), leavened bread (yeast) • Recycling nutrients (through decomposition) • Industrial enzymes (bioremediation) • Plant growth hormones • Antibiotics (penicillin) • Lichens = symbiosis between fungi and ...