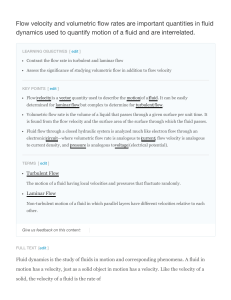
Control volume analysis (Part 2) Linear Momentum Equations
... 5. If the CS is selected so that it is perpendicular to the flow where fluid enters or leaves the CV, the surface force exerted at these locations by fluid outside the CV on fluid inside will be due to pressure. Furthermore, when subsonic flow exits from a control volume into the atmosphere, atmosph ...
... 5. If the CS is selected so that it is perpendicular to the flow where fluid enters or leaves the CV, the surface force exerted at these locations by fluid outside the CV on fluid inside will be due to pressure. Furthermore, when subsonic flow exits from a control volume into the atmosphere, atmosph ...
MCAT Fluid dynamics
... 6:-When a body is moving with terminal velocity then it has zero acceleration. 7:-At terminal velocity fluid friction is maximum. 8:-At terminal velocity the net force acting on the body is zero. 9:-Terminal velocity of the body is directly proportional to its mass & density. 10:-Strokes law holds g ...
... 6:-When a body is moving with terminal velocity then it has zero acceleration. 7:-At terminal velocity fluid friction is maximum. 8:-At terminal velocity the net force acting on the body is zero. 9:-Terminal velocity of the body is directly proportional to its mass & density. 10:-Strokes law holds g ...
Flow conditioning
Flow conditioning ensures that the “real world” environment closely resembles the “laboratory” environment for proper performance of inferential flowmeters like orifice, turbine, coriolis, ultrasonic etc.