El. Fields
... •The charge of the line is easy to find, Q = L •But the distance and direction is hard to find •To deal with this problem, you have to divide it up into little segments of length dl •Then calculate the charge dQ = dl for each little piece ...
... •The charge of the line is easy to find, Q = L •But the distance and direction is hard to find •To deal with this problem, you have to divide it up into little segments of length dl •Then calculate the charge dQ = dl for each little piece ...
CHAPTER 5 5.1. Given the current density J = −104[sin(2x)e−2y ax
... 5.8. The continuity equation for mass equates the divergence of the mass rate of flow (mass per second per square meter) to the negative of the density (mass per cubic meter). After setting up a cartesian coordinate system inside a star, Captain Kirk and his intrepid crew make measurements over the ...
... 5.8. The continuity equation for mass equates the divergence of the mass rate of flow (mass per second per square meter) to the negative of the density (mass per cubic meter). After setting up a cartesian coordinate system inside a star, Captain Kirk and his intrepid crew make measurements over the ...
Lecture 4 Electric potential
... • Work is independent of the particular path. • Although we proved it for a uniform field, it is true for any field that is a only a function of r and is along r. • It only depends on the end points i and f. •This means we can define a function at every point in space and when we take the difference ...
... • Work is independent of the particular path. • Although we proved it for a uniform field, it is true for any field that is a only a function of r and is along r. • It only depends on the end points i and f. •This means we can define a function at every point in space and when we take the difference ...
Lecture 4 Electric potential
... Chapter 24 Problem 26. What is the magnitude of the net electric potential at the center? 1. A thin rod of charge -3.0 µC that forms a full circle of radius 6.0 cm 2. A second thin rod of charge 2.0 µC that forms a circular arc of radius 4.0 cm, subtending an angle of 90° about the center of the fu ...
... Chapter 24 Problem 26. What is the magnitude of the net electric potential at the center? 1. A thin rod of charge -3.0 µC that forms a full circle of radius 6.0 cm 2. A second thin rod of charge 2.0 µC that forms a circular arc of radius 4.0 cm, subtending an angle of 90° about the center of the fu ...
Chapter 15
... Q) How can a positively charged object be used to leave another metallic object with a net negative charge? ...
... Q) How can a positively charged object be used to leave another metallic object with a net negative charge? ...
Physics 1301: Lecture 1 - Home Page
... Electron parallel resistivity (not anomalous!) becomes important in ionosphere. Gives diffusion in current on scale Lres le e / where e is electron collision frequency (103-104 s–1 in ionosphere). This gives 150 m-5 km for ionospheric resonator ( ~ 1 s–1) and 1.5-50 km for FLR’s ( ~ 0.01 s–1 ...
... Electron parallel resistivity (not anomalous!) becomes important in ionosphere. Gives diffusion in current on scale Lres le e / where e is electron collision frequency (103-104 s–1 in ionosphere). This gives 150 m-5 km for ionospheric resonator ( ~ 1 s–1) and 1.5-50 km for FLR’s ( ~ 0.01 s–1 ...
Final Exam - KFUPM Faculty List
... In CO2 there are 2 CO σ-bonds, 2 CO π-bonds and 4 lone pairs, 2 on each oxygen. At each oxygen the σ-pair structure is formed by a triangle made up from the CO σ-bond and the 2 lone pairs. For these 3 electron pairs on each oxygen three hybrid orbitals are needed and thus an sp2 hybrid on each oxyge ...
... In CO2 there are 2 CO σ-bonds, 2 CO π-bonds and 4 lone pairs, 2 on each oxygen. At each oxygen the σ-pair structure is formed by a triangle made up from the CO σ-bond and the 2 lone pairs. For these 3 electron pairs on each oxygen three hybrid orbitals are needed and thus an sp2 hybrid on each oxyge ...
Using facets as a tool to interpret a survey on quantization
... Some statements about Atomic Structure from the interviews: Atomic Layout •Atoms are made up of protons, electrons, and neutrons. •Protons and neutrons form the nucleus at the center of the atom, and the electrons surround the nucleus. •Neutrons form the nucleus, and protons and electrons surround ...
... Some statements about Atomic Structure from the interviews: Atomic Layout •Atoms are made up of protons, electrons, and neutrons. •Protons and neutrons form the nucleus at the center of the atom, and the electrons surround the nucleus. •Neutrons form the nucleus, and protons and electrons surround ...
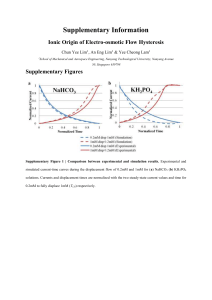
Supplementary Information
... where I-1(t) is the inverse of experimental current, while A, B and n are the coefficients assigned for fitting. The R-squared values for the fittings were as high as 0.98, indicating the regression function is capable of capturing the experimental trend. Once A, B and n are determined, the displace ...
... where I-1(t) is the inverse of experimental current, while A, B and n are the coefficients assigned for fitting. The R-squared values for the fittings were as high as 0.98, indicating the regression function is capable of capturing the experimental trend. Once A, B and n are determined, the displace ...
Chapter 1 ELECTROMAGNETICS OF METALS
... response is a change in the phase of the induced currents with respect to the driving field for frequencies approaching the reciprocal of the characteristic electron relaxation time τ of the metal, as will be discussed in section 1.2. Before presenting an elementary description of the optical proper ...
... response is a change in the phase of the induced currents with respect to the driving field for frequencies approaching the reciprocal of the characteristic electron relaxation time τ of the metal, as will be discussed in section 1.2. Before presenting an elementary description of the optical proper ...
(a) Find the change in electric potential between points A and B.
... A battery produces a specified potential difference between conductors attached to the battery terminals. A 12-V battery is connected between two parallel plates. The separation between the plates is d= 0.30 cm, and we assume the electric field between the plates to be uniform.؟ ...
... A battery produces a specified potential difference between conductors attached to the battery terminals. A 12-V battery is connected between two parallel plates. The separation between the plates is d= 0.30 cm, and we assume the electric field between the plates to be uniform.؟ ...
PHY2100 Physics Practical II
... than a digital one in this experiment. Description An electric current consists of moving charge carriers (typically negatively charged electrons). In the presence of a perpendicular magnetic field, these charge carriers will be deflected, creating a potential difference perpendicular to both the ma ...
... than a digital one in this experiment. Description An electric current consists of moving charge carriers (typically negatively charged electrons). In the presence of a perpendicular magnetic field, these charge carriers will be deflected, creating a potential difference perpendicular to both the ma ...
PH202 chapter 20 solutions
... P20.50. Prepare: The charges are point charges. Please refer to Figure P20.50. Solve: Placing the 1 nC charge at the origin and calling it q1, the q2 charge is in the first quadrant, the q3 charge is in the fourth quadrant, the q4 charge is in the third quadrant, and the q5 charge is in the second q ...
... P20.50. Prepare: The charges are point charges. Please refer to Figure P20.50. Solve: Placing the 1 nC charge at the origin and calling it q1, the q2 charge is in the first quadrant, the q3 charge is in the fourth quadrant, the q4 charge is in the third quadrant, and the q5 charge is in the second q ...
PPT - LSU Physics & Astronomy
... TOTAL CHARGE ENCLOSED! • The results of a complicated integral is a very simple formula: it avoids long calculations! ...
... TOTAL CHARGE ENCLOSED! • The results of a complicated integral is a very simple formula: it avoids long calculations! ...
Ch 18 – Electric Forces and Electric Fields
... the two charges (Coulomb’s law). Coulomb’ law is covered in more detail below. Conductivity of solids Materials can be classified based on their ability to transfer electric charge. 1. Conductors are materials like metals that have electrons which are loosely bound to the outskirts of their atoms ...
... the two charges (Coulomb’s law). Coulomb’ law is covered in more detail below. Conductivity of solids Materials can be classified based on their ability to transfer electric charge. 1. Conductors are materials like metals that have electrons which are loosely bound to the outskirts of their atoms ...