( NONLINEAR OPTICS PHYC/ECE 568) Homework #4, Due Thu Sept. 24
... a. Calculate the bandwidth associated with a phase-matched SHG process in terms of the group velocities vg( 1) and vg(2 1). In the low-depletion approximation, this corresponds to the width of the Sinc2 function which is taken to be (kL)=2 with L denoting the length of the nonlinear crystal ...
... a. Calculate the bandwidth associated with a phase-matched SHG process in terms of the group velocities vg( 1) and vg(2 1). In the low-depletion approximation, this corresponds to the width of the Sinc2 function which is taken to be (kL)=2 with L denoting the length of the nonlinear crystal ...
At what intensity is the laser set?
... Though Einstein is most famous for his work in describing relativity in mechanics, his Nobel Prize was for understanding a very simple experiment. It was long understood that if you directed light of a certain wavelength at a piece of metal, it would emit electrons. In classical theory, the energy o ...
... Though Einstein is most famous for his work in describing relativity in mechanics, his Nobel Prize was for understanding a very simple experiment. It was long understood that if you directed light of a certain wavelength at a piece of metal, it would emit electrons. In classical theory, the energy o ...
File - ce
... terms of numbers, the diode laser is the most common laser today. The 2 common families of diode lasers are composed of: * Ga AIAs (Gallium/Aluminum/Arsenide) with a wavelength output in the 750 to 950 nanometers (used in CD &CD/ROM players), * InGaAsP (Indium/Gallium/Arsenide/Phosphide) with a wave ...
... terms of numbers, the diode laser is the most common laser today. The 2 common families of diode lasers are composed of: * Ga AIAs (Gallium/Aluminum/Arsenide) with a wavelength output in the 750 to 950 nanometers (used in CD &CD/ROM players), * InGaAsP (Indium/Gallium/Arsenide/Phosphide) with a wave ...
A1979HZ30700001
... communication. This was prior to the establishment of feasibility of lowloss lightwave propagation on glass fibers Work at Bell Laboratories had created a rather refined technique of guiding a number of laser beams along a single path. This transmission technique used a cascaded series of lenslike f ...
... communication. This was prior to the establishment of feasibility of lowloss lightwave propagation on glass fibers Work at Bell Laboratories had created a rather refined technique of guiding a number of laser beams along a single path. This transmission technique used a cascaded series of lenslike f ...
MeriameBerboucha
... Herriott cell used to produce optical time-delay so that pulses reach each other at the same time. Figure 5: Schematic of IGNIS, the OPCPA laser system that shall be used for the research and development phase before the construction of LCLS-II. Figure 1: Top left and right: laser enclosure for IGNI ...
... Herriott cell used to produce optical time-delay so that pulses reach each other at the same time. Figure 5: Schematic of IGNIS, the OPCPA laser system that shall be used for the research and development phase before the construction of LCLS-II. Figure 1: Top left and right: laser enclosure for IGNI ...
Frequency Domain Optical Coherence Tomography (FDOCT)
... IMSURE Summer Research Fellow At Beckman Laser Institute University of California at Irvine Irvine, CA 92612 Email: [email protected] Faculty mentor: Prof. Zhongping Chen Lab mentor: Jun Zhang ...
... IMSURE Summer Research Fellow At Beckman Laser Institute University of California at Irvine Irvine, CA 92612 Email: [email protected] Faculty mentor: Prof. Zhongping Chen Lab mentor: Jun Zhang ...
Laser Fundamentals
... If the energy from this photon is of the precise wavelength, it will stimulate the production of another photon of the same wavelength and resulting in a cascading effect. The highly reflective mirror and partially reflective mirror continue the reaction by directing photons back through the medium ...
... If the energy from this photon is of the precise wavelength, it will stimulate the production of another photon of the same wavelength and resulting in a cascading effect. The highly reflective mirror and partially reflective mirror continue the reaction by directing photons back through the medium ...
Lesson 3 - MrSimonPorter
... monochromatic light, but the phases of all the waves will be different, they will travelling in different directions, and their polarisation will be different. ...
... monochromatic light, but the phases of all the waves will be different, they will travelling in different directions, and their polarisation will be different. ...
Two laser wavelength Thomson Scattering for high electron
... Thomson scattering (TS) is one of the main diagnostics in nuclear fusion experiments for electron temperature and –density measurements. Most of the TS systems are realized with pulsed, high power Nd:YAG lasers as light source with a wavelength at λ=1064 nm, together with interference filter polychr ...
... Thomson scattering (TS) is one of the main diagnostics in nuclear fusion experiments for electron temperature and –density measurements. Most of the TS systems are realized with pulsed, high power Nd:YAG lasers as light source with a wavelength at λ=1064 nm, together with interference filter polychr ...
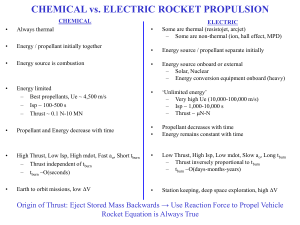
Photonic laser thruster

A photonic laser thruster is an amplified laser thruster that generates thrust directly from the laser photon momentum, rather than laser-heating propellant. The concept of single-bounce laser-pushed lightsails that utilize the photon momentum was first developed in the 1960s, however, its conversion of laser power to thrust is highly inefficient, thus has been considered impractical. Over 50 years, there had been numerous theoretical and experimental efforts to increase the conversion efficiency by recycling photons, bouncing them repetitively between two reflective mirrors in an empty optical cavity, without success. In December 2006, Young Bae successfully solved this problem and demonstrated the conversion efficiency enhancement by a factor of 100 and a photon thrust of 35 micronewtons by putting the laser energizing media between the two mirrors as in typical lasers, and the photonic laser thruster was born. In August 2015, the photonic laser thruster was demonstrated to increase the conversion efficiency enhancement by a factor over 1,000 and to achieve a photon thrust of 3.5 millinewtons at Y.K. Bae Corporation. In addition, Propelling, slowing and stopping of a small satellite, 1U CubeSat, in simulated zero-gravity were demonstrated. The photonic laser thruster was initially developed for use in nanometer precision spacecraft formation, for forming ultralarge space telescopes and radars. The photonic laser thruster is currently developed for high-precision and high-speed maneuver of small spacecraft, such as formation flying, orbit adjustments, drag compensation, and rendezvous and docking. The photonic laser thruster can be used for beaming thrust from a conventional heavy resource vehicle to a more expensive & lightweight mission vehicle, similar to tankers in aerial refueling.The practical usage of the photonic laser thruster for main space propulsion would require extremely high laser powers and overcoming technological challenges in achieving the laser power and fabricating the required optics. Photonic laser thrusters have a very high specific impulse, and can permit spacecraft reach much higher speeds than with conventional rockets, which are limited by the Tsiolkovsky rocket equation. If the photonic laser thruster is scalable for the use in such main space propulsion, multiple photonic laser thrusters can be used to construct a 'photonic railway' that has been proposed as a potential permanent transport infrastructure for interplanetary or interstellar commutes, allowing the transport craft themselves to carry very little fuel.