Fluids Notes - Net Start Class
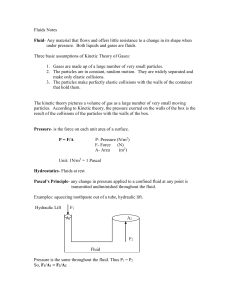
... Fluid- Any material that flows and offers little resistance to a change in its shape when under pressure. Both liquids and gases are fluids. Three basic assumptions of Kinetic Theory of Gases: 1. Gases are made up of a large number of very small particles. 2. The particles are in constant, random mo ...
... Fluid- Any material that flows and offers little resistance to a change in its shape when under pressure. Both liquids and gases are fluids. Three basic assumptions of Kinetic Theory of Gases: 1. Gases are made up of a large number of very small particles. 2. The particles are in constant, random mo ...
Project 1: Computational Modeling of Flow and Surfactant Transport
... About 85% of World energy production still comes from burning fossil fuels in turbulent environment and fossil fuels are expected to remain the main source of energy at least for next 50 years. Therefore turbulent combustion is the key technology for energy conversion systems and will remain so in t ...
... About 85% of World energy production still comes from burning fossil fuels in turbulent environment and fossil fuels are expected to remain the main source of energy at least for next 50 years. Therefore turbulent combustion is the key technology for energy conversion systems and will remain so in t ...
Fluids, elasticity
... In the figure above, the suction cup is held to the ceiling by (a) the suction of the vacuum formed between it and the wall. (b) the unbalanced force of the air molecules bouncing off the bottom of it. (c) the molecular attraction between the suction cup and the ceiling, where they are in contact. ( ...
... In the figure above, the suction cup is held to the ceiling by (a) the suction of the vacuum formed between it and the wall. (b) the unbalanced force of the air molecules bouncing off the bottom of it. (c) the molecular attraction between the suction cup and the ceiling, where they are in contact. ( ...
Blood Flow Measurement in Large Blood Vessels using
... across industries like power generation, oil and gas, material processing and so on. In this article, measurement of blood flow rate in large blood vessels using electromagnetic (EM) flow meter is discussed. The technique is non- invasive since the magnetic field can be generated by coils external t ...
... across industries like power generation, oil and gas, material processing and so on. In this article, measurement of blood flow rate in large blood vessels using electromagnetic (EM) flow meter is discussed. The technique is non- invasive since the magnetic field can be generated by coils external t ...
15.3 Modern Methods of Flow Measurements
... Faraday (1832) was the first person to notice that when the motion of water flowing in a river cuts the vertical components of earth's magnetic field an EMF is induced. In the water, which can be picked up by two electrodes. The EMF, which is directly proportional to the average velocity in the rive ...
... Faraday (1832) was the first person to notice that when the motion of water flowing in a river cuts the vertical components of earth's magnetic field an EMF is induced. In the water, which can be picked up by two electrodes. The EMF, which is directly proportional to the average velocity in the rive ...
CVE 240 – Fluid Mechanics
... particle of mass “m” in the system & is relative to an inertial reference frame. This frame does not rotate and can be either stationary or moving at a constant velocity. It is evaluated at the control surface w.r.t. the inertial reference frame selected. ...
... particle of mass “m” in the system & is relative to an inertial reference frame. This frame does not rotate and can be either stationary or moving at a constant velocity. It is evaluated at the control surface w.r.t. the inertial reference frame selected. ...
MasteringPhysics: Assignmen
... Bernoulli's equation is a simple relation that can give useful insight into the balance among fluid pressure, flow speed, and elevation. It applies exclusively to ideal fluids with steady flow, that is, fluids with a constant density and no internal friction forces, whose flow patterns do not change ...
... Bernoulli's equation is a simple relation that can give useful insight into the balance among fluid pressure, flow speed, and elevation. It applies exclusively to ideal fluids with steady flow, that is, fluids with a constant density and no internal friction forces, whose flow patterns do not change ...
Intermittency in Some Simple Models for Turbulent Transport 1 Introduction Arghir Dani Zarnescu
... The matter of interest is then how rare these large fluctuations are. In many situations, based on the Central Limit Theorem as a heuristical principle, one would expect things to organize themselves so that in the average the distribution of the variable of interest is Gaussian. But large fluctuati ...
... The matter of interest is then how rare these large fluctuations are. In many situations, based on the Central Limit Theorem as a heuristical principle, one would expect things to organize themselves so that in the average the distribution of the variable of interest is Gaussian. But large fluctuati ...
Properties of Solids and Fluids
... • High viscosity fluids take longer to pour from their containers than low viscosity fluids. • Demonstration ...
... • High viscosity fluids take longer to pour from their containers than low viscosity fluids. • Demonstration ...
Study of Reaction turbines
... Net head is proportional to the useful power actually delivered to the fluid. It is traditional to call this power the water horsepower, even if the fluid being pumped is not water, and even if the power is not measured in units of horsepower. By dimensional reasoning, we must multiply the net head ...
... Net head is proportional to the useful power actually delivered to the fluid. It is traditional to call this power the water horsepower, even if the fluid being pumped is not water, and even if the power is not measured in units of horsepower. By dimensional reasoning, we must multiply the net head ...
Physics 207: Lecture 2 Notes
... Any change in the pressure applied to an enclosed fluid is transmitted to every portion of the fluid and to the walls of the containing vessel. Pascal’s Principle explains the working of hydraulic lifts ...
... Any change in the pressure applied to an enclosed fluid is transmitted to every portion of the fluid and to the walls of the containing vessel. Pascal’s Principle explains the working of hydraulic lifts ...
Turbulence

In fluid dynamics, turbulence or turbulent flow is a flow regime characterized by chaotic property changes. This includes low momentum diffusion, high momentum convection, and rapid variation of pressure and flow velocity in space and time.Flow in which the kinetic energy dies out due to the action of fluid molecular viscosity is called laminar flow. While there is no theorem relating the non-dimensional Reynolds number (Re) to turbulence, flows at Reynolds numbers larger than 5000 are typically (but not necessarily) turbulent, while those at low Reynolds numbers usually remain laminar. In Poiseuille flow, for example, turbulence can first be sustained if the Reynolds number is larger than a critical value of about 2040; moreover, the turbulence is generally interspersed with laminar flow until a larger Reynolds number of about 4000.In turbulent flow, unsteady vortices appear on many scales and interact with each other. Drag due to boundary layer skin friction increases. The structure and location of boundary layer separation often changes, sometimes resulting in a reduction of overall drag. Although laminar-turbulent transition is not governed by Reynolds number, the same transition occurs if the size of the object is gradually increased, or the viscosity of the fluid is decreased, or if the density of the fluid is increased. Nobel Laureate Richard Feynman described turbulence as ""the most important unsolved problem of classical physics.""























