link1
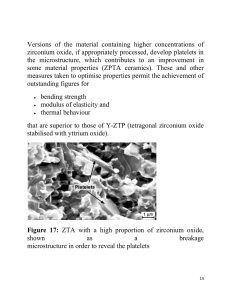
... that are superior to those of Y-ZTP (tetragonal zirconium oxide stabilised with yttrium oxide). ...
... that are superior to those of Y-ZTP (tetragonal zirconium oxide stabilised with yttrium oxide). ...
Oxidation Numbers
... reduction: a decrease in the oxidation number Cl2(g) + 2e− → 2Cl−(aq) Sn4+(aq) + 2e− → Sn2+(aq) (oxidation # becoming less positive or more negative) ...
... reduction: a decrease in the oxidation number Cl2(g) + 2e− → 2Cl−(aq) Sn4+(aq) + 2e− → Sn2+(aq) (oxidation # becoming less positive or more negative) ...
Chapter 4c - Loy Research Group
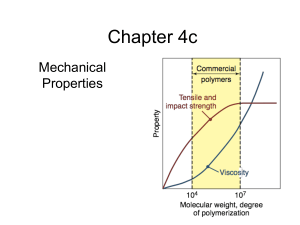
... Stress-strain curves are very dependent on the test method. A modulus determined under compression is generally higher than one derived from a tensile experiment, as shown below for polystyrene. Tensile testing is most sensitive to material flaws and microscopic cracks. Compression tests tend to be ...
... Stress-strain curves are very dependent on the test method. A modulus determined under compression is generally higher than one derived from a tensile experiment, as shown below for polystyrene. Tensile testing is most sensitive to material flaws and microscopic cracks. Compression tests tend to be ...
Net Ionic Equations
... Example: H2 combining with O2 to form water: 2 H2 + O2 2H2O An electron is transferred from H to O: the H2 is oxidized and the O2 is reduced. We use the oxidation number (oxidation state) to keep track of electron shifts in chemical reactions. It is defined as “the charge which an atom appears to ...
... Example: H2 combining with O2 to form water: 2 H2 + O2 2H2O An electron is transferred from H to O: the H2 is oxidized and the O2 is reduced. We use the oxidation number (oxidation state) to keep track of electron shifts in chemical reactions. It is defined as “the charge which an atom appears to ...
Balancing reaction equations, oxidation state, and reduction
... Example: H2 combining with O2 to form water: 2 H2 + O2 → 2H2O An electron is transferred from H to O: the H2 is oxidized and the O2 is reduced. We use the oxidation number (oxidation state) to keep track of electron shifts in chemical reactions. It is defined as “the charge which an atom appears to ...
... Example: H2 combining with O2 to form water: 2 H2 + O2 → 2H2O An electron is transferred from H to O: the H2 is oxidized and the O2 is reduced. We use the oxidation number (oxidation state) to keep track of electron shifts in chemical reactions. It is defined as “the charge which an atom appears to ...
a review- study of thermal spray coatings for corrosive wear
... or non-metallic materials are deposited in a molten or semi-molten condition to form a coating”. The processes comprise: direct current (d.c.) arcs or radio frequency (r.f.) discharges-generated plasmas, plasma transferred arcs (PTA), wire arcs, flames, high velocity oxyfuel flames (HVOF), high velo ...
... or non-metallic materials are deposited in a molten or semi-molten condition to form a coating”. The processes comprise: direct current (d.c.) arcs or radio frequency (r.f.) discharges-generated plasmas, plasma transferred arcs (PTA), wire arcs, flames, high velocity oxyfuel flames (HVOF), high velo ...
1. INTRODUCTION This Chapter briefly introduces
... A solid material is said to be in thin film form when it is built up, as a thin layer on a solid support, called substrate, ab initio by controlled condensation of the individual atomic, molecular, or ionic species, either directly by a physical process, or via a chemical and/ or electrochemical rea ...
... A solid material is said to be in thin film form when it is built up, as a thin layer on a solid support, called substrate, ab initio by controlled condensation of the individual atomic, molecular, or ionic species, either directly by a physical process, or via a chemical and/ or electrochemical rea ...
Resistance Heating
... only short length of it will be required for a particular resistance (and hence heat) or for the same length of the wire and the currrent, heat produced will be more. (2) High Melting Temperature. If the melting temperature of the heating element is high, it would be possible to obtain higher operat ...
... only short length of it will be required for a particular resistance (and hence heat) or for the same length of the wire and the currrent, heat produced will be more. (2) High Melting Temperature. If the melting temperature of the heating element is high, it would be possible to obtain higher operat ...
Describe - The Parker E
... are dissolved by chemical action. It is commonly used in the production of printed circuit boards (PCB’s), where the tracks needed for the electricity to pass through when the circuit is made are protected from the etching solution. Etching is also used to provide decorative finishes on metals and o ...
... are dissolved by chemical action. It is commonly used in the production of printed circuit boards (PCB’s), where the tracks needed for the electricity to pass through when the circuit is made are protected from the etching solution. Etching is also used to provide decorative finishes on metals and o ...
Solid State Synthesis
... a topotactic transformation is characterized by internal atomic displacements, which may include loss or gain of material so that the initial and final lattices are in coherence. epitaxy - The growth of the crystals of one mineral on the crystal face of another mineral, such that the crystalline sub ...
... a topotactic transformation is characterized by internal atomic displacements, which may include loss or gain of material so that the initial and final lattices are in coherence. epitaxy - The growth of the crystals of one mineral on the crystal face of another mineral, such that the crystalline sub ...
Suitable Surface Conditions
... Flame, laser and plasma cutting will change the structure of the steel composition in the immediate area of the heat source. These areas may present thinner coating thicknesses and a lack of adhesion, reducing the ability of the zinc alloy layers to bond with the base metal. The high temperatures ut ...
... Flame, laser and plasma cutting will change the structure of the steel composition in the immediate area of the heat source. These areas may present thinner coating thicknesses and a lack of adhesion, reducing the ability of the zinc alloy layers to bond with the base metal. The high temperatures ut ...
2014 Abstract Booklet
... (Ag,Cu)(In,Ga)(S,Se)2 compound semiconductor family forms a range of chalcopyrite alloys with high solubility and high performances in photovoltaic devices. The current record performance small devices exceeds 20% while active and manufacturable modules exceed 17% efficiency in 900 cm2 areas and 15% ...
... (Ag,Cu)(In,Ga)(S,Se)2 compound semiconductor family forms a range of chalcopyrite alloys with high solubility and high performances in photovoltaic devices. The current record performance small devices exceeds 20% while active and manufacturable modules exceed 17% efficiency in 900 cm2 areas and 15% ...
Superalloy

A superalloy, or high-performance alloy, is an alloy that exhibits several key characteristics: excellent mechanical strength, resistance to thermal creep deformation, good surface stability and resistance to corrosion or oxidation. The crystal structure is typically face-centered cubic austenitic. Examples of such alloys are Hastelloy, Inconel, Waspaloy, Rene alloys, Haynes alloys, Incoloy, MP98T, TMS alloys, and CMSX single crystal alloys.Superalloy development has relied heavily on both chemical and process innovations. Superalloys develop high temperature strength through solid solution strengthening. An important strengthening mechanism is precipitation strengthening which forms secondary phase precipitates such as gamma prime and carbides. Oxidation or corrosion resistance is provided by elements such as aluminium and chromium.The primary application for such alloys is in turbine engines, both aerospace and marine.