Grains and grain boundaries in highly crystalline monolayer
... deposition (CVD), characterized defects such as grain boundaries at the atomic scale and demonstrated that these grain boundaries can strongly affect graphene’s electrical, optical and mechanical properties2–11 . Much less is known about the grain structure and properties of defects in other 2D mate ...
... deposition (CVD), characterized defects such as grain boundaries at the atomic scale and demonstrated that these grain boundaries can strongly affect graphene’s electrical, optical and mechanical properties2–11 . Much less is known about the grain structure and properties of defects in other 2D mate ...
NIckel AdsorptIoN oNto cArboN ANode dust modIfIed by AcetIc AcId
... Many applications of carbon materials are strongly influenced by their surface chemistry. Thus their use as adsorbents in aqueous solution, in catalysis or electrochemical process are three examples in which the surface chemistry, microporous structure, high adsorption capacity and high degree of su ...
... Many applications of carbon materials are strongly influenced by their surface chemistry. Thus their use as adsorbents in aqueous solution, in catalysis or electrochemical process are three examples in which the surface chemistry, microporous structure, high adsorption capacity and high degree of su ...
Lecture 6.
... evaporate, leaving salt crystals behind. These salt crystals expand as they are heated up, exerting pressure on the confining rock. Salt crystallization may also take place when solutions decompose rocks (for example, limestone and chalk) to form salt solutions of sodium sulfate orsodium carbonate, ...
... evaporate, leaving salt crystals behind. These salt crystals expand as they are heated up, exerting pressure on the confining rock. Salt crystallization may also take place when solutions decompose rocks (for example, limestone and chalk) to form salt solutions of sodium sulfate orsodium carbonate, ...
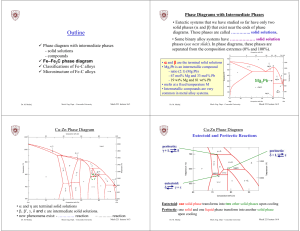
Dielectric Properties of Materials
... Find polarization (P) in dielectric material with dielectric constant, r = 2.8, when D = 3 × 10-8C/m2. An electric field of 6 × 104 volt/meter is applied on a sample of Neon gas at N.T.P. Calculate the dipole moment induced if the dielectric constant of Neon at N.T.P. is 1.000134. Also find out the ...
... Find polarization (P) in dielectric material with dielectric constant, r = 2.8, when D = 3 × 10-8C/m2. An electric field of 6 × 104 volt/meter is applied on a sample of Neon gas at N.T.P. Calculate the dipole moment induced if the dielectric constant of Neon at N.T.P. is 1.000134. Also find out the ...
Band Theories
... Electronic Structure of Covalent and Metallic Crystals Crystals of Covalent Network and Metallic solids can be thought of as Giant Molecules Both localized and delocalized bonding is possible. Use band theory to describe electronic structure in covalent Network and Metallic Crystals ...
... Electronic Structure of Covalent and Metallic Crystals Crystals of Covalent Network and Metallic solids can be thought of as Giant Molecules Both localized and delocalized bonding is possible. Use band theory to describe electronic structure in covalent Network and Metallic Crystals ...
Metal polymer multiscale material formed by arranging
... spin coating of silicon chips. PVP/PMMA films were applied for arranging gold/silver-core/shell nanoparticles on the film surfaces. The method of spontaneous demixing during spin coating was applied for formation of self-patterned polymer films. A fast demixing is caused by the fast evaporation of e ...
... spin coating of silicon chips. PVP/PMMA films were applied for arranging gold/silver-core/shell nanoparticles on the film surfaces. The method of spontaneous demixing during spin coating was applied for formation of self-patterned polymer films. A fast demixing is caused by the fast evaporation of e ...
Crystallographic preferred orientations may develop in
... The development of at least partially ‘‘amorphous’’ and/or ‘‘nanocrystalline’’ materials within fault principal slip zones has been shown to dramatically reduce their frictional shear resistance [Goldsby and Tullis, 2002], so it is proposed that the generation of these materials facilitates shear lo ...
... The development of at least partially ‘‘amorphous’’ and/or ‘‘nanocrystalline’’ materials within fault principal slip zones has been shown to dramatically reduce their frictional shear resistance [Goldsby and Tullis, 2002], so it is proposed that the generation of these materials facilitates shear lo ...
Solid

Solid is one of the four fundamental states of matter (the others being liquid, gas, and plasma). It is characterized by structural rigidity and resistance to changes of shape or volume. Unlike a liquid, a solid object does not flow to take on the shape of its container, nor does it expand to fill the entire volume available to it like a gas does. The atoms in a solid are tightly bound to each other, either in a regular geometric lattice (crystalline solids, which include metals and ordinary ice) or irregularly (an amorphous solid such as common window glass).The branch of physics that deals with solids is called solid-state physics, and is the main branch of condensed matter physics (which also includes liquids). Materials science is primarily concerned with the physical and chemical properties of solids. Solid-state chemistry is especially concerned with the synthesis of novel materials, as well as the science of identification and chemical composition.