Open Access proceedings Journal of Physics: Conference series
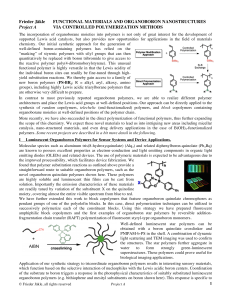
... between the unpaired electron in the core with the unpaired electrons in the outer shell. This can create a number of final states which will be seen in the photoelectron spectrum. For some materials, where plasmon loss peaks occur, there is an enhanced probability for loss of a specific amount of e ...
... between the unpaired electron in the core with the unpaired electrons in the outer shell. This can create a number of final states which will be seen in the photoelectron spectrum. For some materials, where plasmon loss peaks occur, there is an enhanced probability for loss of a specific amount of e ...
syllabus 2014
... Group I and group 2 elements: General introduction, electronic configuration, occurrence, anomalous properties of the first element of each group, diagonal relationship, trends in the variation of properties (such as ionization enthalpy, atomic and ionic radii), trends in chemical reactivity with ox ...
... Group I and group 2 elements: General introduction, electronic configuration, occurrence, anomalous properties of the first element of each group, diagonal relationship, trends in the variation of properties (such as ionization enthalpy, atomic and ionic radii), trends in chemical reactivity with ox ...
PHYSICS CHEMISTRY BIOLOGY
... Group I and group 2 elements: General introduction, electronic configuration, occurrence, anomalous properties of the first element of each group, diagonal relationship, trends in the variation of properties (such as ionization enthalpy, atomic and ionic radii), trends in chemical reactivity with ox ...
... Group I and group 2 elements: General introduction, electronic configuration, occurrence, anomalous properties of the first element of each group, diagonal relationship, trends in the variation of properties (such as ionization enthalpy, atomic and ionic radii), trends in chemical reactivity with ox ...
Coordination chemistry with selected topics in bioinorganic chemistry
... intermolecular interactions. The interactions: chemical bonds and intermolecular forces will be defined and sorted by their energies to illustrate the relative strength of coordination bond on the energy scale. The qualitative description of the valence bond and molecular orbital theories is present ...
... intermolecular interactions. The interactions: chemical bonds and intermolecular forces will be defined and sorted by their energies to illustrate the relative strength of coordination bond on the energy scale. The qualitative description of the valence bond and molecular orbital theories is present ...
AP Chemistry - Allen County Schools
... • periodic relationships, such as atomic radii, ionization energies, electron affinities, oxidation states • horizontal, vertical, & diagonal relationships with examples from alkali metals, alkaline earth metals, halogens, & the first series of transition metals ...
... • periodic relationships, such as atomic radii, ionization energies, electron affinities, oxidation states • horizontal, vertical, & diagonal relationships with examples from alkali metals, alkaline earth metals, halogens, & the first series of transition metals ...
RAJ EAP talk - Rob Jackson`s Website
... Crystal field calculation of the optical transitions • The RE ions are predicted to substitute at the Y sites, and relaxed coordinates of the RE ion and the nearest neighbour F ions are used as input for a crystal field calculation. • Crystal field parameters Bkq are calculated, which can then be u ...
... Crystal field calculation of the optical transitions • The RE ions are predicted to substitute at the Y sites, and relaxed coordinates of the RE ion and the nearest neighbour F ions are used as input for a crystal field calculation. • Crystal field parameters Bkq are calculated, which can then be u ...
Structural basis for the fast phase change of DVD-RAM
... pattern of Ge2Sb2Te5 (953 K) and GeTe (1073 K) liquids show a typical halo pattern peculiar to non-crystalline materials, reflecting the lack of the long-range periodicity. These diffraction patterns show a highly disordered state (liquid state) in which both Ge2Sb2Te5 and GeTe have to undergo durin ...
... pattern of Ge2Sb2Te5 (953 K) and GeTe (1073 K) liquids show a typical halo pattern peculiar to non-crystalline materials, reflecting the lack of the long-range periodicity. These diffraction patterns show a highly disordered state (liquid state) in which both Ge2Sb2Te5 and GeTe have to undergo durin ...
COMPOUNDS Chapter 2 : Preliminary course Chemistry 2
... Elements and compounds have fixed physical and chemical properties. They are pure ...
... Elements and compounds have fixed physical and chemical properties. They are pure ...
Solid

Solid is one of the four fundamental states of matter (the others being liquid, gas, and plasma). It is characterized by structural rigidity and resistance to changes of shape or volume. Unlike a liquid, a solid object does not flow to take on the shape of its container, nor does it expand to fill the entire volume available to it like a gas does. The atoms in a solid are tightly bound to each other, either in a regular geometric lattice (crystalline solids, which include metals and ordinary ice) or irregularly (an amorphous solid such as common window glass).The branch of physics that deals with solids is called solid-state physics, and is the main branch of condensed matter physics (which also includes liquids). Materials science is primarily concerned with the physical and chemical properties of solids. Solid-state chemistry is especially concerned with the synthesis of novel materials, as well as the science of identification and chemical composition.