Passenger Protein Determines Translocation Versus Retention in
... luminal proteins are recovered in the soluble fractions and membrane integrated proteins in the pelleted membrane (Chuck and Lingappa, 1992). In the absence of MM, washing with buffer as a control and alkali treatment resulted in recovery of the protein predominately in the soluble fraction (Fig. 1D ...
... luminal proteins are recovered in the soluble fractions and membrane integrated proteins in the pelleted membrane (Chuck and Lingappa, 1992). In the absence of MM, washing with buffer as a control and alkali treatment resulted in recovery of the protein predominately in the soluble fraction (Fig. 1D ...
Introduction to the BLAST Suite and BLASTN
... Each sequence in the database is then broken into words or short sequences for comparison to the query. When a search is submitted, BLASTN first takes your query DNA sequence and breaks it into words that are quite short (11 nucleotides). It then compares these words to those in the database. As BLA ...
... Each sequence in the database is then broken into words or short sequences for comparison to the query. When a search is submitted, BLASTN first takes your query DNA sequence and breaks it into words that are quite short (11 nucleotides). It then compares these words to those in the database. As BLA ...
G a - Pontificia Universidad Javeriana, Cali
... Most of biological functions are mediated by protein interactions. These interactions can be physical, such as when two proteins form a complex, or “logical,” such as when one or more proteins control the behavior of one or more other proteins without physical interaction. ...
... Most of biological functions are mediated by protein interactions. These interactions can be physical, such as when two proteins form a complex, or “logical,” such as when one or more proteins control the behavior of one or more other proteins without physical interaction. ...
Cloning and sequencing of a gene encoding acidophilic amylase
... with apparent molecular masses of 90 and 160 kDa (Fig. 1). The same bands of starch degradation were observed when SDS-PAGE was performed under non-reducing conditions (data not shown). Therefore, the 160 kDa form was apparently not a disulphide-linkeddimer of the 90 kDa form. The amount of protein ...
... with apparent molecular masses of 90 and 160 kDa (Fig. 1). The same bands of starch degradation were observed when SDS-PAGE was performed under non-reducing conditions (data not shown). Therefore, the 160 kDa form was apparently not a disulphide-linkeddimer of the 90 kDa form. The amount of protein ...
Hemoglobin
... extracellular protein, fibrillin, which is an integral constituent of the noncollagenous microfibrils of the extracellular matrix. Several forms of familial hypercholesterolemia are the result of genetic defects in the gene encoding the receptor for low-density lipoprotein (LDL). These defects resul ...
... extracellular protein, fibrillin, which is an integral constituent of the noncollagenous microfibrils of the extracellular matrix. Several forms of familial hypercholesterolemia are the result of genetic defects in the gene encoding the receptor for low-density lipoprotein (LDL). These defects resul ...
Sequence and phylogenetic analysis of the gp200 protein of
... Ehrlichia (E.) canis is a Gram-negative obligate intracellular bacterium responsible for canine monocytic ehrlichiosis. Currently, the genetic diversity of E. canis strains worldwide is poorly defined. In the present study, sequence analysis of the nearly full-length 16S rDNA (1,620 bp) and the comp ...
... Ehrlichia (E.) canis is a Gram-negative obligate intracellular bacterium responsible for canine monocytic ehrlichiosis. Currently, the genetic diversity of E. canis strains worldwide is poorly defined. In the present study, sequence analysis of the nearly full-length 16S rDNA (1,620 bp) and the comp ...
Molecular Characterization of a Hamster Oviduct
... of the mature form of the HOGP region. The amino acid sequence of HOGP appeared to have eight potential N-glycosylation sites. Northern blot analysis revealed that a single message of approximately 2.5 kb was present inoviductal RNA but not inthe RNA of several other hamster tissues. The HOGP showed ...
... of the mature form of the HOGP region. The amino acid sequence of HOGP appeared to have eight potential N-glycosylation sites. Northern blot analysis revealed that a single message of approximately 2.5 kb was present inoviductal RNA but not inthe RNA of several other hamster tissues. The HOGP showed ...
Structure and biosynthesis of the signal
... The signal-sequence receptor (SSR) has previously been shown to be a component of the environment which nascent polypeptides meet on passage through the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) membrane. We report here on the primary structure of the SSR as deduced from cDNA clones and from direct protein sequenc ...
... The signal-sequence receptor (SSR) has previously been shown to be a component of the environment which nascent polypeptides meet on passage through the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) membrane. We report here on the primary structure of the SSR as deduced from cDNA clones and from direct protein sequenc ...
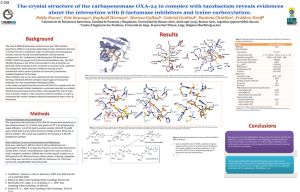
... carbapenems, the “carbapenem hydrolyzing class D β-lactamases” (CHDL). Within this group, mainly found in Acinetobacter spp., the OXA24/OXA-40 group is one of the most prevalent. Class D enzymes are generally characterized by a poor sensitivity to clavulanic acid, sulbactam and tazobactam, the -lact ...
Citrate synthase proteins in extremophilic organisms: Studies within
... native structures and sequences of amino acids. An evolutionary divergence from a common ancestor may lead diverse sequences to fold to nearly the same native structure. One particularly interesting example is citrate synthase (CS), an enzyme that is found in most living organisms, from bacteria to ...
... native structures and sequences of amino acids. An evolutionary divergence from a common ancestor may lead diverse sequences to fold to nearly the same native structure. One particularly interesting example is citrate synthase (CS), an enzyme that is found in most living organisms, from bacteria to ...
GFP (Green fluorescent protein)
... • The GFP gene can be introduced into organisms and maintained in their genome through breeding, injection with a viral vector, or cell transformation. To date, the GFP gene has been introduced and expressed in many bacteria, yeast and other fungi, fish (such as zebra fish), plant, fly, and mammalia ...
... • The GFP gene can be introduced into organisms and maintained in their genome through breeding, injection with a viral vector, or cell transformation. To date, the GFP gene has been introduced and expressed in many bacteria, yeast and other fungi, fish (such as zebra fish), plant, fly, and mammalia ...
LNBI 9043 - Lupin Allergy: Uncovering Structural Features and
... On the other hand, with the rapid introduction of novel foods and new ingredients in traditional foods, the number of reports of allergic reactions to lupin proteins is also rising, either as primary lupin allergy or as a result of cross-reactivity to other legume proteins, particularly peanut, soyb ...
... On the other hand, with the rapid introduction of novel foods and new ingredients in traditional foods, the number of reports of allergic reactions to lupin proteins is also rising, either as primary lupin allergy or as a result of cross-reactivity to other legume proteins, particularly peanut, soyb ...
Bryan 2012 Research Day Poster
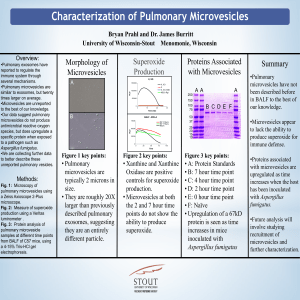
... Fig. 3: Protein analysis of pulmonary microvesicle samples at different time points from BALF of C57 mice, using a 4-15% Tris-HCl gel electrophoresis. ...
... Fig. 3: Protein analysis of pulmonary microvesicle samples at different time points from BALF of C57 mice, using a 4-15% Tris-HCl gel electrophoresis. ...
Gene Section NOL3 (nucleolar protein 3 (apoptosis repressor with CARD domain))
... thick boxes) and 3 small introns. The translational start site is in exon 2. Alternative splicing occurs between exons 2 and 3. This involves two splice donors separated by 10 nucleotides in exon 2 connecting to a single splice acceptor in exon 3 (Stoss et al., 1999). Because the separation between ...
... thick boxes) and 3 small introns. The translational start site is in exon 2. Alternative splicing occurs between exons 2 and 3. This involves two splice donors separated by 10 nucleotides in exon 2 connecting to a single splice acceptor in exon 3 (Stoss et al., 1999). Because the separation between ...
Amino Acids, Proteins, and Enzymes
... • Collagens are the most important protein in mammals. They form about 30% of total body proteins. • There are more than 20 types of collagens, the most common type is collagen I which constitutes about 90% of cell collagens. • Structure of collagen: three helical polypeptide chains (trimeric) twist ...
... • Collagens are the most important protein in mammals. They form about 30% of total body proteins. • There are more than 20 types of collagens, the most common type is collagen I which constitutes about 90% of cell collagens. • Structure of collagen: three helical polypeptide chains (trimeric) twist ...
Proteins and their Ligands: Their Importance and how to Crystallize
... The most important point concerning preparing co-crystallization trials is the knowledge of the corresponding kinetical parameters. Proteins bind their natural ligand(s) with high affinity, which means in the nM- up to low mM range. To successfully crystallize a protein with the ligand(s) bound, the ...
... The most important point concerning preparing co-crystallization trials is the knowledge of the corresponding kinetical parameters. Proteins bind their natural ligand(s) with high affinity, which means in the nM- up to low mM range. To successfully crystallize a protein with the ligand(s) bound, the ...
Redalyc.Influence of Mg2+ ions on the interaction between 3,5
... homology template for HTLV-I IN. The catalytic domain of Avian Sarcoma Virus (ASV) Integrase (PDB: 1VSD) (16) showed the highest homology score. The homology model was constructed using Prime software (Schrodinger, Inc). The HTLV-I IN secondary structure was determined by alignment of its core domai ...
... homology template for HTLV-I IN. The catalytic domain of Avian Sarcoma Virus (ASV) Integrase (PDB: 1VSD) (16) showed the highest homology score. The homology model was constructed using Prime software (Schrodinger, Inc). The HTLV-I IN secondary structure was determined by alignment of its core domai ...
anatomy of a feed tag - Westway Feed Products
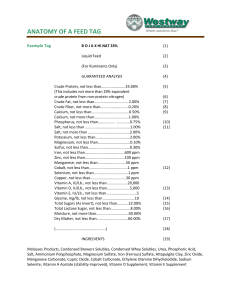
... The Ingredients listing may be even more informative than guarantees regarding quality. All feed label regulations require an ingredient listing. It is commonly believed that the ingredients must be listed in order of amount used in the formula. This is true in pet food and human food labeling, but ...
... The Ingredients listing may be even more informative than guarantees regarding quality. All feed label regulations require an ingredient listing. It is commonly believed that the ingredients must be listed in order of amount used in the formula. This is true in pet food and human food labeling, but ...
Comparison of the Structure of the Extrinsic 33 kDa Protein from
... structure of the 33 kDa protein may be different, at least in its free form, among different plant species. The cleavage sites of the 33 kDa protein by protease were reported to be different between higher plant and cyanobacterium. The higher plant 33 kDa protein was cleaved at 16Y by chymotrypsin a ...
... structure of the 33 kDa protein may be different, at least in its free form, among different plant species. The cleavage sites of the 33 kDa protein by protease were reported to be different between higher plant and cyanobacterium. The higher plant 33 kDa protein was cleaved at 16Y by chymotrypsin a ...
PowerPoint 演示文稿
... • (1) Bacteriophage and viral transcipts and (2) many mRNAs for hormones in eukaryotes (e.g. pro-opiomelanocortin) are translated to give a single polypeptide chain that is cleaved subsequently by specific proteases to produce multiple mature protein from one translation product. The parent polypept ...
... • (1) Bacteriophage and viral transcipts and (2) many mRNAs for hormones in eukaryotes (e.g. pro-opiomelanocortin) are translated to give a single polypeptide chain that is cleaved subsequently by specific proteases to produce multiple mature protein from one translation product. The parent polypept ...
Cloning and sequence analysis of cnaA gene encoding the catalytic
... calcineurin A from ¢lamentous fungi suggested its requirement for hyphal growth and cell cycle regulation [5,6], a putative role of this protein phosphatase in sporulation, salt stress response and the alkaline pH-mediated signal transduction pathway in fungi has not been examined. Interestingly, a ...
... calcineurin A from ¢lamentous fungi suggested its requirement for hyphal growth and cell cycle regulation [5,6], a putative role of this protein phosphatase in sporulation, salt stress response and the alkaline pH-mediated signal transduction pathway in fungi has not been examined. Interestingly, a ...
Evolution and Function of the Plant Cell Wall
... their role(s) in plant cell wall synthesis. The apparent disparate functions of the GT8 family (i.e. the GAUTs and GATLs as proven and putative plant cell wall polysaccharide biosynthetic a-galacturonosyltransferases, the eukaryotic GolSs as a-galactosyltransferases that synthesize the first step in ...
... their role(s) in plant cell wall synthesis. The apparent disparate functions of the GT8 family (i.e. the GAUTs and GATLs as proven and putative plant cell wall polysaccharide biosynthetic a-galacturonosyltransferases, the eukaryotic GolSs as a-galactosyltransferases that synthesize the first step in ...
Homology modeling

Homology modeling, also known as comparative modeling of protein, refers to constructing an atomic-resolution model of the ""target"" protein from its amino acid sequence and an experimental three-dimensional structure of a related homologous protein (the ""template""). Homology modeling relies on the identification of one or more known protein structures likely to resemble the structure of the query sequence, and on the production of an alignment that maps residues in the query sequence to residues in the template sequence. It has been shown that protein structures are more conserved than protein sequences amongst homologues, but sequences falling below a 20% sequence identity can have very different structure.Evolutionarily related proteins have similar sequences and naturally occurring homologous proteins have similar protein structure.It has been shown that three-dimensional protein structure is evolutionarily more conserved than would be expected on the basis of sequence conservation alone.The sequence alignment and template structure are then used to produce a structural model of the target. Because protein structures are more conserved than DNA sequences, detectable levels of sequence similarity usually imply significant structural similarity.The quality of the homology model is dependent on the quality of the sequence alignment and template structure. The approach can be complicated by the presence of alignment gaps (commonly called indels) that indicate a structural region present in the target but not in the template, and by structure gaps in the template that arise from poor resolution in the experimental procedure (usually X-ray crystallography) used to solve the structure. Model quality declines with decreasing sequence identity; a typical model has ~1–2 Å root mean square deviation between the matched Cα atoms at 70% sequence identity but only 2–4 Å agreement at 25% sequence identity. However, the errors are significantly higher in the loop regions, where the amino acid sequences of the target and template proteins may be completely different.Regions of the model that were constructed without a template, usually by loop modeling, are generally much less accurate than the rest of the model. Errors in side chain packing and position also increase with decreasing identity, and variations in these packing configurations have been suggested as a major reason for poor model quality at low identity. Taken together, these various atomic-position errors are significant and impede the use of homology models for purposes that require atomic-resolution data, such as drug design and protein–protein interaction predictions; even the quaternary structure of a protein may be difficult to predict from homology models of its subunit(s). Nevertheless, homology models can be useful in reaching qualitative conclusions about the biochemistry of the query sequence, especially in formulating hypotheses about why certain residues are conserved, which may in turn lead to experiments to test those hypotheses. For example, the spatial arrangement of conserved residues may suggest whether a particular residue is conserved to stabilize the folding, to participate in binding some small molecule, or to foster association with another protein or nucleic acid. Homology modeling can produce high-quality structural models when the target and template are closely related, which has inspired the formation of a structural genomics consortium dedicated to the production of representative experimental structures for all classes of protein folds. The chief inaccuracies in homology modeling, which worsen with lower sequence identity, derive from errors in the initial sequence alignment and from improper template selection. Like other methods of structure prediction, current practice in homology modeling is assessed in a biennial large-scale experiment known as the Critical Assessment of Techniques for Protein Structure Prediction, or CASP.