manualE6901
... pTXB1 (NEB #N6707) contains a mini-intein from the Mycobacterium xenopi gyrA gene (Mxe GyrA intein; 198 amino acid residues) that has been modified to undergo thiol-induced cleavage at its N-terminus (3,5). The vector allows for the purification of a target protein without any extra amino acids by c ...
... pTXB1 (NEB #N6707) contains a mini-intein from the Mycobacterium xenopi gyrA gene (Mxe GyrA intein; 198 amino acid residues) that has been modified to undergo thiol-induced cleavage at its N-terminus (3,5). The vector allows for the purification of a target protein without any extra amino acids by c ...
Optimal dietary amino acid ratio for broilers based on dietary amino
... Experimental diets with different limiting AAs were created by dilution of the CD with corn starch to achieve 70% of the EAA level in CD and refilled with crystalline EAAs, except the EAA under study. In all experimental diets, the remaining nutrient and energy contents were the same respectively. T ...
... Experimental diets with different limiting AAs were created by dilution of the CD with corn starch to achieve 70% of the EAA level in CD and refilled with crystalline EAAs, except the EAA under study. In all experimental diets, the remaining nutrient and energy contents were the same respectively. T ...
Substrate Specificity and Mechanism from the Structure of
... hydroxyl groups exposed to the solvent and not forming any direct hydrogen bonds to the enzyme. The residues 99PLGAGLSSSAS109 corresponding to motif 2 (Figure 1), form a phosphate-binding loop which wraps around the b-phosphate group, forming hydrogen bonds with the main-chain amide groups of Gly101 ...
... hydroxyl groups exposed to the solvent and not forming any direct hydrogen bonds to the enzyme. The residues 99PLGAGLSSSAS109 corresponding to motif 2 (Figure 1), form a phosphate-binding loop which wraps around the b-phosphate group, forming hydrogen bonds with the main-chain amide groups of Gly101 ...
Candida antarctica Anders G. Sandström
... Enzymes are used in industry either isolated or in living whole-cell systems. Many energy-efficient processes have been developed using enzymes, as many enzymes have their temperature optimum at room temperature.12 Enzymes are large polypeptides that are easy to produce with modern recombinant gene ...
... Enzymes are used in industry either isolated or in living whole-cell systems. Many energy-efficient processes have been developed using enzymes, as many enzymes have their temperature optimum at room temperature.12 Enzymes are large polypeptides that are easy to produce with modern recombinant gene ...
Molecular Clocks
... The rate of this reaction is preset by the sequence and structure of the peptide or protein and associated peptides or proteins as genetically specified in the DNA. The rate may also be modified by changes in protein structure and solvent conditions in-vivo. This rate can be set to have a half-time ...
... The rate of this reaction is preset by the sequence and structure of the peptide or protein and associated peptides or proteins as genetically specified in the DNA. The rate may also be modified by changes in protein structure and solvent conditions in-vivo. This rate can be set to have a half-time ...
Gene Section ABL (v-abl Abelson murine leukemia viral oncogene homolog 1)
... Inhibits cell growth through a direct interaction with Rb in the nucleus. ...
... Inhibits cell growth through a direct interaction with Rb in the nucleus. ...
XSL Formatter - H:\XML
... them to the processing pathway, as well as to an archive. Once processing is complete and if there are no errors in the submission, the files are automatically loaded into GenBank. The processing time is related to the number of submissions that day; therefore, processing can take from one to many h ...
... them to the processing pathway, as well as to an archive. Once processing is complete and if there are no errors in the submission, the files are automatically loaded into GenBank. The processing time is related to the number of submissions that day; therefore, processing can take from one to many h ...
HIGHLY VISCOUS DOUGH FORMING PROPERTIES OF MARAMA PROTEIN
... strong protein network. Marama protein, thus, appeared to have some structural stability, but only when small deformations were applied. The complex viscosity (ŋ*) decreased at increasing frequency for marama protein, which was similar to gluten (Table 2). According to a review by Tunick (2011), bre ...
... strong protein network. Marama protein, thus, appeared to have some structural stability, but only when small deformations were applied. The complex viscosity (ŋ*) decreased at increasing frequency for marama protein, which was similar to gluten (Table 2). According to a review by Tunick (2011), bre ...
PDF
... (44% identity) [11] and from the moderately thermophilic, methanogenic archaeon, Methanosarcina thermophila (38% identity) [14]. However, systematic analyses of the amino acid sequences of analogous mesophilic, moderately thermophilic and hyperthermophilic proteins, even in the case of small redox p ...
... (44% identity) [11] and from the moderately thermophilic, methanogenic archaeon, Methanosarcina thermophila (38% identity) [14]. However, systematic analyses of the amino acid sequences of analogous mesophilic, moderately thermophilic and hyperthermophilic proteins, even in the case of small redox p ...
Protein Structure Prediction Based on Neural Networks
... template protein, which has a known 3D structure. Although the computational method has several advantages over the experimental methods, its accuracy is templateintensive. This method assumes that the assignments from the chemical properties to the spatial regions between the query protein and the ...
... template protein, which has a known 3D structure. Although the computational method has several advantages over the experimental methods, its accuracy is templateintensive. This method assumes that the assignments from the chemical properties to the spatial regions between the query protein and the ...
PDF
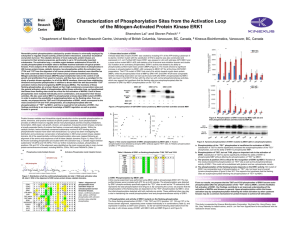
... (19–22). In this site, ‘‘x’’ refers to any amino acid, ‘‘B’’ to a residue with a hydrophobic side chain and the ‘‘S兾T’’ to the serine or threonine residue that is the site of phosphate addition. A second consensus site of R⫺6-x⫺5-x⫺4-R⫺3-x⫺2-x⫺1-S兾T-B⫹1 has been identified for mammalian PKA enzymes ...
... (19–22). In this site, ‘‘x’’ refers to any amino acid, ‘‘B’’ to a residue with a hydrophobic side chain and the ‘‘S兾T’’ to the serine or threonine residue that is the site of phosphate addition. A second consensus site of R⫺6-x⫺5-x⫺4-R⫺3-x⫺2-x⫺1-S兾T-B⫹1 has been identified for mammalian PKA enzymes ...
Print
... form a linear polymer constitutes the primary structure of the protein. Linear polypeptide chains are often cross-linked, most commonly by two cysteine residues linked together to form a cystine unit. 2. Secondary structure: The folding of a polypeptide backbone by means of internal hydrogen bonds b ...
... form a linear polymer constitutes the primary structure of the protein. Linear polypeptide chains are often cross-linked, most commonly by two cysteine residues linked together to form a cystine unit. 2. Secondary structure: The folding of a polypeptide backbone by means of internal hydrogen bonds b ...
Bosque, a software system for phylogenetic analysis
... 2. Install the software on your computer 3. Execute Bosque. The first time you will need to specify where do you want to leave the file containing the local database 4. Create a Project, by giving it any descriptive name. 5. Create a Tree Project within your recently created Project (step 3). To cre ...
... 2. Install the software on your computer 3. Execute Bosque. The first time you will need to specify where do you want to leave the file containing the local database 4. Create a Project, by giving it any descriptive name. 5. Create a Tree Project within your recently created Project (step 3). To cre ...
The Three-dimensional Structure of 4-Hydroxybenzoyl
... droxyl for a chloro group at the para-position of the aromatic ring. In the last step, the thioester linkage between the CoA moiety and the 4-hydroxybenzoyl group is cleaved by 4-hydroxybenzoyl-CoA thioesterase, hereafter referred to simply as thioesterase. The genes encoding these three enzymes are ...
... droxyl for a chloro group at the para-position of the aromatic ring. In the last step, the thioester linkage between the CoA moiety and the 4-hydroxybenzoyl group is cleaved by 4-hydroxybenzoyl-CoA thioesterase, hereafter referred to simply as thioesterase. The genes encoding these three enzymes are ...
Statistical Analysis of Amino Acid Patterns in Transmembrane
... Thus, structural information in a membrane protein sequence can be statistically interpreted. Elements of the structural simplicity of these proteins suggest the existence of commonly used patterns in transmembrane helix-helix interactions. First, the space that natural selection can sample in searc ...
... Thus, structural information in a membrane protein sequence can be statistically interpreted. Elements of the structural simplicity of these proteins suggest the existence of commonly used patterns in transmembrane helix-helix interactions. First, the space that natural selection can sample in searc ...
Predicting Protein Stability Changes upon Mutation Using Database
... of interactions. Local interactions along the chain are described by torsion potentials, based on propensities of amino acids to be associated with backbone torsion angle domains. Non-local interactions along the sequence are represented by distance potentials, derived from propensities of amino aci ...
... of interactions. Local interactions along the chain are described by torsion potentials, based on propensities of amino acids to be associated with backbone torsion angle domains. Non-local interactions along the sequence are represented by distance potentials, derived from propensities of amino aci ...
Field Guide to Protein Folds
... The cyclin-box is an approximately 100-residue domain found in all cyclin and cyclin-like domains that acts as a generalized adaptor motif to recognize diverse proteins and DNAs that are involved in cell cycle and transcriptional regulation. It consists of five helices with a central helix (helix 3) ...
... The cyclin-box is an approximately 100-residue domain found in all cyclin and cyclin-like domains that acts as a generalized adaptor motif to recognize diverse proteins and DNAs that are involved in cell cycle and transcriptional regulation. It consists of five helices with a central helix (helix 3) ...
A Survey of Flexible Protein Binding Mechanisms and their
... quantitative prediction of the dynamics and specificity of protein recognition and assembly. Such understanding may lead to the ability to design partners that form more stable complexes, which can then act as “network” drugs. Understanding interactions will also help us to find ways of inhibiting p ...
... quantitative prediction of the dynamics and specificity of protein recognition and assembly. Such understanding may lead to the ability to design partners that form more stable complexes, which can then act as “network” drugs. Understanding interactions will also help us to find ways of inhibiting p ...
Protein proteinase inhibitors from avian egg whites
... secretion of ovoinhibitor in oviduct is controlled by estrogen and progesterone, and is also stimulated by insulin and dexamethasone. Ovoinhibitors from chicken, turkey, Japanese quail, penguin and ostrich have been isolated and studied in detail. The protein is immunologically related to the a2-pro ...
... secretion of ovoinhibitor in oviduct is controlled by estrogen and progesterone, and is also stimulated by insulin and dexamethasone. Ovoinhibitors from chicken, turkey, Japanese quail, penguin and ostrich have been isolated and studied in detail. The protein is immunologically related to the a2-pro ...
Chapter 1: Biological Introduction: RING domain proteins
... this has not been applied thus far for RING fingers. The spectroscopic properties of RING domains can be investigated indirectly using a variety of spectroscopic techniques, due to the fact that one can substitute the zinc ion by other metals such as cobalt(II) or cadmium(II) (Lovering et al., 1993). ...
... this has not been applied thus far for RING fingers. The spectroscopic properties of RING domains can be investigated indirectly using a variety of spectroscopic techniques, due to the fact that one can substitute the zinc ion by other metals such as cobalt(II) or cadmium(II) (Lovering et al., 1993). ...
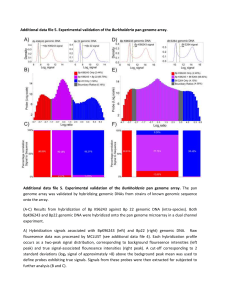
Additional file 5
... B) Probes exhibiting true signals were subdivided into those showing (red) signals only in the Bp K96243 hybridization, (purple) signals in both the BpK96243 and Bp22 hybridization, and (blue) signals only in the Bp22 hybridization. Y-axis : Probe abundance (log2 scale). X-axis : Hybridization rati ...
... B) Probes exhibiting true signals were subdivided into those showing (red) signals only in the Bp K96243 hybridization, (purple) signals in both the BpK96243 and Bp22 hybridization, and (blue) signals only in the Bp22 hybridization. Y-axis : Probe abundance (log2 scale). X-axis : Hybridization rati ...
Simulation of Enzyme Reaction - diss.fu
... In principle all models that are used to investigate electrostatic properties of macromolecules are derived from the Poisson equation. It is dependent from the considered problem how the equation is used: If the charge distribution of a given system is homogeneous with ε = 1 and can be described exp ...
... In principle all models that are used to investigate electrostatic properties of macromolecules are derived from the Poisson equation. It is dependent from the considered problem how the equation is used: If the charge distribution of a given system is homogeneous with ε = 1 and can be described exp ...
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
... Comparison with CNT Although the amino acid sequence varies, the structure of the hairpin tip – capping loop motif is conserved between the two proteins, suggesting that this structural motif may be a common Na+binding motif in membrane transporter proteins. While vcINDY and CNT share a similar core ...
... Comparison with CNT Although the amino acid sequence varies, the structure of the hairpin tip – capping loop motif is conserved between the two proteins, suggesting that this structural motif may be a common Na+binding motif in membrane transporter proteins. While vcINDY and CNT share a similar core ...
Homology modeling

Homology modeling, also known as comparative modeling of protein, refers to constructing an atomic-resolution model of the ""target"" protein from its amino acid sequence and an experimental three-dimensional structure of a related homologous protein (the ""template""). Homology modeling relies on the identification of one or more known protein structures likely to resemble the structure of the query sequence, and on the production of an alignment that maps residues in the query sequence to residues in the template sequence. It has been shown that protein structures are more conserved than protein sequences amongst homologues, but sequences falling below a 20% sequence identity can have very different structure.Evolutionarily related proteins have similar sequences and naturally occurring homologous proteins have similar protein structure.It has been shown that three-dimensional protein structure is evolutionarily more conserved than would be expected on the basis of sequence conservation alone.The sequence alignment and template structure are then used to produce a structural model of the target. Because protein structures are more conserved than DNA sequences, detectable levels of sequence similarity usually imply significant structural similarity.The quality of the homology model is dependent on the quality of the sequence alignment and template structure. The approach can be complicated by the presence of alignment gaps (commonly called indels) that indicate a structural region present in the target but not in the template, and by structure gaps in the template that arise from poor resolution in the experimental procedure (usually X-ray crystallography) used to solve the structure. Model quality declines with decreasing sequence identity; a typical model has ~1–2 Å root mean square deviation between the matched Cα atoms at 70% sequence identity but only 2–4 Å agreement at 25% sequence identity. However, the errors are significantly higher in the loop regions, where the amino acid sequences of the target and template proteins may be completely different.Regions of the model that were constructed without a template, usually by loop modeling, are generally much less accurate than the rest of the model. Errors in side chain packing and position also increase with decreasing identity, and variations in these packing configurations have been suggested as a major reason for poor model quality at low identity. Taken together, these various atomic-position errors are significant and impede the use of homology models for purposes that require atomic-resolution data, such as drug design and protein–protein interaction predictions; even the quaternary structure of a protein may be difficult to predict from homology models of its subunit(s). Nevertheless, homology models can be useful in reaching qualitative conclusions about the biochemistry of the query sequence, especially in formulating hypotheses about why certain residues are conserved, which may in turn lead to experiments to test those hypotheses. For example, the spatial arrangement of conserved residues may suggest whether a particular residue is conserved to stabilize the folding, to participate in binding some small molecule, or to foster association with another protein or nucleic acid. Homology modeling can produce high-quality structural models when the target and template are closely related, which has inspired the formation of a structural genomics consortium dedicated to the production of representative experimental structures for all classes of protein folds. The chief inaccuracies in homology modeling, which worsen with lower sequence identity, derive from errors in the initial sequence alignment and from improper template selection. Like other methods of structure prediction, current practice in homology modeling is assessed in a biennial large-scale experiment known as the Critical Assessment of Techniques for Protein Structure Prediction, or CASP.