Analysing Social Network Sites
... 1. is a feeling that members have of belonging, 2. a feeling that members matter: to one another and to the group 3. a shared faith that members’ needs will be met 4. through their commitment to be together Are these features then necessarily restricted to the real world, or can we successfully recr ...
... 1. is a feeling that members have of belonging, 2. a feeling that members matter: to one another and to the group 3. a shared faith that members’ needs will be met 4. through their commitment to be together Are these features then necessarily restricted to the real world, or can we successfully recr ...
A Level Sociology
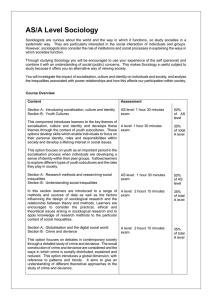
... AS/A Level Sociology Sociologists are curious about the world and the way in which it functions, so study societies in a systematic way. They are particularly interested in the social interaction of individuals and groups. However, sociologists also consider the role of institutions and social proce ...
... AS/A Level Sociology Sociologists are curious about the world and the way in which it functions, so study societies in a systematic way. They are particularly interested in the social interaction of individuals and groups. However, sociologists also consider the role of institutions and social proce ...
THE SOCIOLOGICAL SPIRIT (Second edition) Earl Babbie Chapter
... The Role of Reason: Theory To understand the function of theory, we need to consider a few of its elements. First, concepts are the mental images we use to bring order to the mass of specific experiences we have. ...
... The Role of Reason: Theory To understand the function of theory, we need to consider a few of its elements. First, concepts are the mental images we use to bring order to the mass of specific experiences we have. ...
Chapter 1
... Features of Symbolic Interactionism Focus on interpersonal and micro-level communication 2. Social life is possible only because people attach subjective meaning to things 3. As active agents people create their social circumstances 4. Increases our tolerance of people who may be different from us ...
... Features of Symbolic Interactionism Focus on interpersonal and micro-level communication 2. Social life is possible only because people attach subjective meaning to things 3. As active agents people create their social circumstances 4. Increases our tolerance of people who may be different from us ...
「社會學動動腦」 授課人:苗延威
... • Social mobility is the movement of individuals or groups in social position over time. • It may refer to classes,ethnic groups, or entire nations, and may measure health status, literacy, or education — but more commonly it refers to individuals or families, and their change in income. • It also t ...
... • Social mobility is the movement of individuals or groups in social position over time. • It may refer to classes,ethnic groups, or entire nations, and may measure health status, literacy, or education — but more commonly it refers to individuals or families, and their change in income. • It also t ...
Modernity post- modernity debate
... postmodern times we can no longer tell the Fragmentation and choice has been ‘uncertainty’, globalisation and the growing power of the media. predictable and stable formed by structures difference between reality and fiction. For created: specialist schools, CTCs and like family life and work. examp ...
... postmodern times we can no longer tell the Fragmentation and choice has been ‘uncertainty’, globalisation and the growing power of the media. predictable and stable formed by structures difference between reality and fiction. For created: specialist schools, CTCs and like family life and work. examp ...
What is Sociology?
... thinkers and some common themes which link contemporary sociology with its roots in the twin revolutions of the revolutions century. Three basic questions are: (a) what is human nature? (b) why is society structured as it is? and (c) how and why do societies change? ...
... thinkers and some common themes which link contemporary sociology with its roots in the twin revolutions of the revolutions century. Three basic questions are: (a) what is human nature? (b) why is society structured as it is? and (c) how and why do societies change? ...
Origin of Sociology
... Durkheim) tried to find ways to re-establish social order. • They believed that the science of society is possible to explain social problems. ...
... Durkheim) tried to find ways to re-establish social order. • They believed that the science of society is possible to explain social problems. ...
Chapter 1 Slides
... Sociology includes micro-level analyses focusing on individuals, such as studies of small groups and attitude change Sociology includes macro-level analyses focusing on social structures, such as studies of political and economic systems ...
... Sociology includes micro-level analyses focusing on individuals, such as studies of small groups and attitude change Sociology includes macro-level analyses focusing on social structures, such as studies of political and economic systems ...
Gurke Joseph Dr. Lydia Fisher UNST-141G
... social and cultural ideologies is, according to sociologists Peter L. Berger and Thomas Luckmann, “the first ‘moment’ in the continuing dialectical process of the social construction of reality…wherein individuals, by their own human activity, create their social worlds” (264). The machine is partic ...
... social and cultural ideologies is, according to sociologists Peter L. Berger and Thomas Luckmann, “the first ‘moment’ in the continuing dialectical process of the social construction of reality…wherein individuals, by their own human activity, create their social worlds” (264). The machine is partic ...