PPT - LSU Physics & Astronomy
... Figure 22N-14 shows an arrangement of four charged particles, with angle q = 34° and distance d = 2.20 cm. The two negatively charged particles on the y axis are electrons that are fixed in place; the particle at the right has a charge q2 = +5e (a) Find distance D such that the net force on the part ...
... Figure 22N-14 shows an arrangement of four charged particles, with angle q = 34° and distance d = 2.20 cm. The two negatively charged particles on the y axis are electrons that are fixed in place; the particle at the right has a charge q2 = +5e (a) Find distance D such that the net force on the part ...
ECE Lecture 22: Electrostatics – Coulomb`s Law
... ECE 3300 Electrostatics – Coulomb’s Law COULOMB’S LAW: Electric charges produce electric fields ...
... ECE 3300 Electrostatics – Coulomb’s Law COULOMB’S LAW: Electric charges produce electric fields ...
Electric Force and Potential Energy
... electrostatic equilibrium, there is no net electric field. All the charge resides on the surface. The field lines point normal to the surface at every point on the surface. Equipotential: On the surface of an electrical conductor, in electrostatic equilibrium, there is a constant electrical potentia ...
... electrostatic equilibrium, there is no net electric field. All the charge resides on the surface. The field lines point normal to the surface at every point on the surface. Equipotential: On the surface of an electrical conductor, in electrostatic equilibrium, there is a constant electrical potentia ...
Electrostatics Summary
... • Opposite charges attract. Like charges repel. This is an important property of objects carrying static electricity. II. The atom and charges The PROTONS (+ charge) and neutrons are in the nucleus The electrons (- charge) surround it. Outermost electrons are “loosely held” and can be made to trans ...
... • Opposite charges attract. Like charges repel. This is an important property of objects carrying static electricity. II. The atom and charges The PROTONS (+ charge) and neutrons are in the nucleus The electrons (- charge) surround it. Outermost electrons are “loosely held” and can be made to trans ...
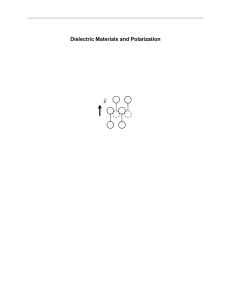
Dielectric Materials and Polarization Chapter 6
... composed of the freely mobile electrons. In an insulator, or dielectric, something else must happen because there are no free electrons. What can, and does, happen is that the electric field pulls the electron and pushes the positively charged nucleus. The result is a distorted object with a net ato ...
... composed of the freely mobile electrons. In an insulator, or dielectric, something else must happen because there are no free electrons. What can, and does, happen is that the electric field pulls the electron and pushes the positively charged nucleus. The result is a distorted object with a net ato ...
Exam 1 - UF Physics
... 11. Three identical charges q = −1 µC are placed in the (x, y)-plane at coordinates (−1, 0), (1, 0), and (0, 1). How much work is needed to move the last charge in the list to a new position, (0, 0), while holding the other two in their original positions? All distances are in meters. ...
... 11. Three identical charges q = −1 µC are placed in the (x, y)-plane at coordinates (−1, 0), (1, 0), and (0, 1). How much work is needed to move the last charge in the list to a new position, (0, 0), while holding the other two in their original positions? All distances are in meters. ...
SOLID-STATE PHYSICS 3, Winter 2008 O. Entin-Wohlman
... Since ²k depends solely on |k|, the sum over k here vanishes (each k−contribution is cancelled by the contribution of −k) and consequently there is no average current in the system described by the free Hamiltonian. ♣Exercise. Find the thermal average of the density in a system described by the free ...
... Since ²k depends solely on |k|, the sum over k here vanishes (each k−contribution is cancelled by the contribution of −k) and consequently there is no average current in the system described by the free Hamiltonian. ♣Exercise. Find the thermal average of the density in a system described by the free ...
Drift Velocity vs. Electric Field
... “Lattice scattering” or “phonon scattering” increases with increasing temperature. Average velocity of thermal motion for electrons: ~1/1000 x speed of light at 300 K (even under equilibrium conditions). ...
... “Lattice scattering” or “phonon scattering” increases with increasing temperature. Average velocity of thermal motion for electrons: ~1/1000 x speed of light at 300 K (even under equilibrium conditions). ...
Solution
... (b) [6 points] If the charged capacitor is then connected in parallel with a second (initially uncharged) capacitor, and if the potential difference across the first capacitor subsequently drops to 9 V, what is the capacitance of this second capacitor? Charge cannot be destroyed, so it remains on th ...
... (b) [6 points] If the charged capacitor is then connected in parallel with a second (initially uncharged) capacitor, and if the potential difference across the first capacitor subsequently drops to 9 V, what is the capacitance of this second capacitor? Charge cannot be destroyed, so it remains on th ...
Your Paper`s Title Starts Here:
... considered that connected details are subjected to electric field for a very long time. Actually, necessary time of endurance was defined only experimentally. Therefore the purpose of this work is calculation of transients at electroadhesive junction of ionic dielectrics with conductors (semiconduct ...
... considered that connected details are subjected to electric field for a very long time. Actually, necessary time of endurance was defined only experimentally. Therefore the purpose of this work is calculation of transients at electroadhesive junction of ionic dielectrics with conductors (semiconduct ...
Homework week 7
... 1. A positive point charge is situated at on the z-axis at position (0,0,z). A metal plate that stretches to infinity in both the x- and y-directions is situated in the xy-plane. a. What is the direction of the electric field just above the metal plate? b. What do you know about the electric potenti ...
... 1. A positive point charge is situated at on the z-axis at position (0,0,z). A metal plate that stretches to infinity in both the x- and y-directions is situated in the xy-plane. a. What is the direction of the electric field just above the metal plate? b. What do you know about the electric potenti ...
Electromagnetism
... Determine the equivalent resistance of… a. three 90 ohm resistors in series b. three 90 ohm resistors in parallel c. a 10 ohm resistor and 20 ohm resistor in series d. a 10 ohm resistor and 20 ohm resistor in parallel e. 5, 10, and 40 ohm resistors in series f. 20, 30, and 40 ohm resistors in parall ...
... Determine the equivalent resistance of… a. three 90 ohm resistors in series b. three 90 ohm resistors in parallel c. a 10 ohm resistor and 20 ohm resistor in series d. a 10 ohm resistor and 20 ohm resistor in parallel e. 5, 10, and 40 ohm resistors in series f. 20, 30, and 40 ohm resistors in parall ...
Physics 213 — Problem Set 5 (Due before Feb. 26) Spring 1998
... −15 nC. Find (a) the electric field E and (b) the electric potential V in regions A, B, and C of the figure. (Assume V = 0 at infinity.) Sketch plots of both the magnitude of the electric field and the potential versus radius r. SOLUTION: a)Because of the symmetry in this problem, let’s choose spher ...
... −15 nC. Find (a) the electric field E and (b) the electric potential V in regions A, B, and C of the figure. (Assume V = 0 at infinity.) Sketch plots of both the magnitude of the electric field and the potential versus radius r. SOLUTION: a)Because of the symmetry in this problem, let’s choose spher ...
Electric Fields and Potential
... different parallel plates are hooked up to different voltages one becomes more negative and the other one becomes more positive. This difference is what causes the charge to be stored. A capacitor is discharged when there is a conducting path between the two conducting plates. This is when people ca ...
... different parallel plates are hooked up to different voltages one becomes more negative and the other one becomes more positive. This difference is what causes the charge to be stored. A capacitor is discharged when there is a conducting path between the two conducting plates. This is when people ca ...
File
... 1. An atom is the smallest particle of an element that retains the properties of that element. 2. The nucleus is a small, dense region located at the center of an atom. 3. The nucleus is made up of at least one positively charged particle called a proton and usually one or more neutral particles cal ...
... 1. An atom is the smallest particle of an element that retains the properties of that element. 2. The nucleus is a small, dense region located at the center of an atom. 3. The nucleus is made up of at least one positively charged particle called a proton and usually one or more neutral particles cal ...
Chapter 10_Handouts_6
... precipitate is an insoluble solid that results from a chemical reaction in solution. When two or more atom groups of the same kind are present in the formula of a compound, parentheses are placed around the group. Example: Ca(NO3)2 ...
... precipitate is an insoluble solid that results from a chemical reaction in solution. When two or more atom groups of the same kind are present in the formula of a compound, parentheses are placed around the group. Example: Ca(NO3)2 ...